
How to Use Plug: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Plug in Cirkit Designer
Design with Plug in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A plug is a device designed to connect an electrical appliance to a power source, enabling the flow of electricity into the appliance. It is a critical component in electrical systems, ensuring a safe and reliable connection between devices and power outlets. Plugs come in various types and configurations to accommodate different voltage levels, current ratings, and regional standards.
Explore Projects Built with Plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer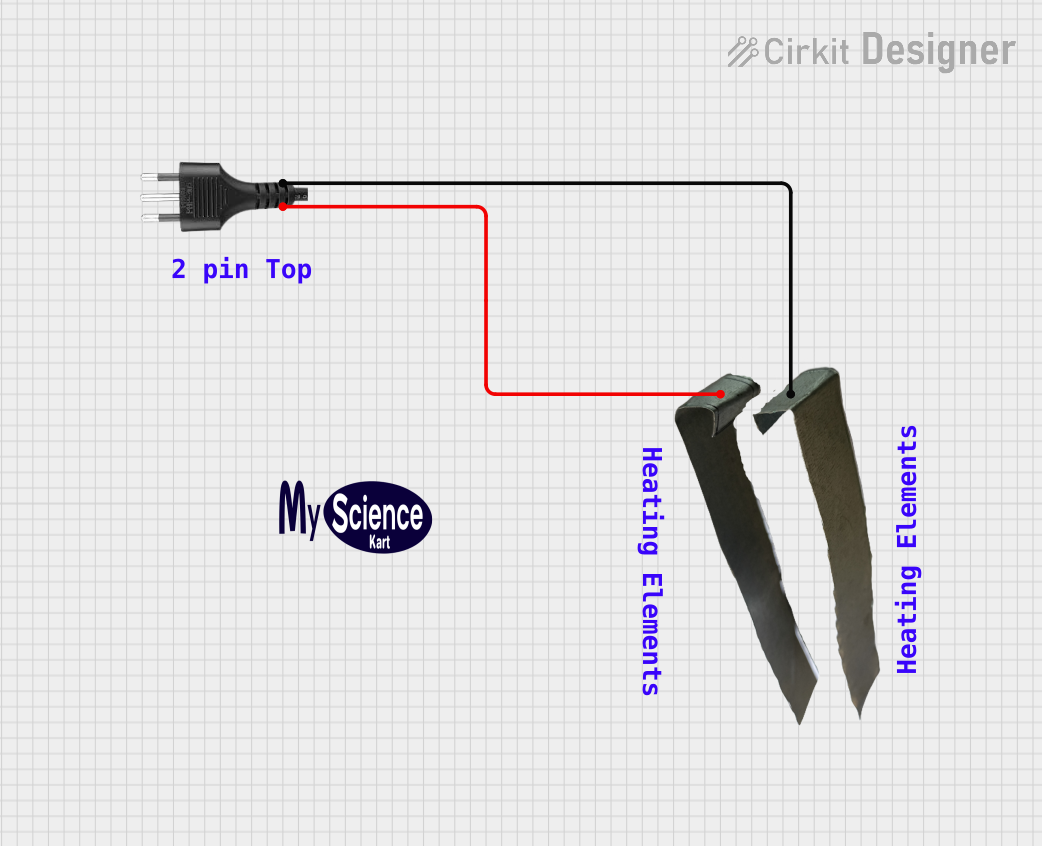
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Plug

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering household appliances such as refrigerators, televisions, and lamps.
- Connecting industrial equipment to power supplies.
- Charging electronic devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Temporary power connections for tools and machinery in workshops.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of a plug vary depending on its type and intended application. Below are general specifications for a standard household plug:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 110V - 240V AC (varies by region) |
| Current Rating | 6A - 16A (depending on plug type) |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz |
| Material | Thermoplastic or thermoset for insulation |
| Pin Material | Brass or nickel-plated brass |
| Safety Features | Insulated pins, grounding pin, shutters |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is an example of a 3-pin plug configuration commonly used in many regions:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Carries the current from the power source to the appliance. |
| Neutral (N) | Completes the circuit by returning current to the power source. |
| Ground (G) | Provides a safety path for fault currents to prevent electric shock. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Plug in a Circuit
- Inspect the Plug: Ensure the plug is in good condition, with no visible damage to the pins or casing.
- Connect to Appliance: Attach the plug to the appliance's power cord securely.
- Insert into Power Outlet: Align the pins with the outlet and push the plug in firmly.
- Turn on Power: If the outlet has a switch, turn it on to supply power to the appliance.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Verify that the plug's voltage rating matches the power source and appliance.
- Grounding: Always use a plug with a grounding pin for appliances with metal casings to ensure safety.
- Overloading: Avoid exceeding the plug's current rating to prevent overheating or damage.
- Regional Standards: Use plugs that comply with the standards of your region (e.g., Type A, Type C, Type G).
- Secure Connections: Ensure the plug fits snugly into the outlet to avoid loose connections.
Example: Using a Plug with an Arduino UNO
If you are powering an Arduino UNO using a plug and a power adapter, follow these steps:
- Use a DC power adapter with a plug that matches your region's outlet type.
- Ensure the adapter provides 7-12V DC output, as required by the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the adapter's barrel jack to the Arduino's power input port.
// Example Arduino code to blink an LED
// This assumes the Arduino is powered via a plug and adapter
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output for the LED
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Loose Connection: The plug does not fit securely into the outlet.
- Solution: Check for debris in the outlet or bent pins on the plug. Replace if necessary.
- Overheating: The plug becomes hot during use.
- Solution: Ensure the current drawn by the appliance does not exceed the plug's rating.
- No Power to Appliance: The appliance does not turn on when the plug is connected.
- Solution: Verify the outlet is functional and the plug is properly inserted. Check the appliance's power cord for damage.
- Sparking: Sparks appear when inserting or removing the plug.
- Solution: Turn off the outlet switch before plugging in or unplugging. Replace worn-out plugs or outlets.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 110V plug in a 220V outlet?
A: No, using a plug rated for 110V in a 220V outlet can damage the appliance and pose a safety hazard. Always match the plug's voltage rating to the power source.
Q: How do I know if my plug is grounded?
A: A grounded plug typically has three pins, with the third pin (ground) being longer or thicker than the others.
Q: Can I replace a damaged plug myself?
A: Yes, but only if you are familiar with electrical wiring. Ensure the replacement plug matches the original specifications and follow proper wiring practices.
Q: Why does my plug have shutters on the pinholes?
A: Shutters are a safety feature to prevent accidental contact with live parts, especially in regions with Type G plugs.