
How to Use Li-Po battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Li-Po battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with Li-Po battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A lithium polymer (Li-Po) battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte. It is known for its lightweight design, high energy density, and flexibility in form factor. These characteristics make Li-Po batteries ideal for applications where weight and size are critical, such as in drones, smartphones, RC vehicles, and electric vehicles. Additionally, their ability to deliver high discharge rates makes them suitable for high-performance devices.
Explore Projects Built with Li-Po battery
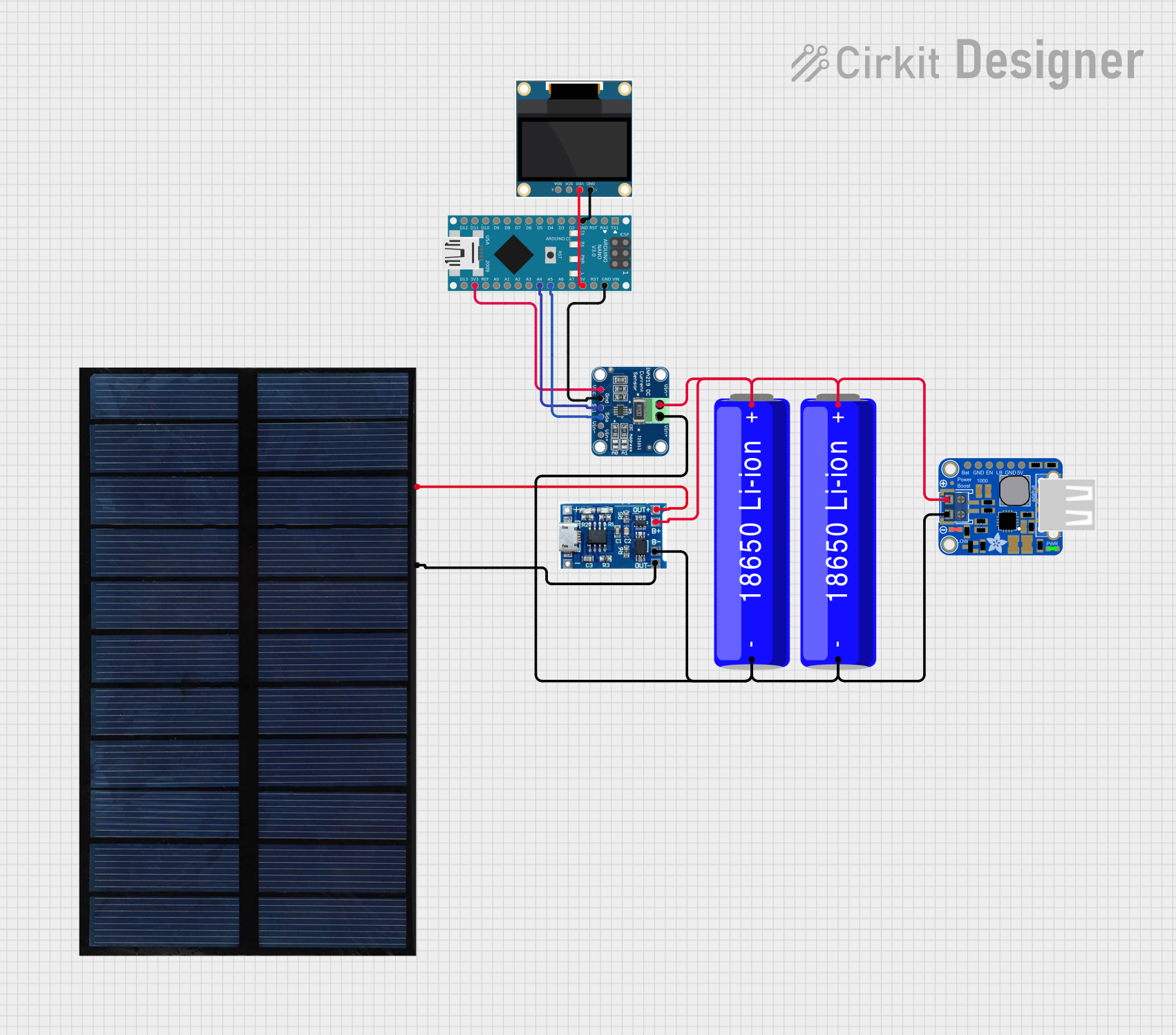
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer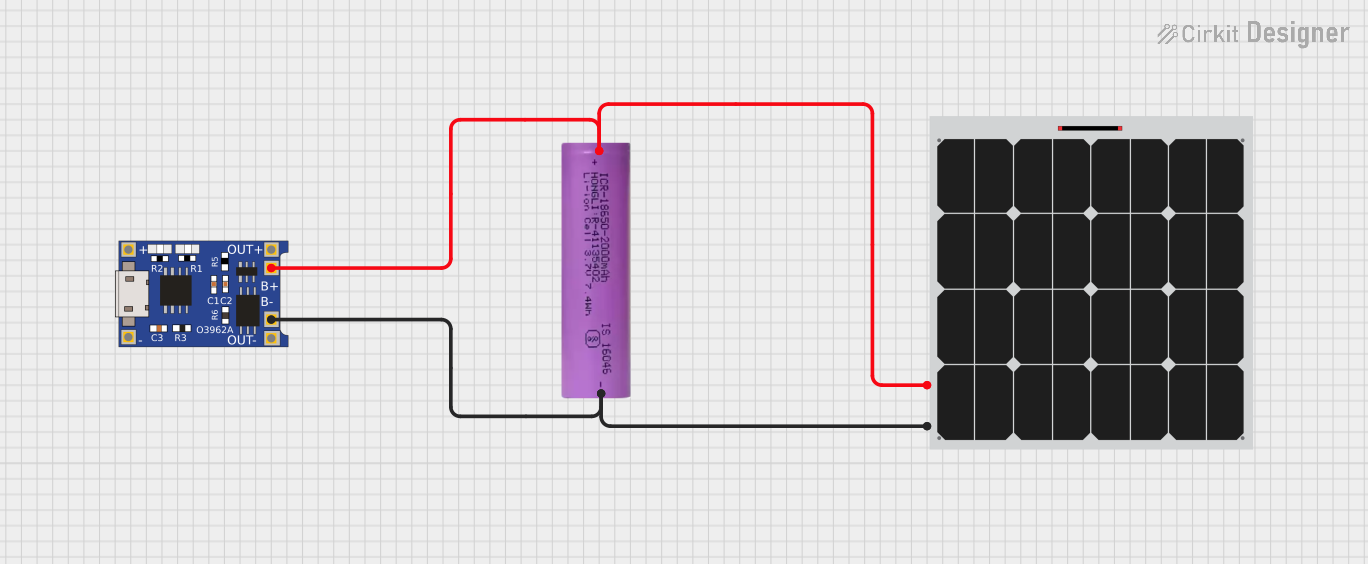
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Li-Po battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, laptops)
- Remote-controlled (RC) vehicles and drones
- Wearable devices
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Backup power supplies and portable chargers
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical Li-Po battery. Note that specific values may vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
| Parameter | Specification Example |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V per cell |
| Fully Charged Voltage | 4.2V per cell |
| Discharge Cutoff Voltage | 3.0V per cell |
| Capacity Range | 100mAh to several thousand mAh |
| Discharge Rate (C-Rating) | 1C to 100C (varies by model) |
| Charging Current | Typically 1C (e.g., 1A for a 1000mAh cell) |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 60°C (discharge), 0°C to 45°C (charge) |
| Weight | Varies (e.g., ~20g for a 1000mAh battery) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Li-Po batteries typically have two or three wires for connection. Below is a description of the common pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Wire Color (Typical) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Red | Positive terminal for power output |
| Negative (-) | Black | Negative terminal for power output |
| Balance Lead | White/Yellow | Used for balancing cells during charging (multi-cell batteries only) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use a Li-Po Battery in a Circuit
Connect the Battery:
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Connect the terminals to the corresponding inputs of your circuit or device.
- If using a multi-cell Li-Po battery, ensure the balance lead is connected to a compatible charger for safe charging.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a Li-Po-specific charger to avoid overcharging or damaging the battery.
- Set the charger to the correct cell count (e.g., 1S, 2S, 3S) and charging current (e.g., 1C).
- Monitor the charging process to ensure safety.
Discharging the Battery:
- Avoid discharging below the cutoff voltage (typically 3.0V per cell) to prevent damage.
- Use a battery management system (BMS) or low-voltage alarm for protection.
Mounting and Handling:
- Secure the battery in your device to prevent physical damage.
- Avoid puncturing, bending, or exposing the battery to high temperatures.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Safety First: Li-Po batteries can catch fire or explode if mishandled. Always follow the manufacturer's guidelines.
- Storage: Store the battery at a 50-60% charge level in a cool, dry place.
- Balancing Cells: For multi-cell batteries, use a balance charger to ensure all cells are charged evenly.
- Avoid Overcharging/Overdischarging: Use a BMS or voltage monitoring system to protect the battery.
Example: Using a Li-Po Battery with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of connecting a Li-Po battery to an Arduino UNO using a voltage regulator to step down the voltage to 5V.
Circuit Diagram
- Components Required:
- 1S Li-Po battery (3.7V nominal)
- Voltage regulator module (e.g., LM7805 or buck converter)
- Arduino UNO
- Jumper wires
Code Example
// Example code to read battery voltage using Arduino UNO
// Ensure the battery voltage is stepped down to a safe level for the Arduino's ADC
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the battery voltage divider
float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(batteryPin, INPUT); // Set the battery pin as input
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue * 5.0 / 1023.0) * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to scale down the battery voltage to a level safe for the Arduino's analog input (0-5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect charger settings or damaged battery.
- Solution: Verify the charger is set to the correct cell count and current. Inspect the battery for physical damage.
Battery Swelling or Puffing:
- Cause: Overcharging, overdischarging, or physical damage.
- Solution: Stop using the battery immediately. Dispose of it safely according to local regulations.
Device Shuts Down Unexpectedly:
- Cause: Battery voltage dropped below the cutoff level.
- Solution: Recharge the battery and ensure a low-voltage alarm or BMS is in place.
Battery Overheats During Use:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Ensure the battery's discharge rate (C-rating) matches the device's requirements. Improve ventilation.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Li-Po battery without a balance charger?
A: It is not recommended for multi-cell batteries. A balance charger ensures all cells are charged evenly, preventing overcharging or undercharging of individual cells.
Q: How do I safely dispose of a Li-Po battery?
A: Discharge the battery completely, then take it to a certified e-waste recycling facility. Do not throw it in regular trash.
Q: What happens if I overdischarge a Li-Po battery?
A: Overdischarging can permanently damage the battery, reducing its capacity and lifespan. Use a low-voltage alarm or BMS to prevent this.
Q: Can I use a Li-Po battery in cold weather?
A: Li-Po batteries perform poorly in cold temperatures. Keep the battery warm or use a different battery type for extreme conditions.