
How to Use rtc: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with rtc in Cirkit Designer
Design with rtc in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Real-Time Clock (RTC) is a timekeeping device designed to maintain accurate time and date information, even when the main power supply is disconnected. This is achieved through the use of a small backup battery. RTCs are essential in applications where precise timekeeping is required, such as data logging, scheduling, and time-stamping events.
The Arduino UNO, when paired with an RTC module, can be used to create projects that require accurate timekeeping, such as alarm clocks, timers, or systems that log data with timestamps.
Explore Projects Built with rtc
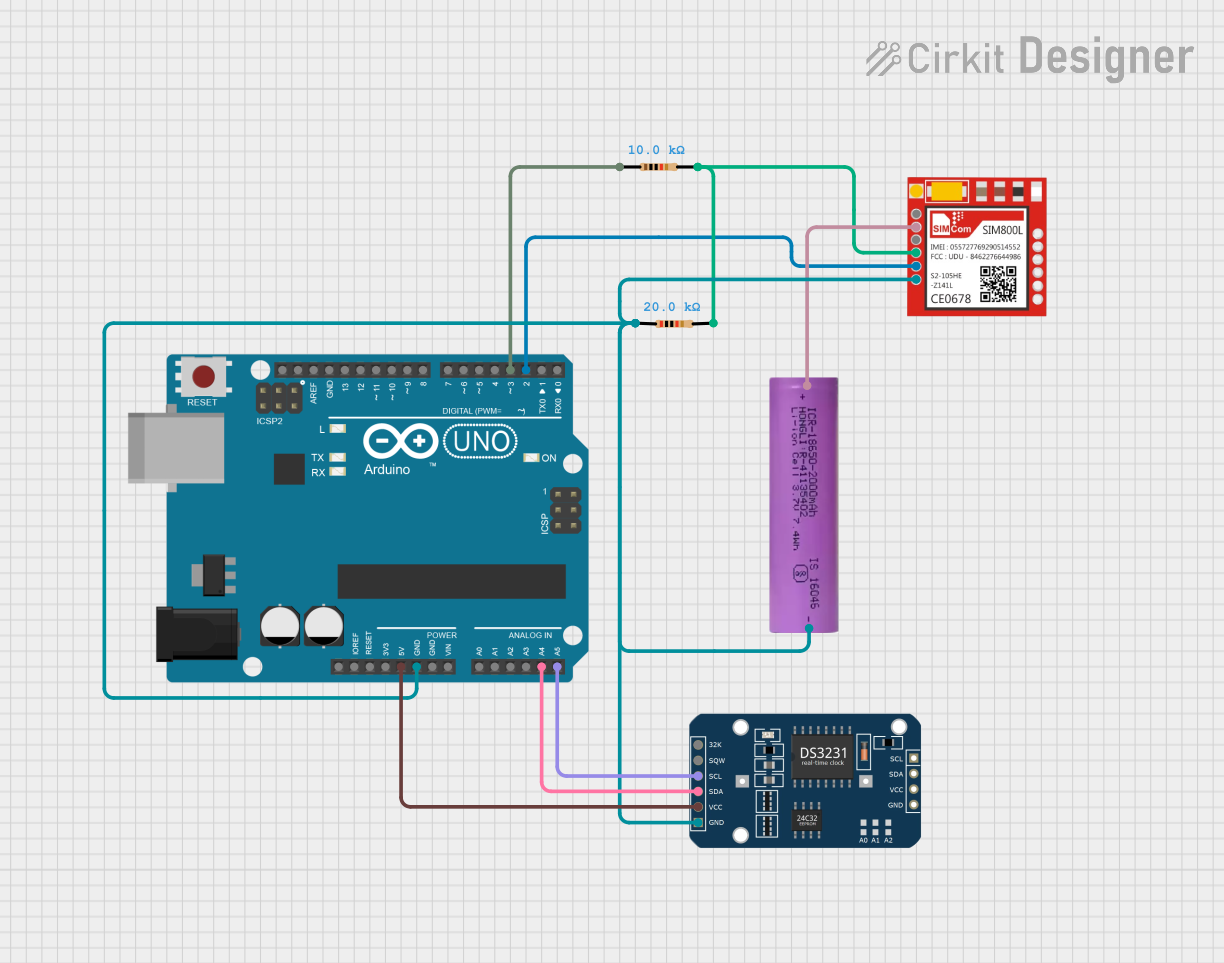
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer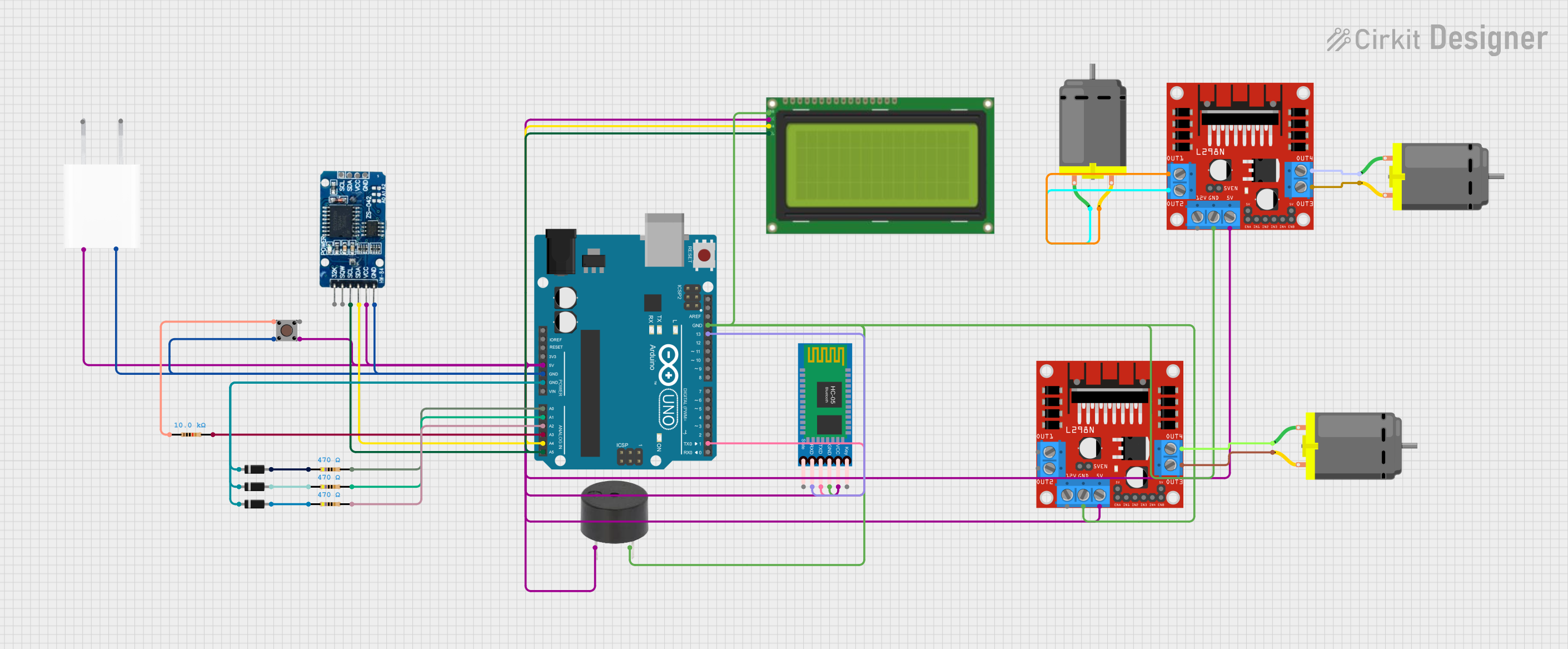
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer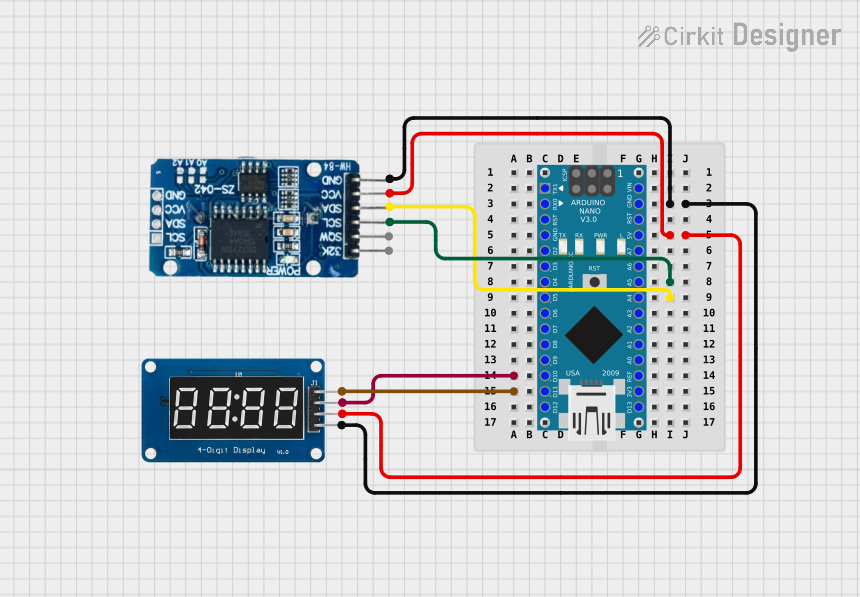
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer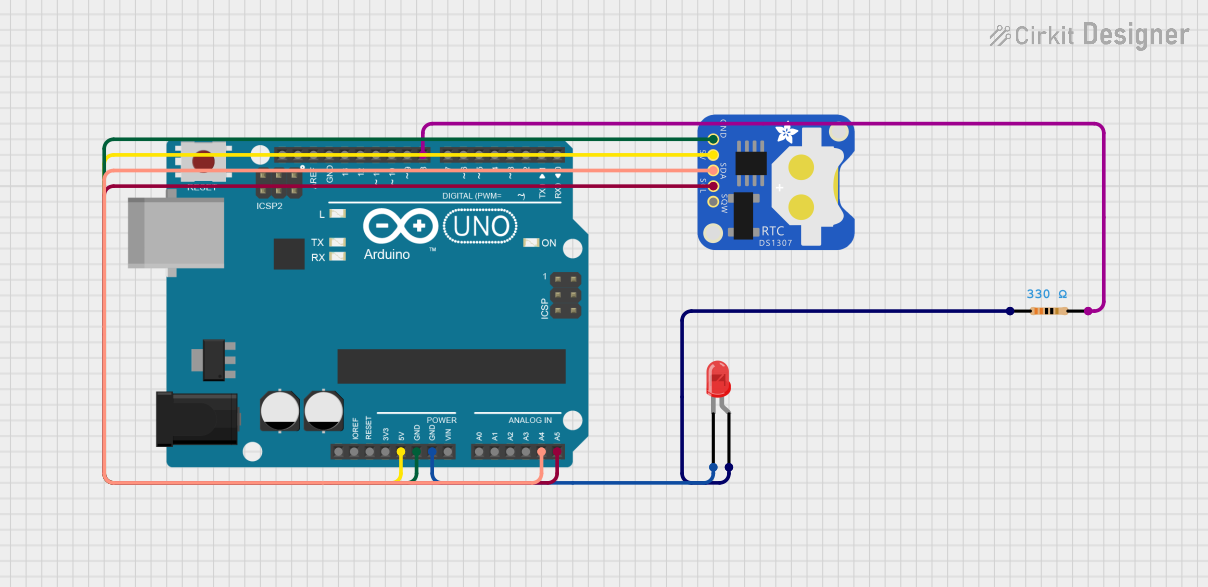
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with rtc

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for an RTC module compatible with the Arduino UNO:
- Manufacturer: Arduino
- Part ID: UNO
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V
- Backup Battery: CR2032 or similar coin cell battery
- Communication Protocol: I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit)
- Typical Accuracy: ±2 ppm to ±20 ppm (depending on the specific RTC chip)
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The RTC module typically has the following pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V or 5V, depending on the module). |
| GND | Ground pin. |
| SDA | Serial Data Line for I2C communication. |
| SCL | Serial Clock Line for I2C communication. |
| BAT | Backup battery pin (optional, for connecting a CR2032 battery). |
| SQW/OUT | Square Wave Output pin (optional, used for generating a clock signal). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the RTC in a Circuit
Connect the RTC Module to the Arduino UNO:
- Connect the
VCCpin of the RTC module to the5Vpin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
GNDpin of the RTC module to theGNDpin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
SDApin of the RTC module to theA4pin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
SCLpin of the RTC module to theA5pin on the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the
Install the Required Library:
- Use the Arduino IDE to install the
RTCliblibrary, which provides functions for interfacing with RTC modules. - To install the library, go to Sketch > Include Library > Manage Libraries, search for
RTClib, and click Install.
- Use the Arduino IDE to install the
Upload Example Code:
- Use the following example code to set the time and read the current time from the RTC module.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <RTClib.h>
// Create an RTC object
RTC_DS1307 rtc;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
if (!rtc.begin()) {
Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
while (1); // Halt the program if the RTC is not found
}
if (!rtc.isrunning()) {
Serial.println("RTC is NOT running, setting the time...");
// Set the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
}
void loop() {
DateTime now = rtc.now(); // Get the current date and time
// Print the current date and time to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.second(), DEC);
Serial.println();
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before updating the time
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always ensure the backup battery is installed to maintain timekeeping when the main power is off.
- Use pull-up resistors on the
SDAandSCLlines if they are not already included on the RTC module. - Avoid placing the RTC module near high-frequency components to minimize interference.
- Regularly check and replace the backup battery to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
RTC Not Detected:
- Ensure the
SDAandSCLpins are correctly connected to the Arduino UNO. - Verify that the
RTCliblibrary is installed and included in your sketch. - Check the power supply to the RTC module.
- Ensure the
Incorrect Time Displayed:
- Ensure the RTC is initialized and the time is set correctly using the
rtc.adjust()function. - Verify that the backup battery is installed and functional.
- Ensure the RTC is initialized and the time is set correctly using the
Time Resets After Power Loss:
- Check the backup battery connection and replace the battery if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the RTC module with other microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the RTC module can be used with other microcontrollers that support I2C communication, such as ESP32, ESP8266, or Raspberry Pi.
Q: How long does the backup battery last?
A: The backup battery can last several years, depending on the RTC module's power consumption and the battery's capacity.
Q: Can I use multiple I2C devices with the RTC module?
A: Yes, I2C supports multiple devices on the same bus. Ensure each device has a unique address.
Q: What happens if the backup battery is removed?
A: The RTC will lose its timekeeping functionality when the main power is off, and the time will need to be reset when power is restored.