
How to Use bdh: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
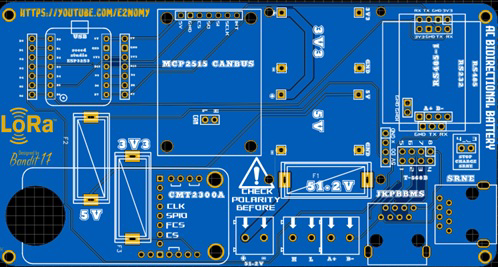
 Design with bdh in Cirkit Designer
Design with bdh in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BDH (Bipolar Digital High) is a versatile electronic component designed for use in digital circuits. It is primarily used for signal processing and amplification, making it an essential component in high-speed data applications. The BDH is known for its ability to handle rapid transitions in digital signals, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments.
Explore Projects Built with bdh

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer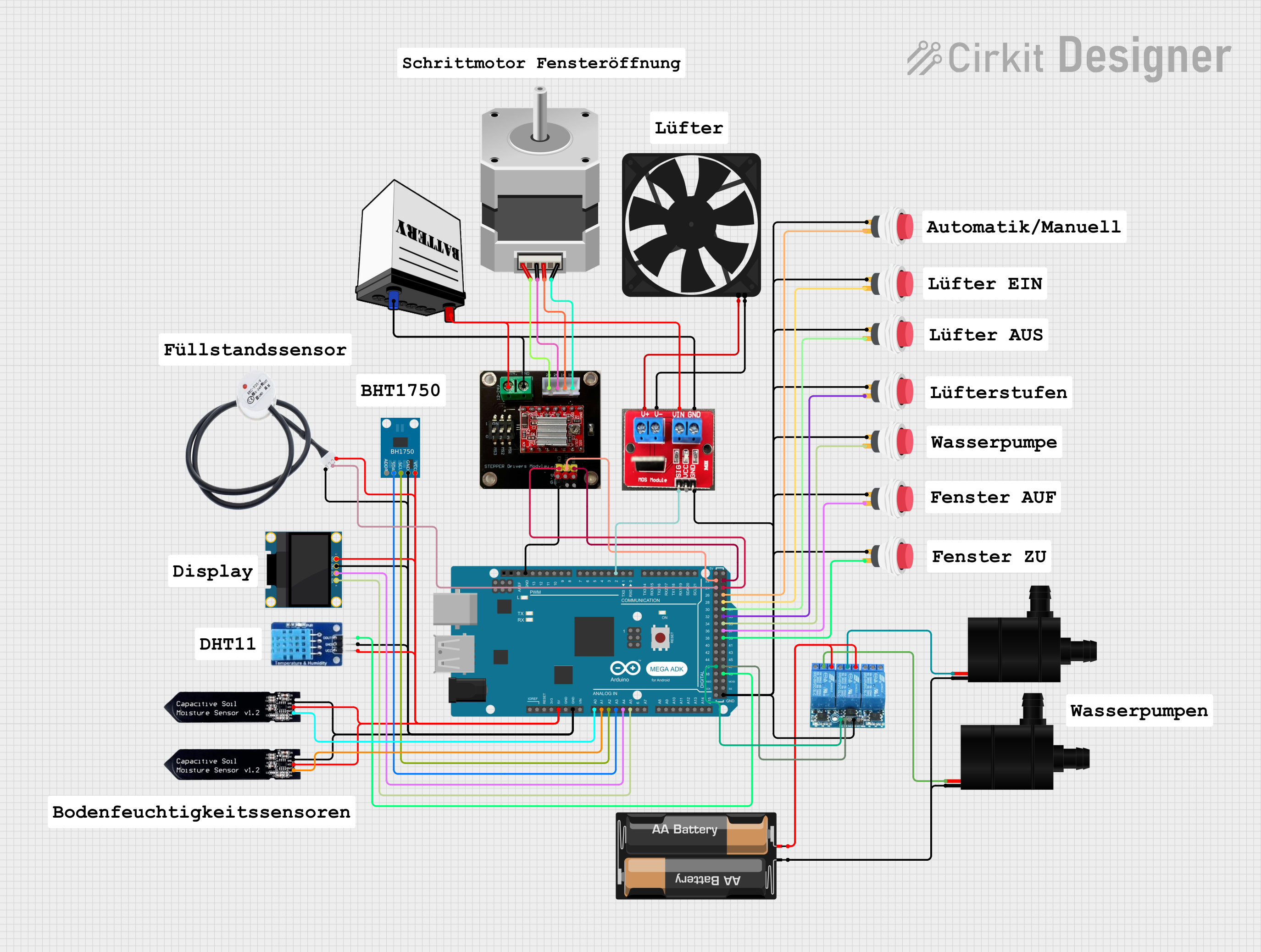
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer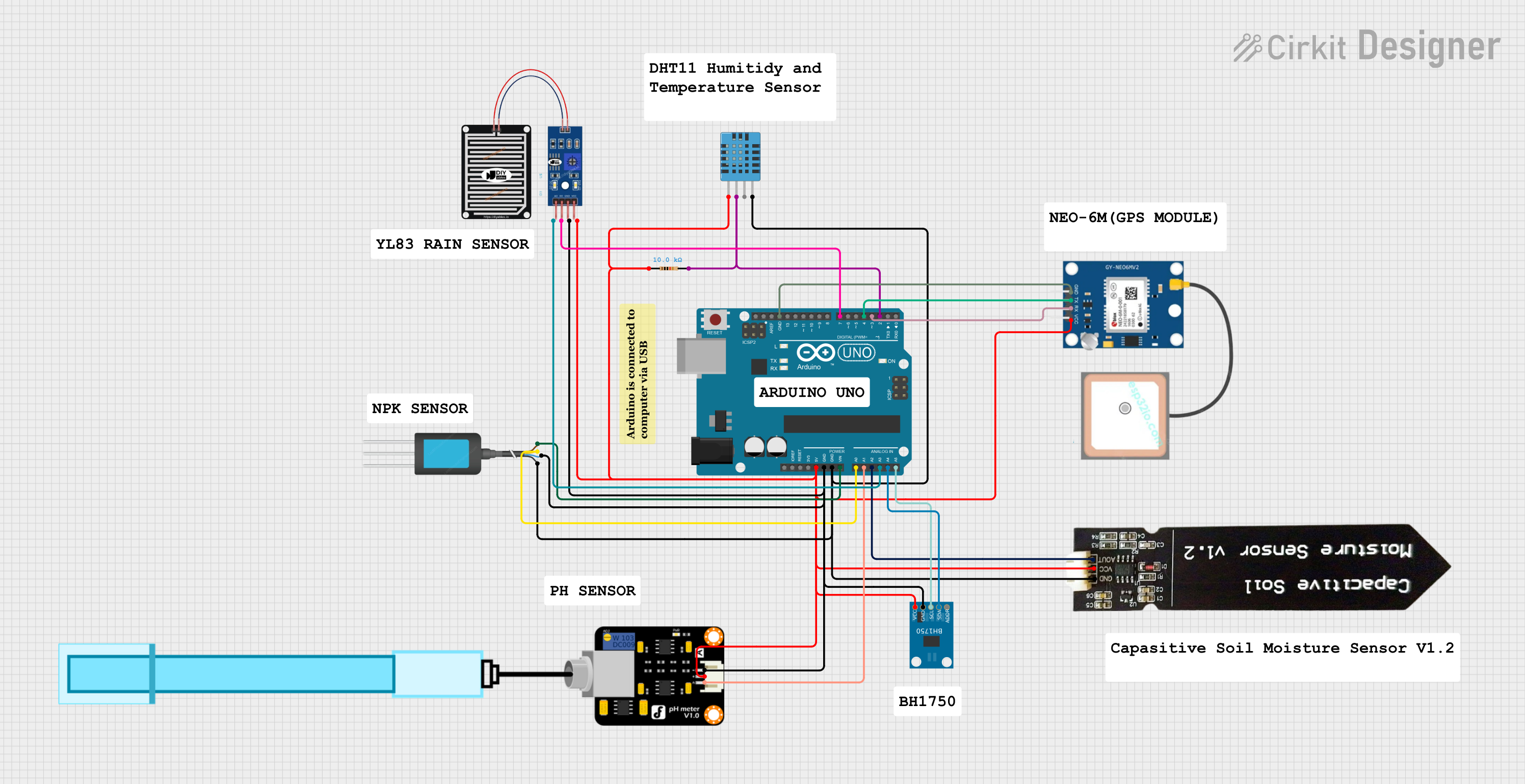
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer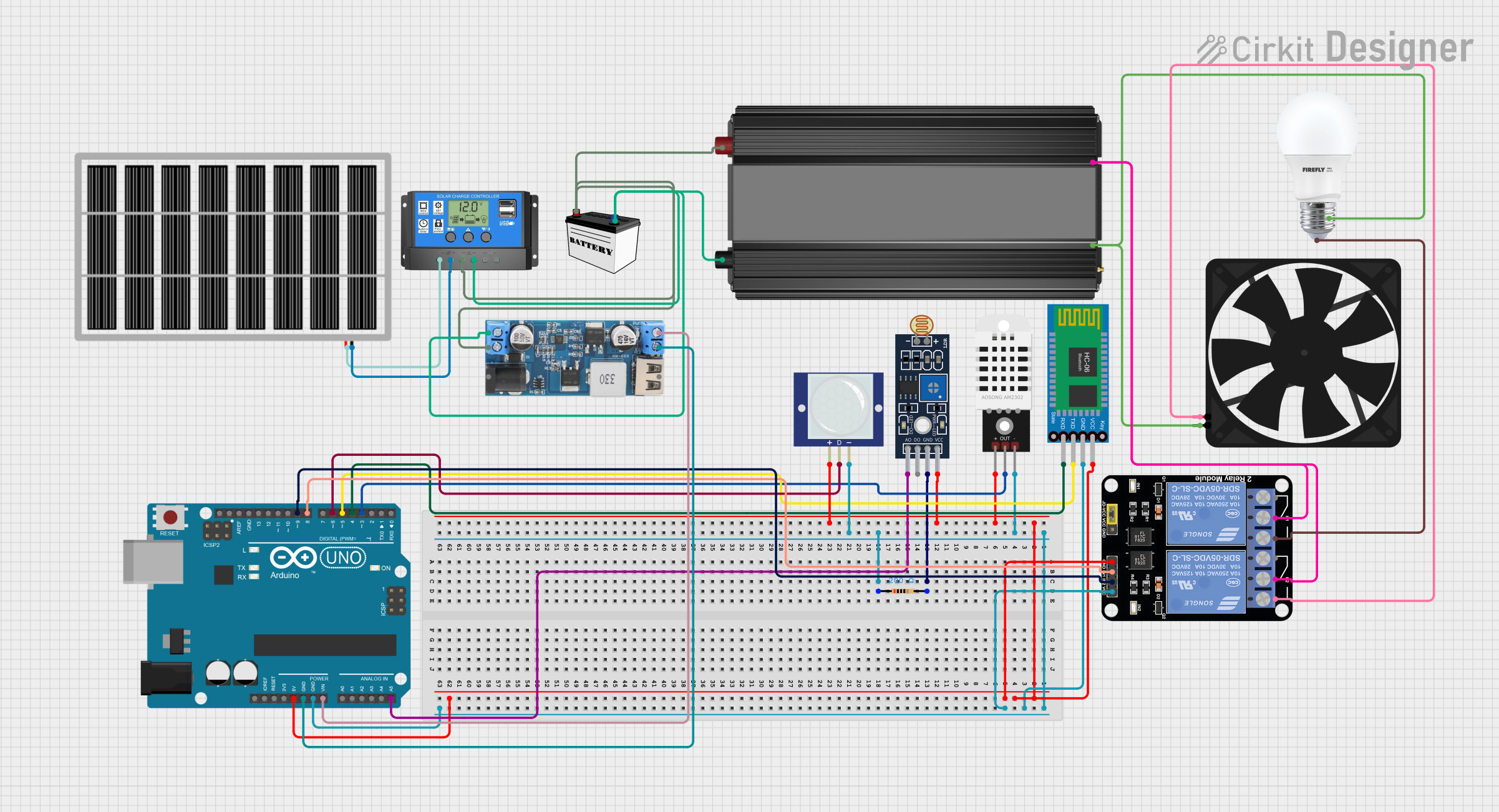
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with bdh

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- High-speed data communication systems
- Digital signal processing circuits
- Amplification of digital signals in microcontroller-based projects
- Logic level conversion in mixed-signal systems
- High-frequency switching applications
Technical Specifications
The BDH component is designed to meet the requirements of modern digital systems. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 3.3V to 5V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to Vcc |
| Output Voltage Range | 0V to Vcc |
| Maximum Output Current | 20mA |
| Propagation Delay | < 10ns |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | DIP, SMD |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BDH component typically comes in an 8-pin package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Positive power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | IN1 | Digital input signal 1 |
| 4 | IN2 | Digital input signal 2 |
| 5 | OUT1 | Amplified digital output corresponding to IN1 |
| 6 | OUT2 | Amplified digital output corresponding to IN2 |
| 7 | NC | No connection (leave unconnected) |
| 8 | EN | Enable pin (active HIGH to enable outputs) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BDH in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin to a stable 3.3V or 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground of the circuit.
- Input Signals: Feed the digital signals to be processed or amplified into the IN1 and IN2 pins.
- Enable the Component: Set the EN pin HIGH to activate the outputs. If the EN pin is LOW, the outputs will be disabled.
- Output Signals: The processed or amplified signals will be available at the OUT1 and OUT2 pins.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the supply voltage (Vcc) to avoid damage to the component.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) between Vcc and GND to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum output current of 20mA to prevent overheating or damage.
- If unused, leave the NC pin unconnected.
- For high-speed applications, minimize the length of the signal traces to reduce signal degradation.
Example: Using BDH with Arduino UNO
The BDH can be easily interfaced with an Arduino UNO for digital signal amplification. Below is an example:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the Vcc pin of the BDH to the 5V pin of the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the BDH to the GND pin of the Arduino.
- Connect the IN1 pin of the BDH to Arduino digital pin 2.
- Connect the OUT1 pin of the BDH to an LED (with a 220Ω resistor in series) to visualize the output.
- Connect the EN pin of the BDH to Arduino digital pin 3.
Arduino Code
// Define pin connections
const int inputPin = 2; // Arduino pin connected to BDH IN1
const int enablePin = 3; // Arduino pin connected to BDH EN
void setup() {
pinMode(inputPin, OUTPUT); // Set inputPin as output
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT); // Set enablePin as output
digitalWrite(enablePin, HIGH); // Enable the BDH component
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(inputPin, HIGH); // Send a HIGH signal to BDH IN1
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms
digitalWrite(inputPin, LOW); // Send a LOW signal to BDH IN1
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal
- Cause: The EN pin is not set HIGH.
- Solution: Ensure the EN pin is connected to a HIGH signal to enable the outputs.
Distorted Output Signal
- Cause: Noise in the power supply or long signal traces.
- Solution: Add decoupling capacitors near the Vcc pin and minimize trace lengths.
Overheating
- Cause: Exceeding the maximum output current of 20mA.
- Solution: Use a current-limiting resistor or ensure the load does not draw more than 20mA.
Component Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or damaged component.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and replace the component if necessary.
FAQs
Q1: Can the BDH handle analog signals?
A1: No, the BDH is designed specifically for digital signals and may not perform well with analog inputs.
Q2: What happens if the EN pin is left floating?
A2: If the EN pin is left floating, the outputs may behave unpredictably. Always connect the EN pin to a defined logic level (HIGH or LOW).
Q3: Can I use the BDH with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, the BDH is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems. Ensure the supply voltage matches the microcontroller's logic level.
Q4: Is the BDH suitable for high-frequency applications?
A4: Yes, the BDH is optimized for high-speed digital signals with a propagation delay of less than 10ns.