
How to Use VL53L7CX: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with VL53L7CX in Cirkit Designer
Design with VL53L7CX in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The VL53L7CX is a state-of-the-art time-of-flight (ToF) distance sensor developed by STMicroelectronics. It uses advanced laser technology to measure distances with high precision and speed. This sensor is capable of multi-zone distance measurement, allowing it to detect objects in multiple regions simultaneously. Its ability to function in various lighting conditions makes it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Explore Projects Built with VL53L7CX
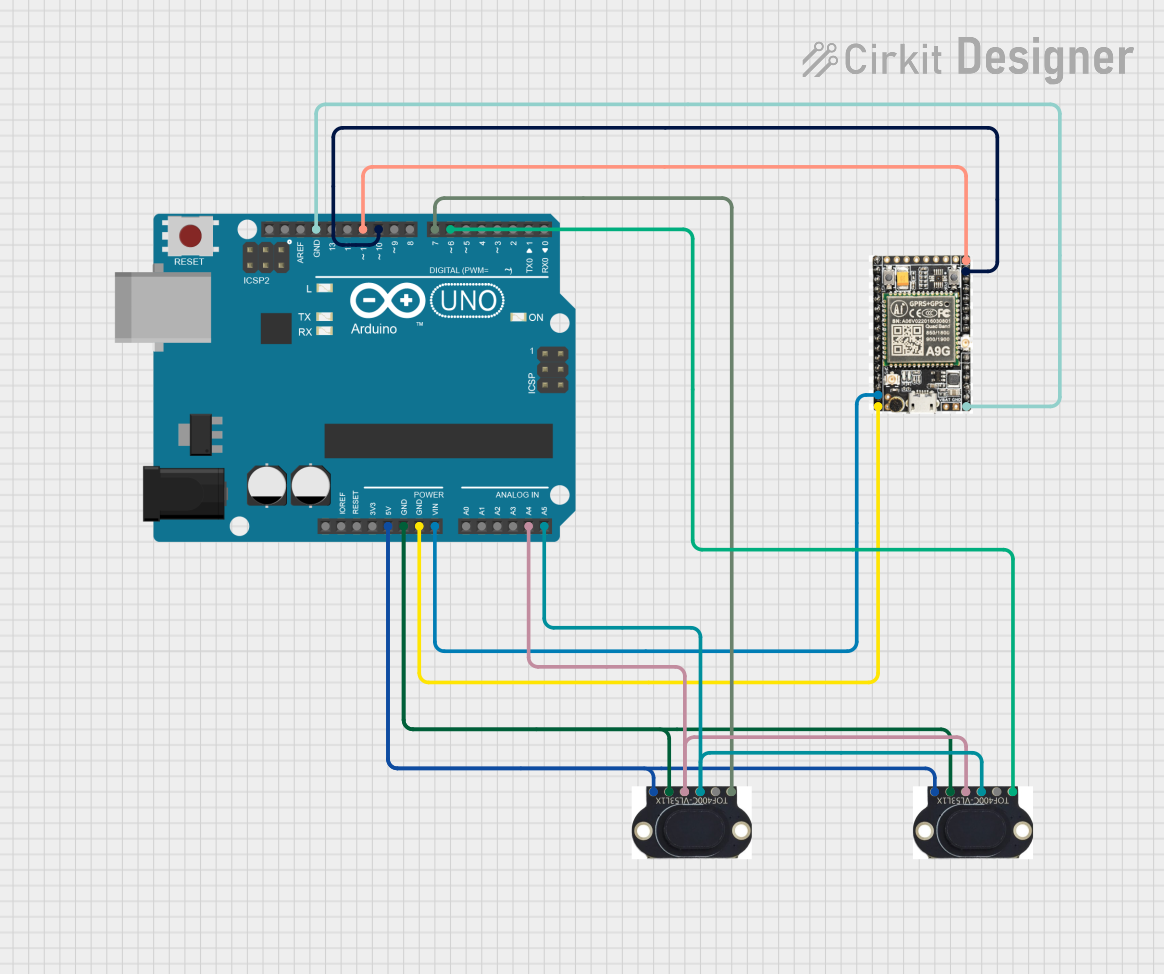
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer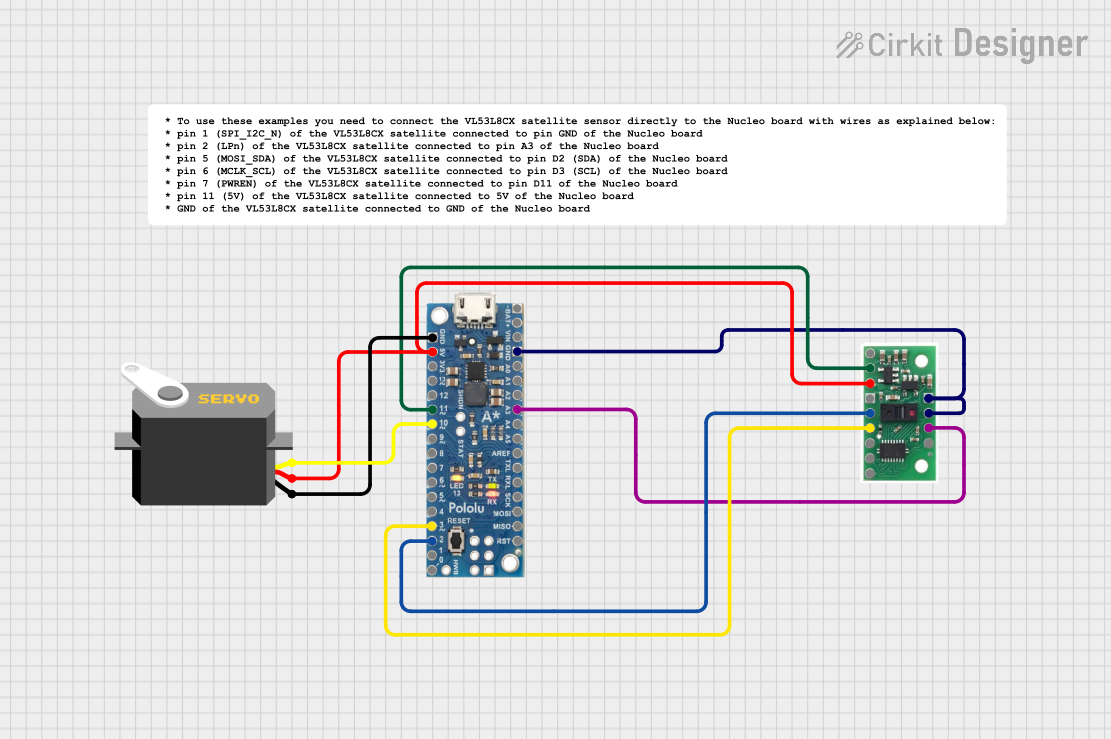
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer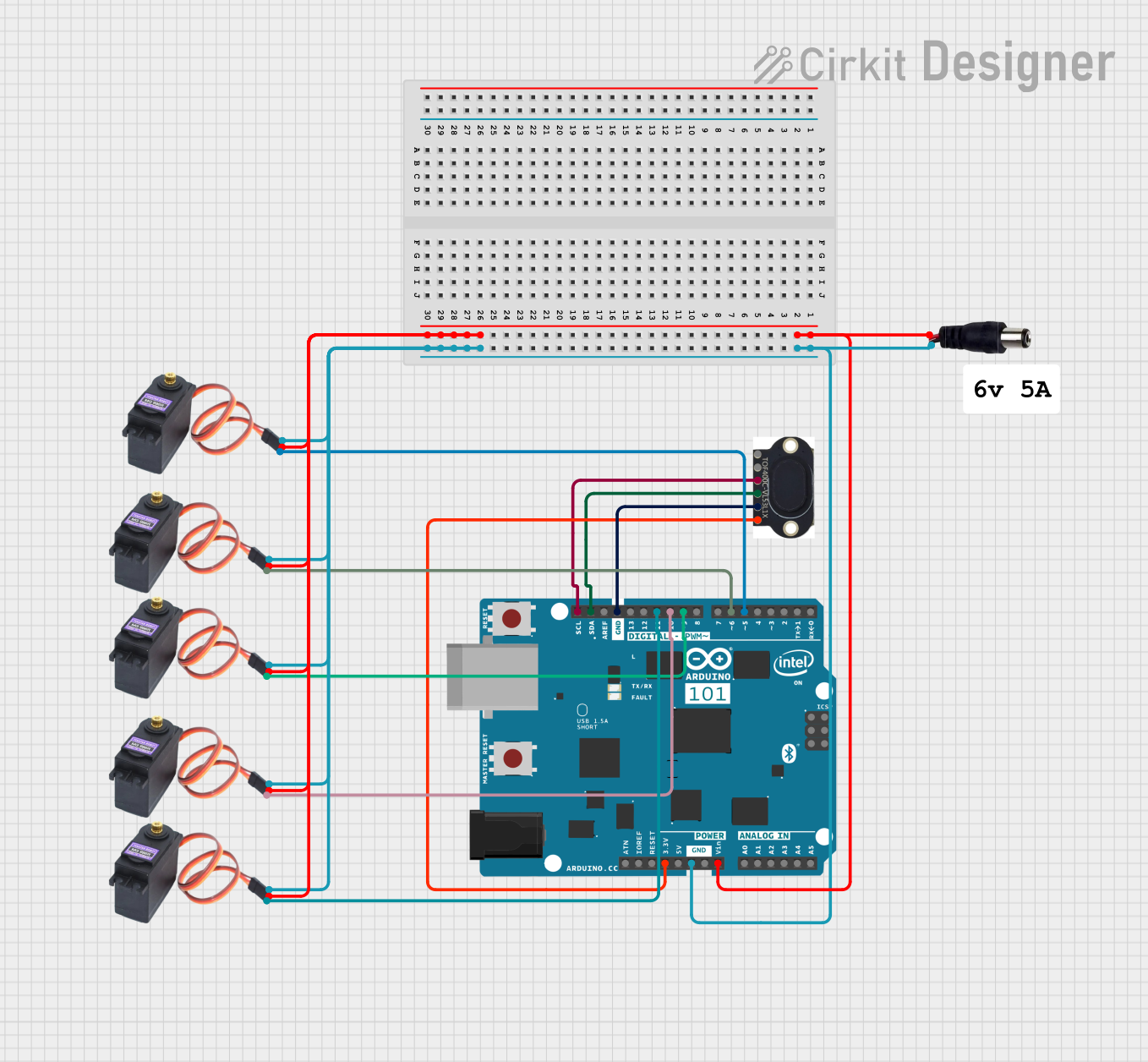
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with VL53L7CX

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics for obstacle detection and navigation
- Drones for altitude measurement and collision avoidance
- Smart home devices, such as automated doors and lighting systems
- Gesture recognition in consumer electronics
- Industrial automation and safety systems
Technical Specifications
The VL53L7CX offers impressive performance and flexibility. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 2.8 V (typical) |
| Interface | I²C (up to 1 MHz) |
| Measurement Range | 0.1 m to 4 m (depending on conditions) |
| Multi-Zone Capability | Up to 64 zones (8x8 grid) |
| Field of View (FoV) | 63° x 63° |
| Distance Accuracy | ±5 mm (typical, under optimal conditions) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30°C to +85°C |
| Power Consumption | 5.4 mW (typical in ranging mode) |
| Dimensions | 4.4 mm x 2.4 mm x 1.0 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The VL53L7CX is typically provided in a compact LGA package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GND | Ground | Ground connection |
| VDD | Power Supply | Main power supply (2.8 V typical) |
| SDA | I²C Data Line | Serial data line for I²C communication |
| SCL | I²C Clock Line | Serial clock line for I²C communication |
| GPIO1 | Input/Output | General-purpose I/O pin (can be used for interrupts or other signals) |
| XSHUT | Input | Shutdown pin (active low) to enable or disable the sensor |
Usage Instructions
The VL53L7CX is straightforward to integrate into a circuit, thanks to its I²C interface and compact design. Below are the steps and considerations for using the sensor:
Circuit Connection
- Connect the VDD pin to a 2.8 V power supply.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I²C data and clock lines of your microcontroller.
- Optionally, connect the XSHUT pin to a GPIO pin on your microcontroller to control the sensor's power state.
- Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines if not already present on your board.
Important Considerations
- Ensure the I²C bus voltage matches the sensor's voltage levels (2.8 V).
- Avoid exposing the sensor to direct sunlight or reflective surfaces, as this may affect accuracy.
- Use a stable power supply to minimize noise and ensure reliable measurements.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the VL53L7CX with an Arduino UNO. This code assumes you are using a library such as the VL53L7CX library provided by ST.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <VL53L7CX.h> // Include the VL53L7CX library
VL53L7CX sensor; // Create a sensor object
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I²C communication
// Initialize the VL53L7CX sensor
if (!sensor.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize VL53L7CX sensor!");
while (1); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
Serial.println("VL53L7CX initialized successfully.");
}
void loop() {
uint16_t distances[64]; // Array to store distances for 64 zones
// Perform a distance measurement
if (sensor.getDistances(distances)) {
Serial.println("Distance measurements (in mm):");
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
Serial.print(distances[i]);
Serial.print(" ");
if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0) Serial.println(); // Print 8 values per line
}
Serial.println();
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read distances.");
}
delay(500); // Wait 500 ms before the next measurement
}
Notes on the Code
- The
VL53L7CXlibrary must be installed in your Arduino IDE. You can find it on GitHub or the Arduino Library Manager. - The
getDistances()function retrieves distance measurements for all 64 zones in millimeters.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Sensor Not Detected on I²C Bus
- Ensure the SDA and SCL lines are correctly connected.
- Verify that pull-up resistors are present on the I²C lines.
- Check the I²C address of the sensor (default is 0x52).
Inaccurate Distance Measurements
- Avoid reflective or transparent surfaces in the sensor's field of view.
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to excessive ambient light.
Sensor Fails to Initialize
- Verify the power supply voltage is 2.8 V.
- Check the connection to the XSHUT pin (ensure it is not floating).
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use an I²C scanner sketch to confirm the sensor's address.
- Test the sensor in a controlled environment to rule out external interference.
- Refer to the VL53L7CX datasheet for detailed electrical and timing requirements.
By following this documentation, you should be able to successfully integrate and use the VL53L7CX in your projects.