
How to Use battery1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with battery1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with battery1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in chemical form and converts it to electrical energy when needed. It provides a stable voltage and current to power electronic circuits. Batteries are essential components in a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices like remote controls and smartphones to larger systems such as electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Explore Projects Built with battery1
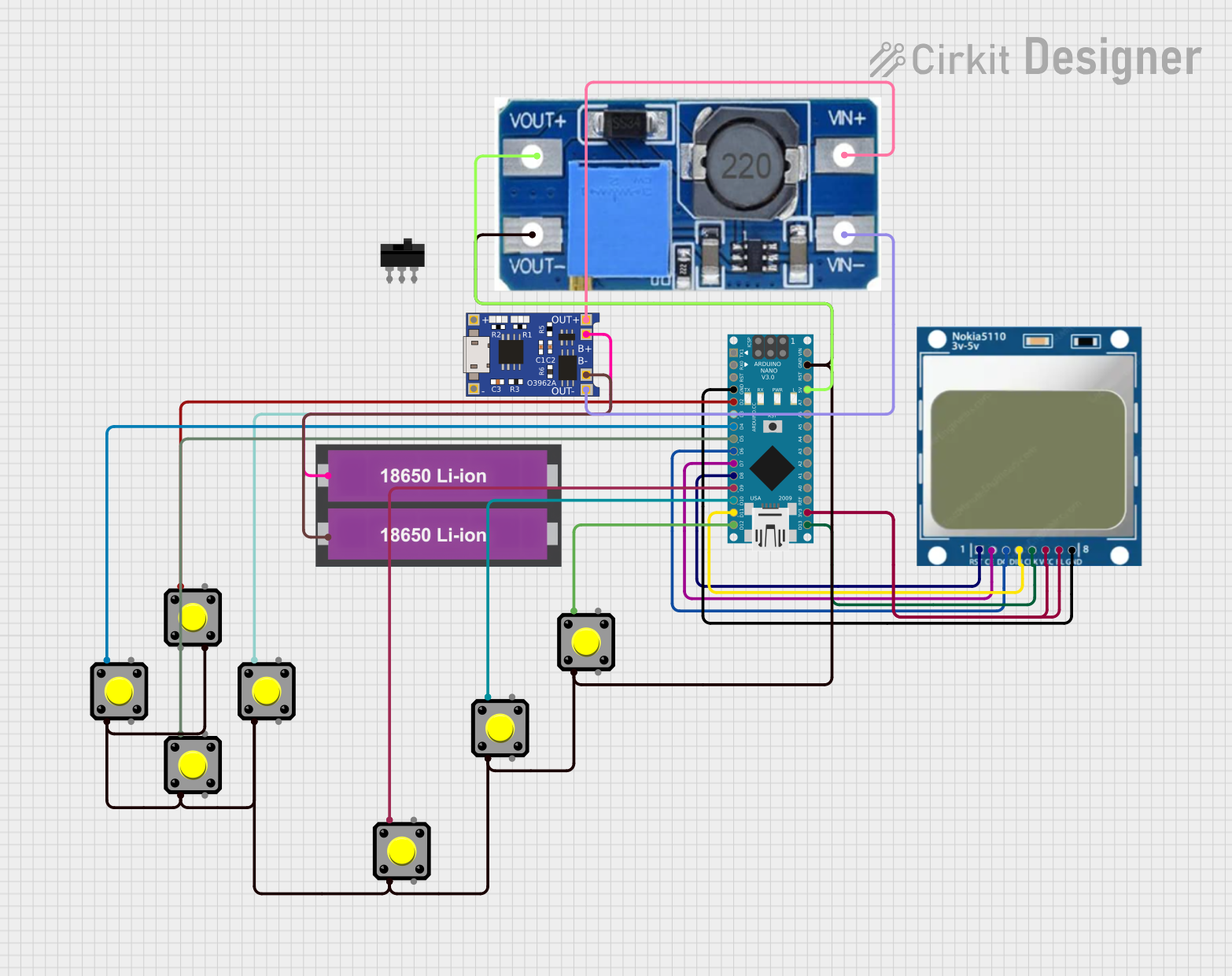
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer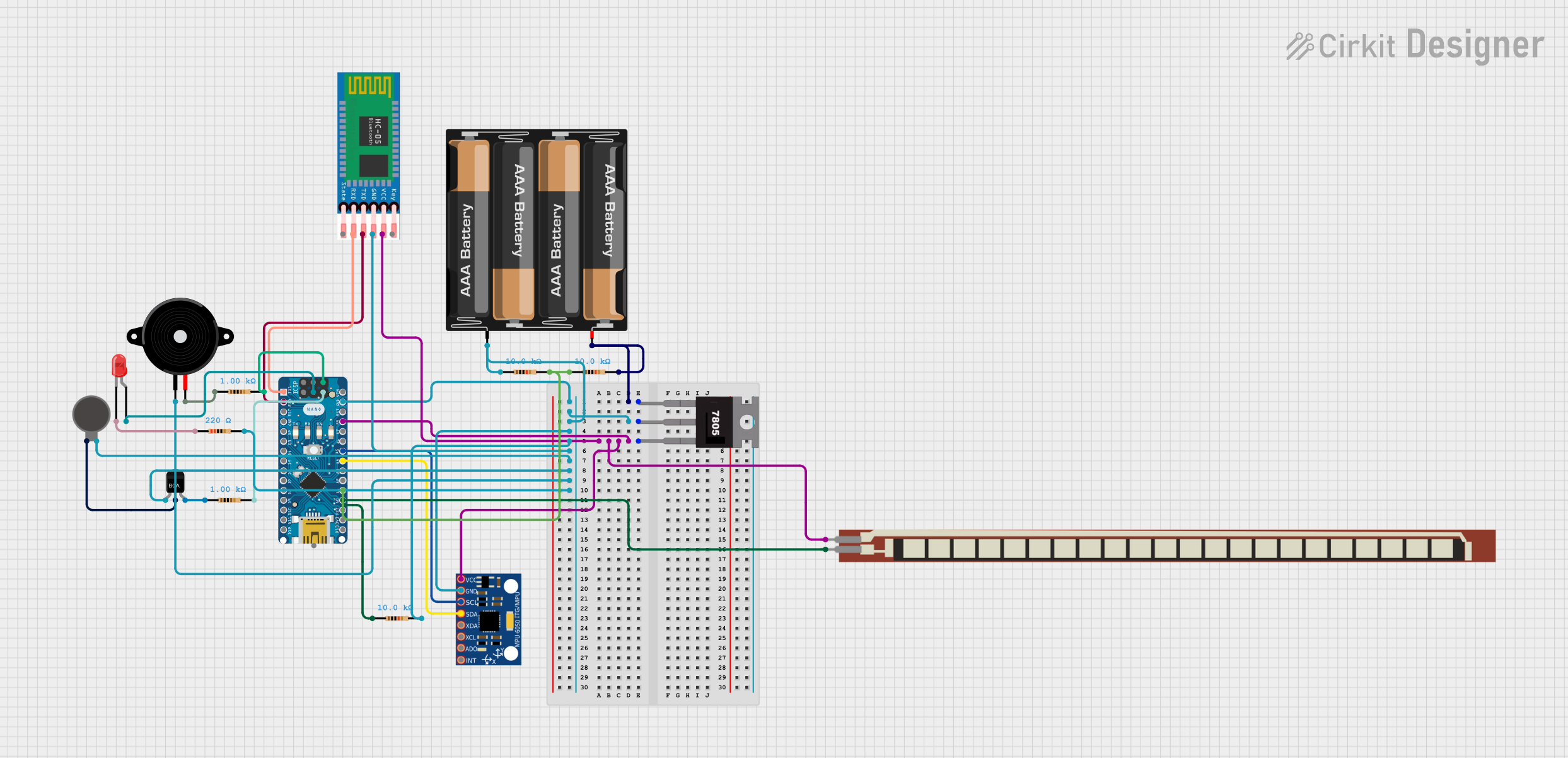
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer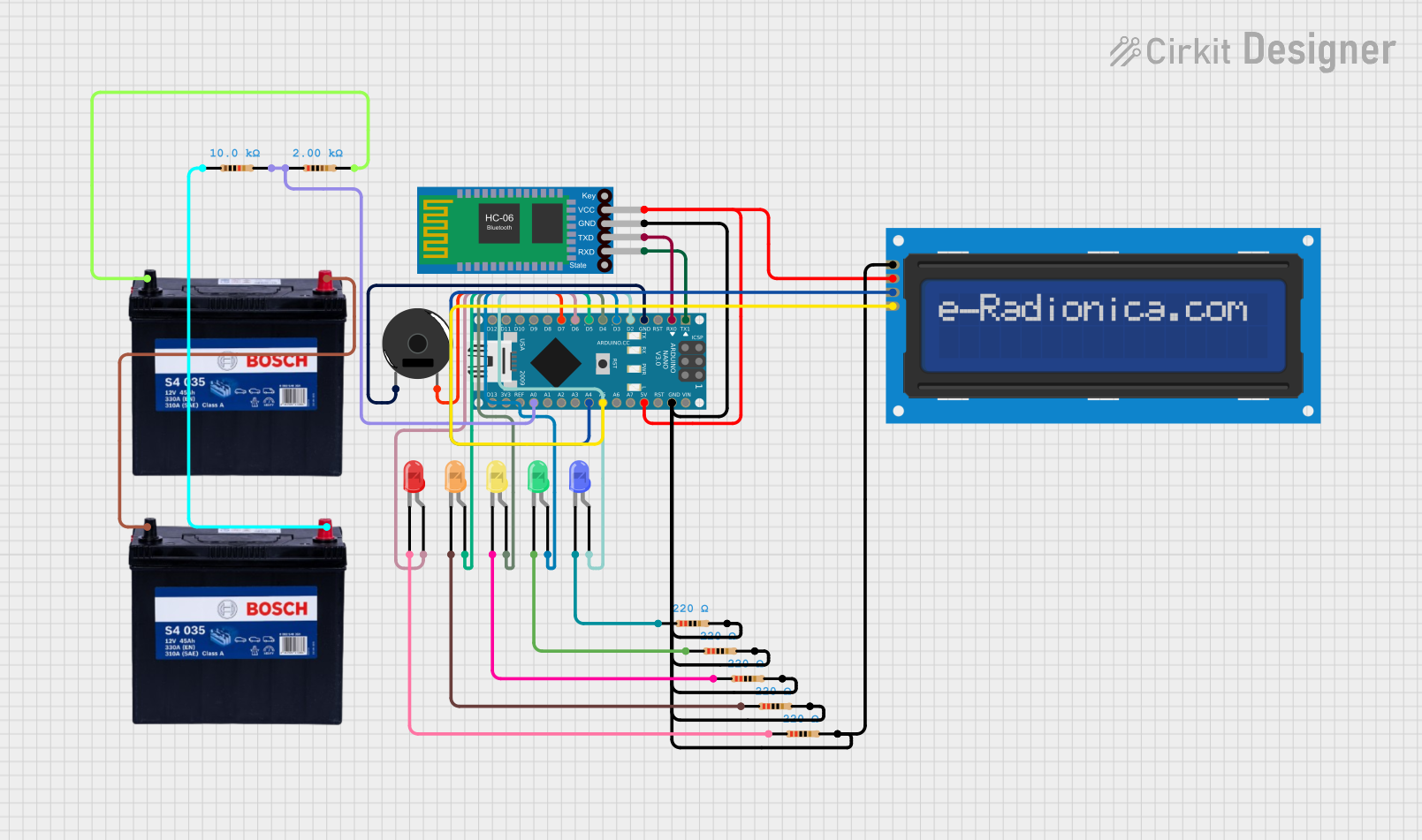
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer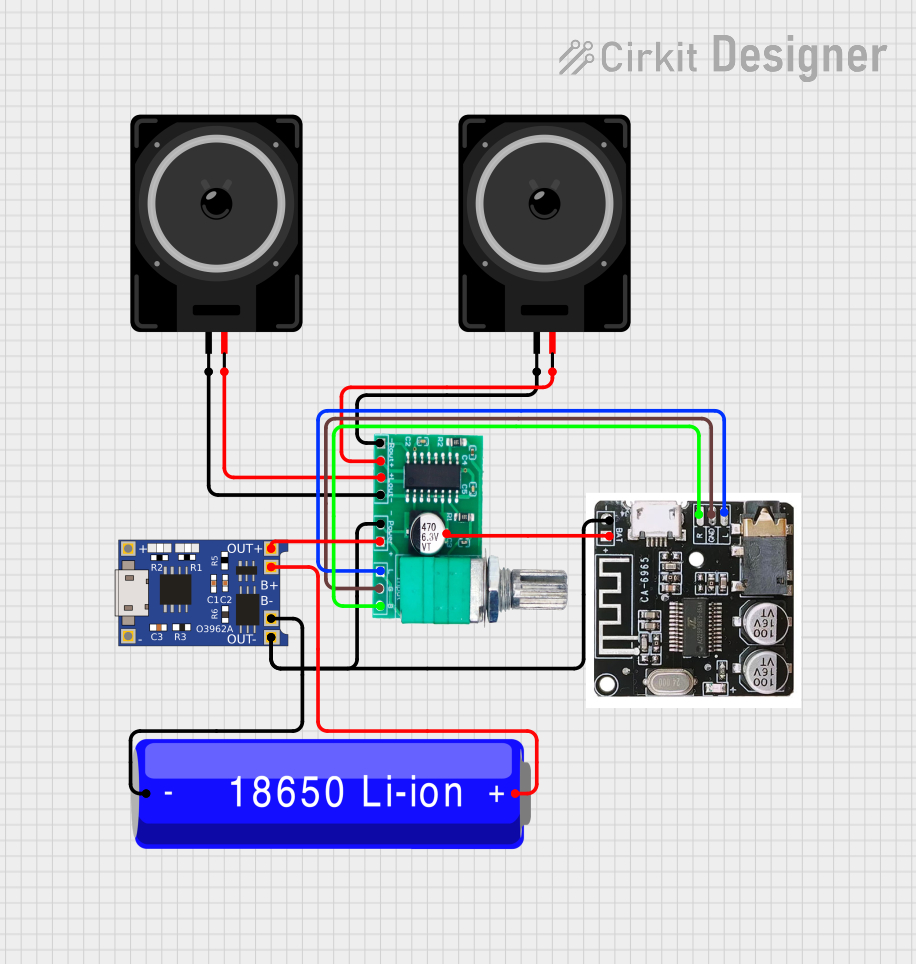
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with battery1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering portable electronic devices (e.g., smartphones, laptops, cameras)
- Backup power supplies (e.g., uninterruptible power supplies, emergency lighting)
- Energy storage in renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panels, wind turbines)
- Electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles
- Toys, remote controls, and other consumer electronics
Technical Specifications
The specifications of a battery vary depending on its type (e.g., alkaline, lithium-ion, lead-acid). Below is a general overview of key technical parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | The nominal voltage provided by the battery. Common values: 1.5V, 3.7V, 12V. |
| Capacity (mAh or Ah) | The amount of charge the battery can store, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh). |
| Chemistry | The chemical composition of the battery (e.g., alkaline, lithium-ion, NiMH). |
| Rechargeable | Indicates whether the battery can be recharged (Yes/No). |
| Operating Temperature | The temperature range in which the battery can safely operate. |
| Dimensions | Physical size of the battery (e.g., AA, AAA, 18650). |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For cylindrical batteries (e.g., AA, AAA, 18650), the pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) Terminal | The terminal where current flows out of the battery. |
| Negative (-) Terminal | The terminal where current flows into the battery. |
For batteries with connectors (e.g., LiPo batteries with JST connectors), the pin configuration may vary. Below is an example for a 2-pin LiPo battery:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| Red Wire (+) | Positive terminal of the battery. |
| Black Wire (-) | Negative terminal of the battery. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Battery in a Circuit
- Identify the Terminals: Ensure you correctly identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Connect to the Circuit: Use appropriate connectors or battery holders to securely connect the battery to your circuit.
- Match Voltage and Current Requirements: Ensure the battery's voltage and current ratings match the requirements of your circuit.
- Use a Voltage Regulator (if needed): If the battery voltage is higher than your circuit's requirements, use a voltage regulator to step it down.
- Recharge (if applicable): For rechargeable batteries, use a compatible charger to avoid overcharging or damaging the battery.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity: Always connect the battery with the correct polarity to avoid damaging the circuit.
- Overdischarge Protection: Avoid discharging the battery below its minimum voltage to prevent damage.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place to extend their lifespan.
- Safety: Do not short-circuit, puncture, or expose the battery to fire or water.
- Battery Holders: Use appropriate battery holders or connectors to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
Example: Connecting a Battery to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of powering an Arduino UNO using a 9V battery:
- Connect the positive terminal of the 9V battery to the Arduino's VIN pin.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery to the Arduino's GND pin.
Sample Code
// This example demonstrates a simple LED blink circuit powered by a battery.
// Ensure the battery voltage matches the Arduino's input voltage requirements.
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Battery Drains Quickly
- Cause: High current draw from the circuit or a faulty battery.
- Solution: Check the circuit's current requirements and use a battery with a higher capacity if needed.
Circuit Does Not Power On
- Cause: Incorrect polarity or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the battery's polarity and ensure all connections are secure.
Battery Overheats
- Cause: Short circuit or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Disconnect the battery immediately and inspect the circuit for faults.
Rechargeable Battery Does Not Charge
- Cause: Incompatible charger or damaged battery.
- Solution: Use a charger designed for the specific battery type and check for physical damage.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a higher voltage battery than my circuit requires?
A: No, using a higher voltage battery can damage your circuit. Use a voltage regulator or a battery with the correct voltage rating.
Q: How do I dispose of old batteries?
A: Dispose of batteries at designated recycling centers to prevent environmental harm.
Q: Can I mix different types of batteries in a device?
A: No, mixing different battery types or brands can cause uneven discharge and damage the device.
Q: How do I know if a battery is fully charged?
A: Use a compatible charger with an indicator light or measure the battery's voltage with a multimeter.