
How to Use Power Supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Power Supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with Power Supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A power supply is an essential component in electronic systems, responsible for converting electrical power from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency required by the connected devices. It ensures that electronic components receive a stable and appropriate amount of power for their operation. Power supplies are used in a wide range of applications, from small consumer electronics to large industrial machines.
Explore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer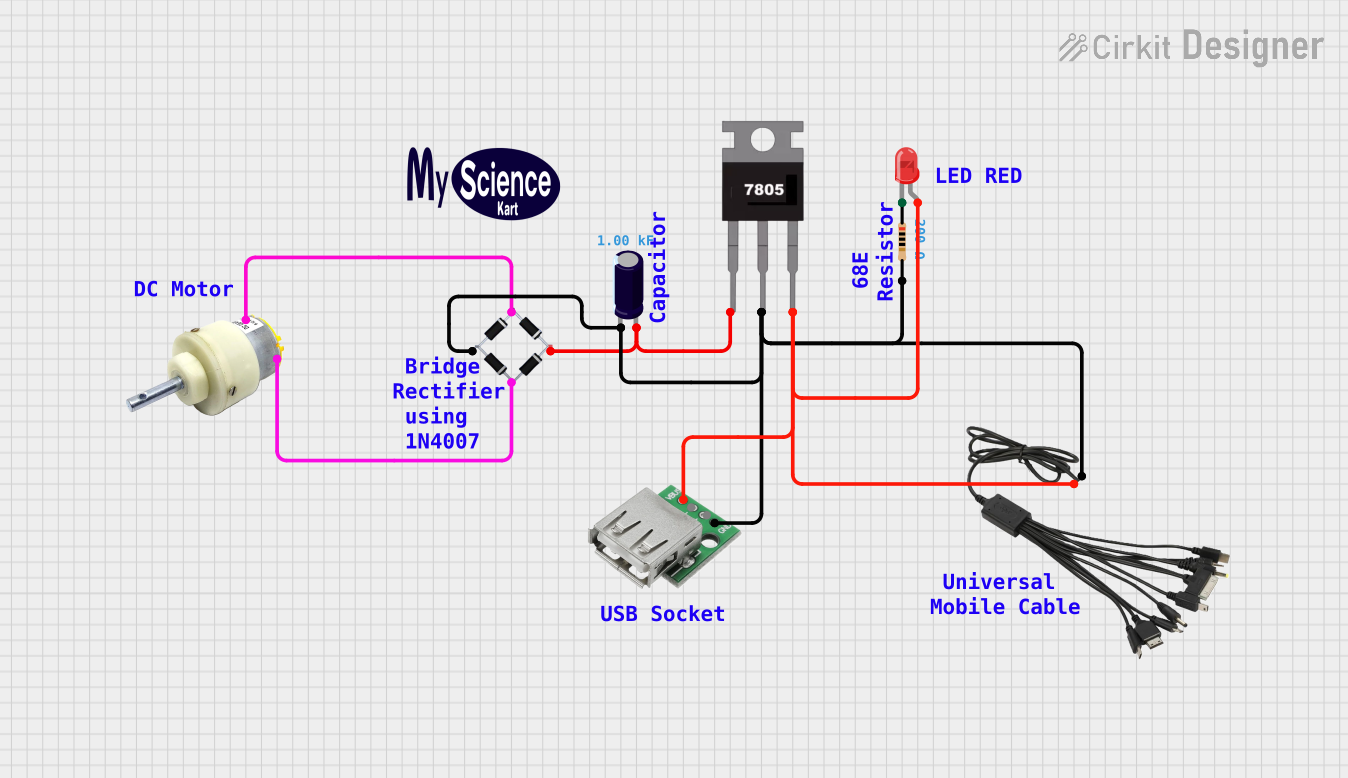
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer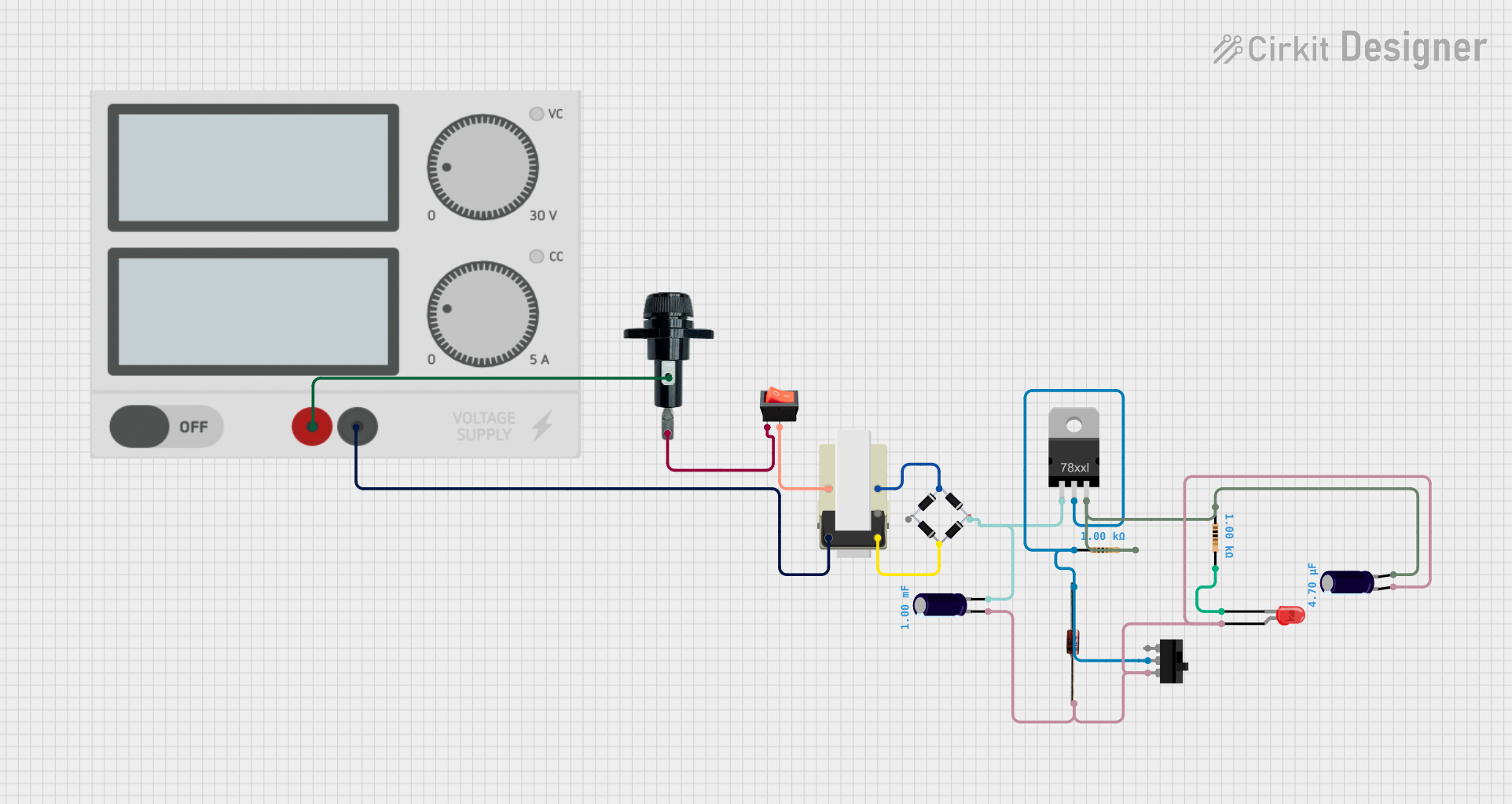
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Power Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Personal computers and servers
- Consumer electronics (TVs, gaming consoles, chargers)
- Industrial control systems
- Telecommunication equipment
- Medical devices
- Laboratory and test equipment
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | The range of voltage the power supply can accept. |
| Output Voltage | The voltage level supplied to the load. |
| Output Current | The maximum current the power supply can provide. |
| Power Rating | The total amount of power the supply can deliver. |
| Efficiency | The percentage of input power that is converted to output power. |
| Regulation | The ability to maintain a constant output voltage/current. |
| Ripple & Noise | The amount of unwanted variation in the output. |
| Protection Features | Overvoltage, overcurrent, short-circuit protections. |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AC Input | Connects to the AC mains supply. |
| 2 | Ground | Safety earth ground connection. |
| 3 | DC Output + | Positive output supplying regulated DC voltage. |
| 4 | DC Output - | Negative output or return path for DC current. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Power Supply in a Circuit
Connect the AC Input: Ensure the power supply is not plugged into an AC outlet. Connect the AC input pins to the AC mains supply, respecting the voltage and frequency specifications.
Grounding: Connect the ground pin to the earth ground in your circuit for safety and noise reduction.
Connect the Load: Attach your load to the DC output pins, ensuring that the load does not exceed the power supply's maximum current and power ratings.
Power On: Once all connections are secure, plug the power supply into the AC outlet and switch it on.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Load Requirements: Ensure the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements of your load.
- Ventilation: Provide adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Safety: Always follow electrical safety standards to prevent accidents.
- Ripple and Noise: Use filtering if sensitive circuits require cleaner DC power.
- Isolation: Use an isolated power supply when necessary to prevent ground loops.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Insufficient Power: Ensure the power supply can handle the load's power consumption.
- Overheating: Check for adequate ventilation and that the load does not exceed the power supply's ratings.
- Noise Issues: Implement filtering or check for damaged components if noise is affecting the circuit.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- No Output Voltage: Verify AC input connections and check for blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Ensure the load is stable and does not exceed the power supply's regulation capabilities.
- Unexpected Shutdowns: Check for overcurrent conditions or thermal protection activation.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a power supply with a higher voltage rating than my load requires? A: Yes, but you must ensure the output voltage is set correctly for your load to prevent damage.
Q: What does it mean when a power supply has an 'auto-ranging' input? A: It means the power supply can accept a range of input voltages without the need to manually switch settings.
Q: How can I reduce electrical noise from the power supply? A: Use proper filtering techniques, ensure good grounding, and keep power supply cables away from sensitive signal lines.
Note: This documentation is a general guide for a generic power supply. Specific models may have additional features or different pin configurations. Always consult the manufacturer's datasheet for precise information.