
How to Use USB Serial TTL: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
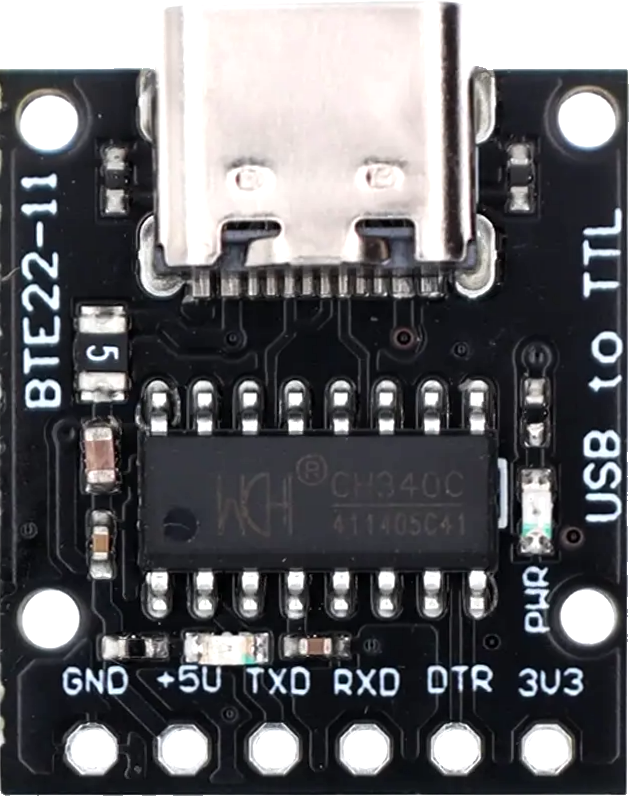
 Design with USB Serial TTL in Cirkit Designer
Design with USB Serial TTL in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The USB Serial TTL is a versatile electronic component that acts as a bridge between a USB port and TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) serial devices. It is widely used for enabling communication between computers and microcontrollers, sensors, or other serial devices. This component is essential for programming, debugging, and data transfer in embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with USB Serial TTL
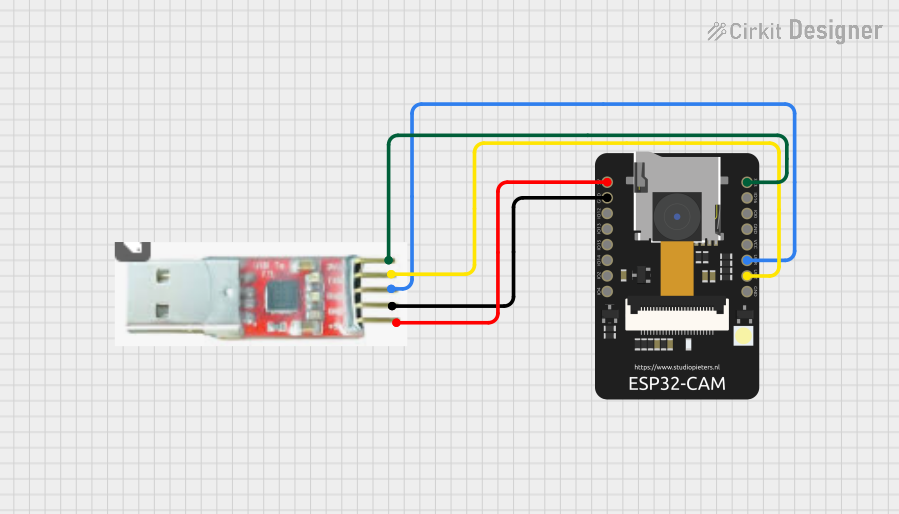
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer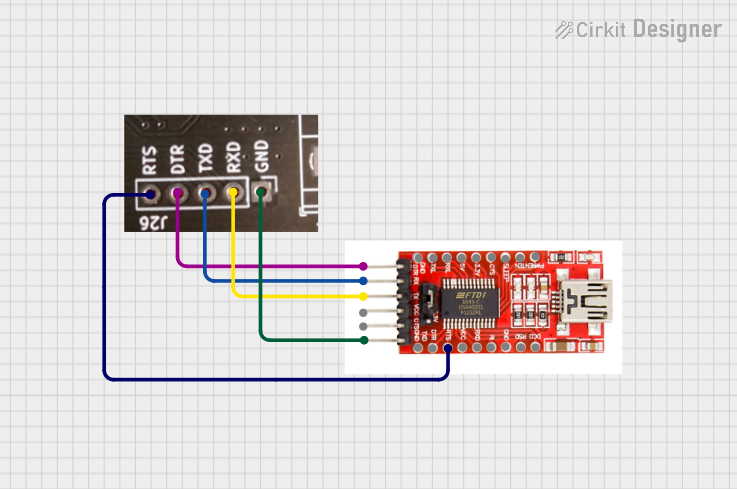
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer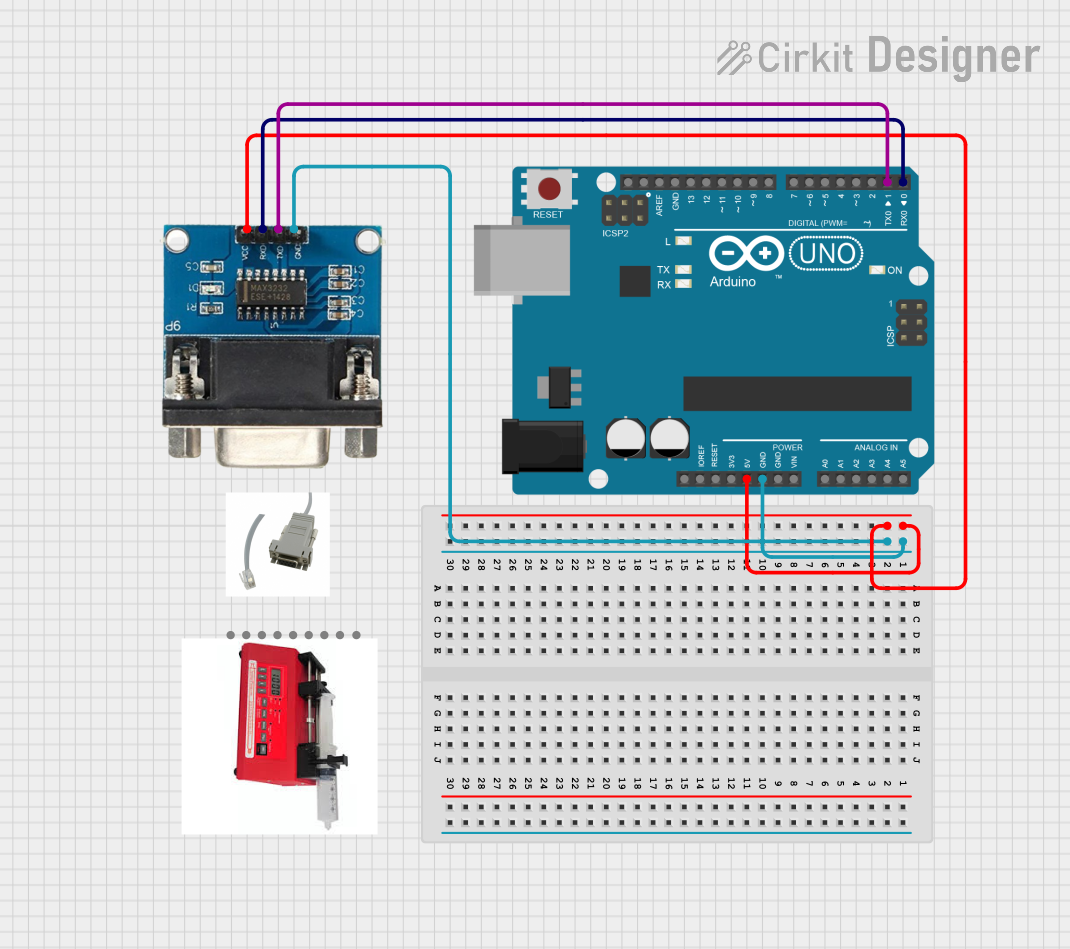
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer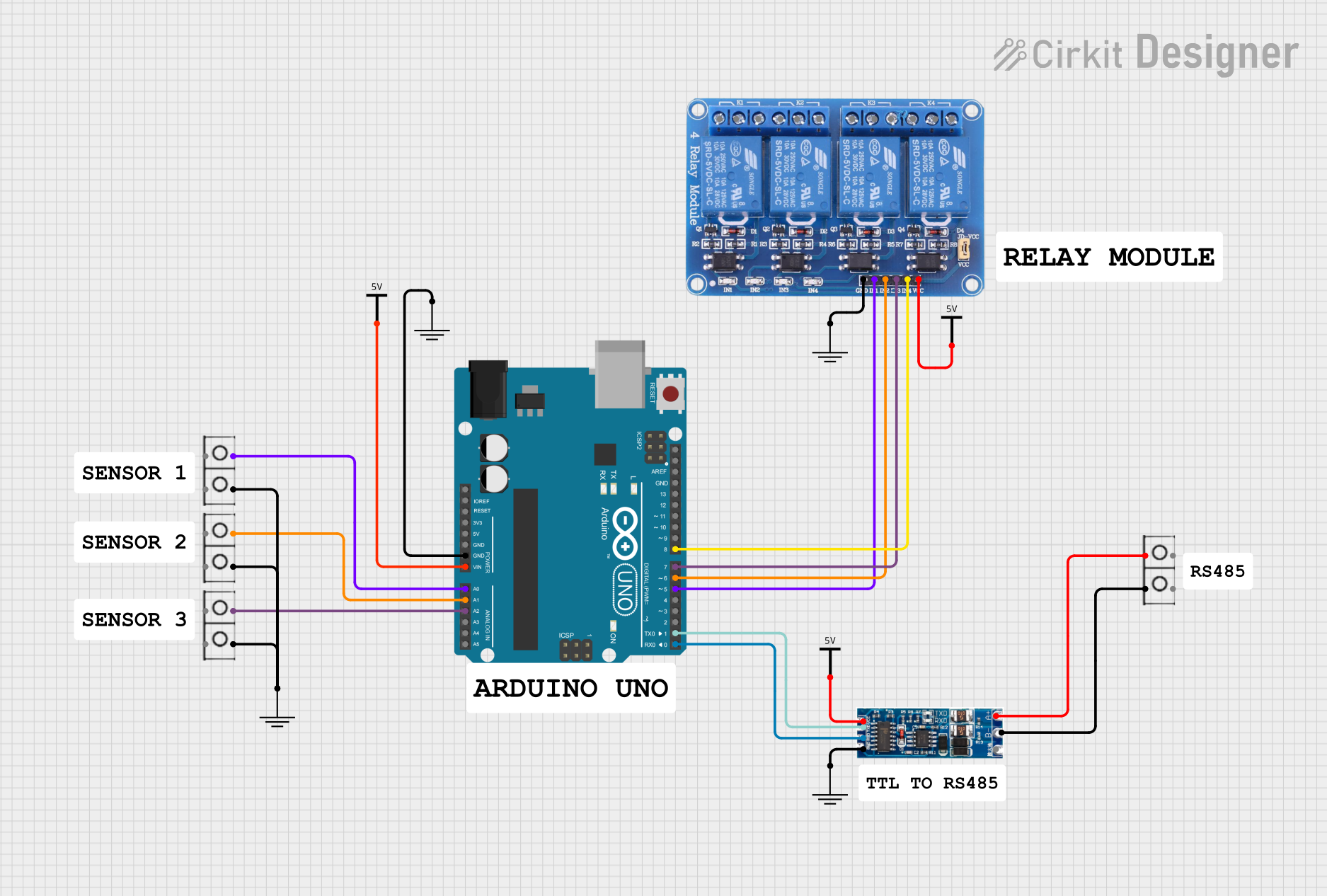
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with USB Serial TTL

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Programming microcontrollers such as Arduino, ESP8266, or ESP32.
- Debugging serial communication in embedded systems.
- Interfacing with sensors or modules that use TTL serial communication.
- Logging data from serial devices to a computer.
- Prototyping and testing serial communication circuits.
Technical Specifications
The USB Serial TTL converter typically comes in a compact module form and includes the following key specifications:
General Specifications
- Input Voltage (USB side): 5V (via USB port)
- Output Voltage (TTL side): 3.3V or 5V (selectable on some modules)
- Communication Protocol: UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter)
- Baud Rate: Supports standard baud rates (e.g., 9600, 115200)
- Chipset: Commonly uses FT232, CH340, or CP2102
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The USB Serial TTL module typically has the following pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| GND | Ground connection. Connect to the ground of the target device. |
| VCC | Power output. Provides 3.3V or 5V (depending on module configuration). |
| TXD | Transmit Data. Sends serial data from the USB to the target device. |
| RXD | Receive Data. Receives serial data from the target device to the USB. |
| DTR | Data Terminal Ready. Used for resetting microcontrollers during programming. |
| CTS (optional) | Clear to Send. Flow control pin (not always used in basic applications). |
Note: Some modules may include additional pins such as RTS (Request to Send) or 3.3V/5V selection jumpers.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the USB Serial TTL in a Circuit
Connect the USB Serial TTL to the Target Device:
- Connect the GND pin of the module to the ground of the target device.
- Connect the TXD pin of the module to the RX pin of the target device.
- Connect the RXD pin of the module to the TX pin of the target device.
- If required, connect the VCC pin to power the target device (ensure voltage compatibility).
Install Drivers:
- Install the appropriate driver for the module's chipset (e.g., FTDI, CH340, or CP2102) on your computer. Drivers are typically available on the manufacturer's website.
Connect to a Computer:
- Plug the USB Serial TTL module into a USB port on your computer. Verify that the device is recognized in the operating system (e.g., as a COM port in Windows or
/dev/ttyUSBxin Linux).
- Plug the USB Serial TTL module into a USB port on your computer. Verify that the device is recognized in the operating system (e.g., as a COM port in Windows or
Configure Serial Communication:
- Use a terminal program (e.g., PuTTY, Tera Term, or Arduino IDE Serial Monitor) to open the COM port.
- Set the baud rate and other serial parameters (e.g., data bits, stop bits, parity) to match the target device.
Program or Debug:
- For programming microcontrollers, use the appropriate IDE (e.g., Arduino IDE) and select the correct COM port.
- For debugging, monitor the serial output or send commands to the target device.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the target device operates at the same voltage level as the USB Serial TTL module (3.3V or 5V).
- Cross TX and RX: Always connect the TXD pin of the module to the RX pin of the target device, and vice versa.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not draw excessive current from the VCC pin of the module. Use an external power source if the target device requires high current.
- Static Protection: Handle the module carefully to avoid damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The USB Serial TTL can be used to upload code to an Arduino UNO. Below is an example Arduino sketch and connection setup:
Wiring
| USB Serial TTL Pin | Arduino UNO Pin |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| TXD | RX (Pin 0) |
| RXD | TX (Pin 1) |
| VCC | 5V |
Arduino Code Example
// Example: Sending "Hello, World!" via Serial
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Hello, World!"); // Send a message to the serial monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Upload the code to the Arduino UNO using the USB Serial TTL module. Open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to view the output.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Device Not Recognized:
- Ensure the correct driver for the module's chipset is installed.
- Try a different USB cable or port.
No Serial Communication:
- Verify the TXD and RXD connections are correct (crossed).
- Check the baud rate and other serial settings in the terminal program.
Target Device Not Powering On:
- Ensure the VCC pin is providing the correct voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- Use an external power source if the target device requires more current.
Corrupted Data or Communication Errors:
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Ensure the baud rate matches between the module and the target device.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the USB Serial TTL to power my target device?
A: Yes, but only if the target device's current requirements are within the module's limits. For high-power devices, use an external power source.
Q: How do I reset my microcontroller during programming?
A: Use the DTR pin to trigger a reset. Some modules automatically handle this when uploading code.
Q: Can I use the USB Serial TTL with a 3.3V device?
A: Yes, but ensure the module supports 3.3V operation. Some modules have a jumper to select between 3.3V and 5V.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the USB Serial TTL module for programming, debugging, and serial communication tasks.