
How to Use HW-125: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with HW-125 in Cirkit Designer
Design with HW-125 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The HW-125 is a compact heat sink designed for efficient heat dissipation from electronic components. Heat sinks are critical in managing the thermal performance of electronics, ensuring components operate within their temperature limits, thus prolonging their life and reliability. The HW-125 is commonly used with power transistors, voltage regulators, MOSFETs, and other heat-generating components in applications such as power supplies, amplifiers, and computing devices.
Explore Projects Built with HW-125
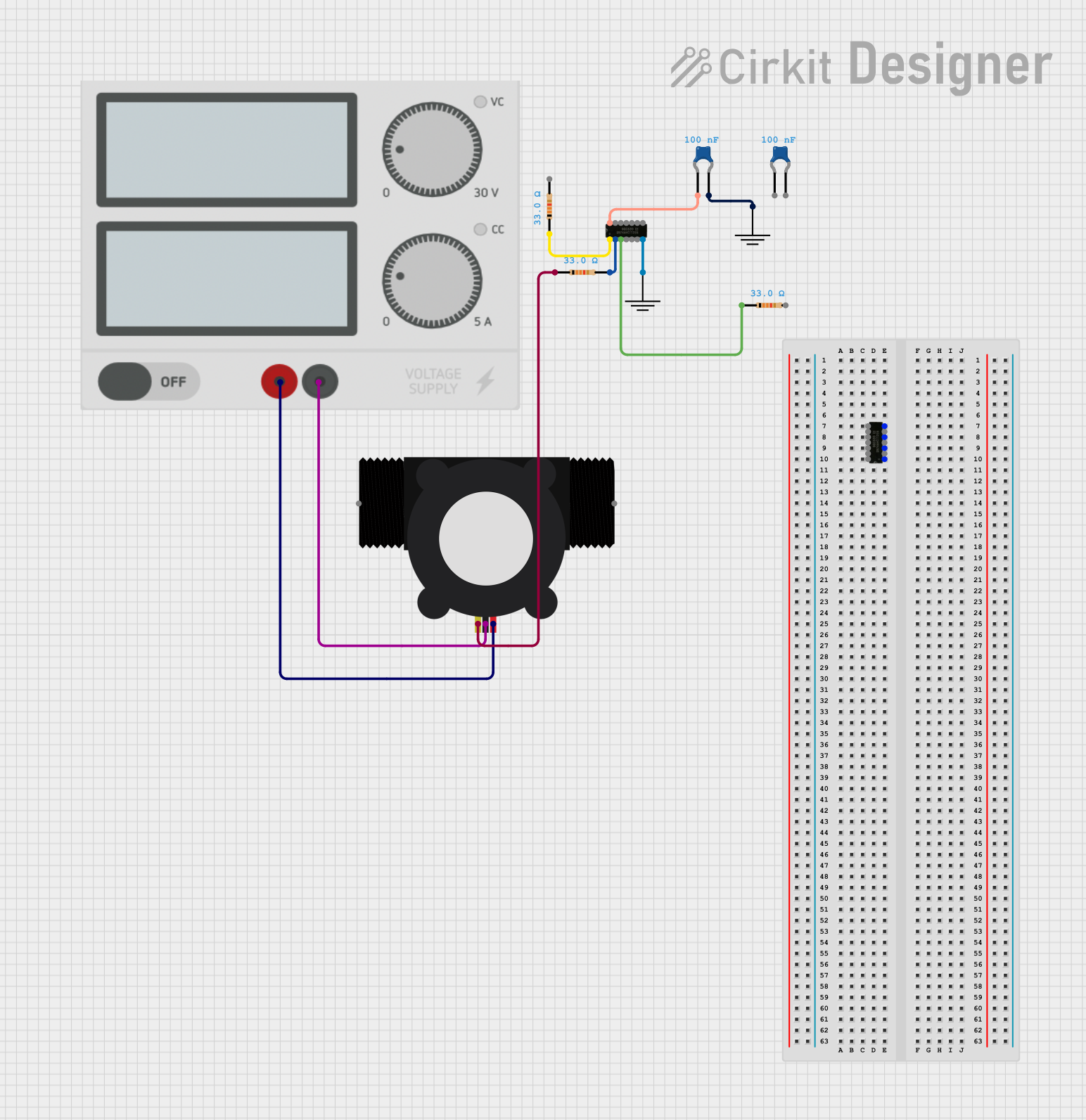
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer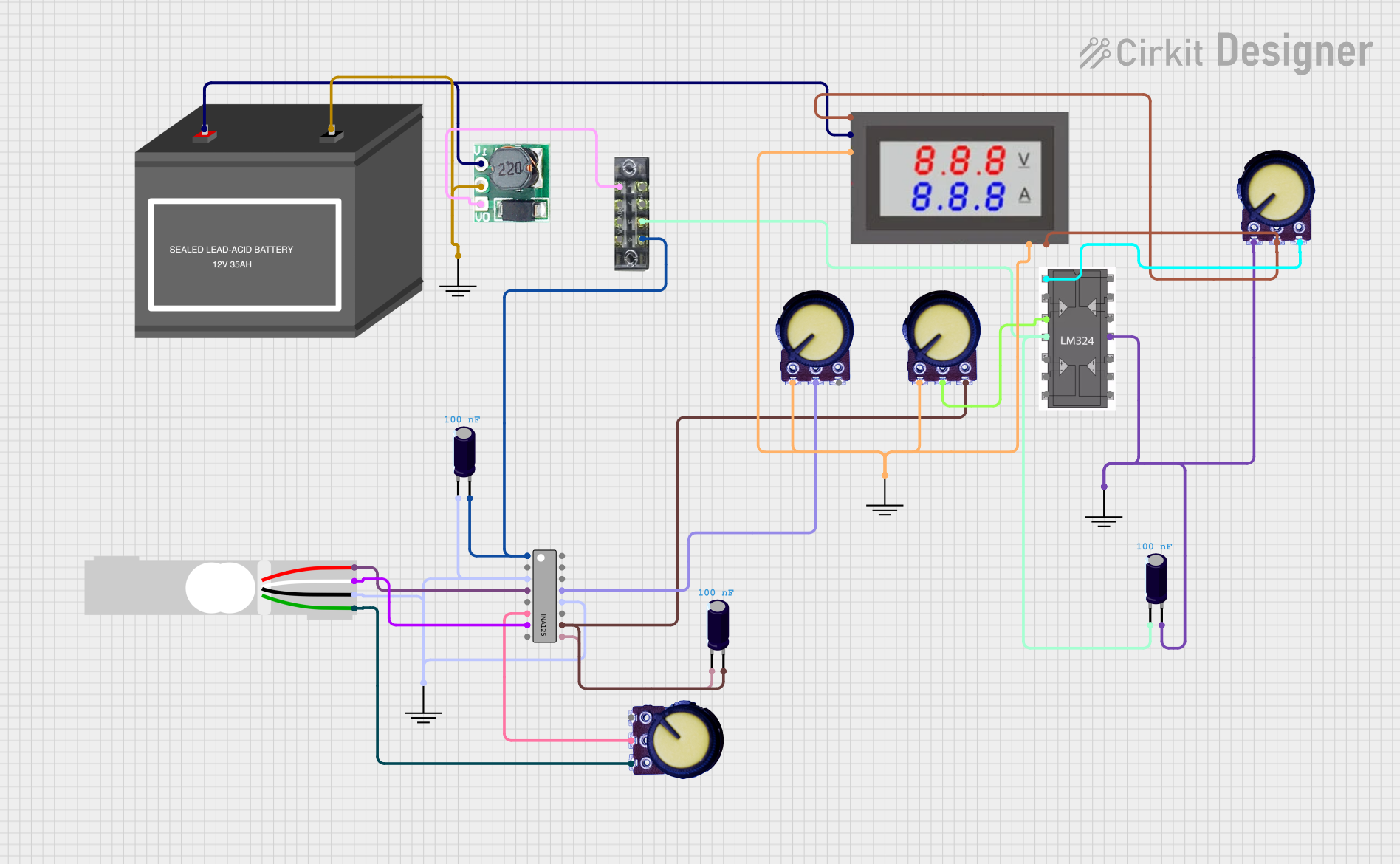
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer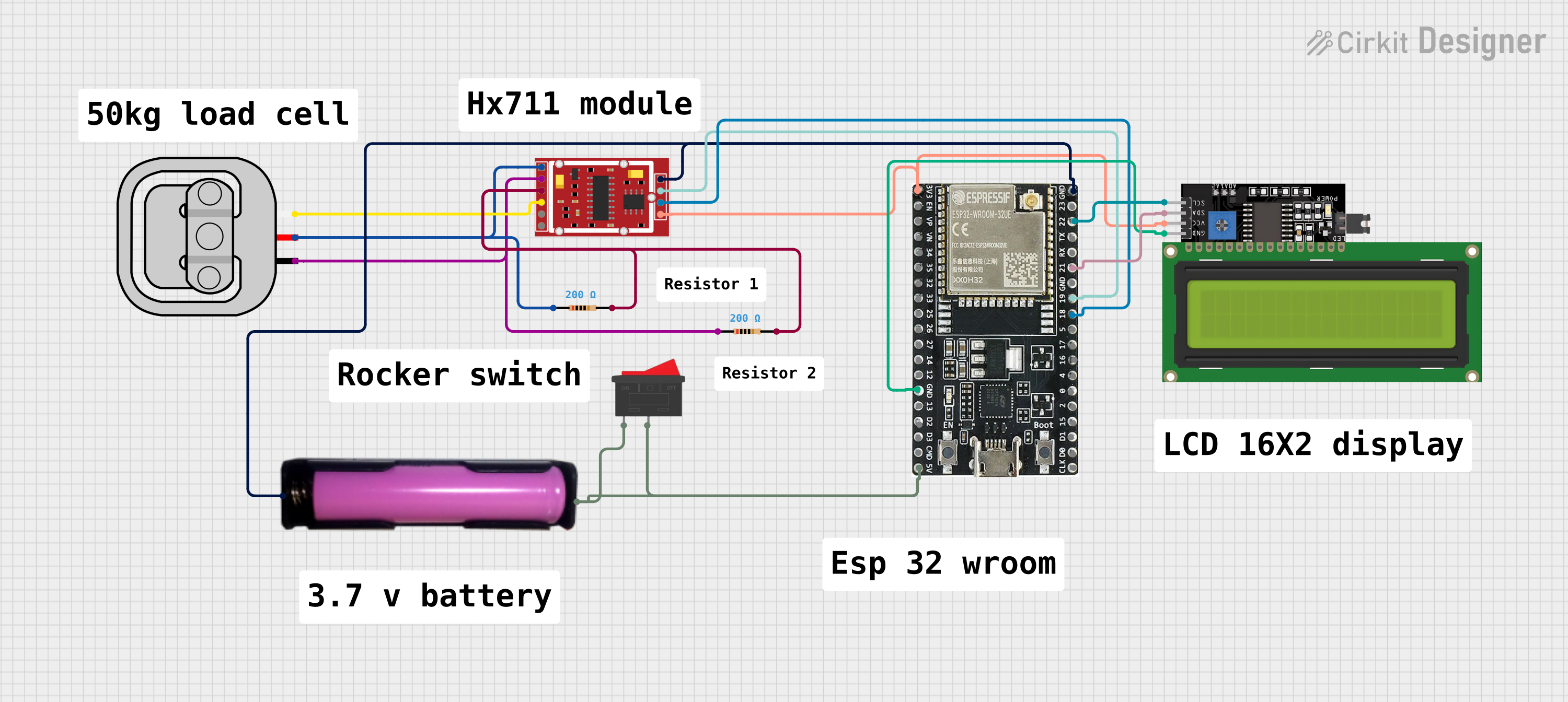
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with HW-125

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Material: Aluminum
- Dimensions: 25mm x 34mm x 12mm (L x W x H)
- Fin Design: Vertical orientation for optimal air flow
- Mounting Method: Through-hole with screws or push pins
- Thermal Resistance: Specific to application and airflow
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The HW-125 does not have pins but is mounted directly to the component requiring heat dissipation. Below is a table describing the mounting specifications:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Mounting Hole | Diameter suitable for M3 screws |
| Base Thickness | Optimal thickness for thermal conduction |
| Fin Height | Designed to maximize surface area within volume |
| Fin Spacing | Allows sufficient airflow between fins |
Usage Instructions
Mounting the HW-125 Heat Sink
- Component Preparation: Ensure the electronic component's surface is clean and free of debris.
- Thermal Interface Material (TIM): Apply a thin, even layer of thermal paste or a thermal pad to the component's surface to improve thermal conductivity.
- Alignment: Carefully align the HW-125 heat sink over the component, ensuring the mounting hole is positioned correctly.
- Securing the Heat Sink: Use appropriate M3 screws or push pins to secure the heat sink onto the component. Do not overtighten, as this may damage the component or the heat sink.
- Airflow: Ensure that there is adequate airflow around the heat sink fins. If necessary, use additional cooling measures such as fans.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Thermal Paste Application: Too much thermal paste can insulate the component rather than transfer heat. Apply sparingly.
- Orientation: Mount the heat sink in an orientation that aligns with the airflow direction within the enclosure for maximum cooling efficiency.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the heat sink for dust buildup, which can significantly reduce its cooling performance. Clean as necessary.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Overheating: If the component is still overheating, check the thermal interface material for proper application and the airflow for obstructions.
- Loose Heat Sink: A heat sink that is not securely attached can lead to poor thermal performance. Ensure it is mounted correctly.
Solutions and Tips
- Reapply TIM: If overheating persists, remove the heat sink, clean off the old thermal paste, and apply a new layer.
- Enhance Airflow: Consider adding a fan or improving the enclosure's ventilation to increase airflow over the heat sink.
FAQs
Q: Can the HW-125 be used with any component? A: The HW-125 is versatile but should be matched with components that fit its size and thermal dissipation capabilities.
Q: Is it necessary to use thermal paste? A: Yes, thermal paste or a thermal pad is crucial for filling microscopic gaps between the component and the heat sink, improving heat transfer.
Q: How do I clean the heat sink? A: Use compressed air to blow dust off the fins. For stubborn dirt, gently use a soft brush or cloth.
Note: This documentation is for the HW-125 heat sink, which is a passive electronic component and does not require electrical connection or Arduino code.