
How to Use lm2596: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with lm2596 in Cirkit Designer
Design with lm2596 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The LM2596 is a step-down (buck) voltage regulator designed to efficiently convert a higher input voltage into a stable, regulated output voltage. It is capable of delivering up to 3A of output current, making it ideal for powering a wide range of electronic devices. With its wide input voltage range (4.5V to 40V) and adjustable or fixed output voltage options, the LM2596 is a versatile component for power management in embedded systems, battery-powered devices, and industrial applications.
Explore Projects Built with lm2596
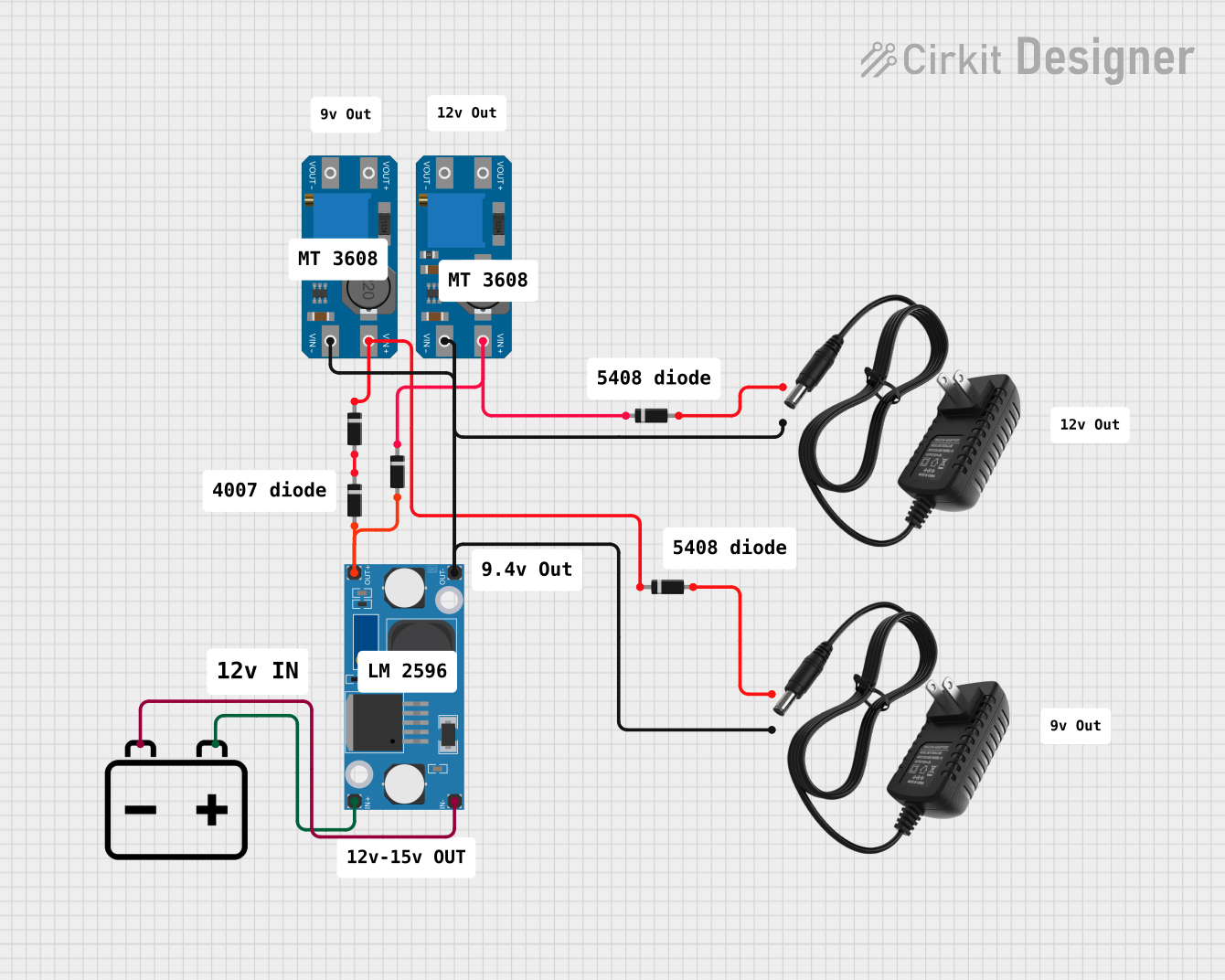
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer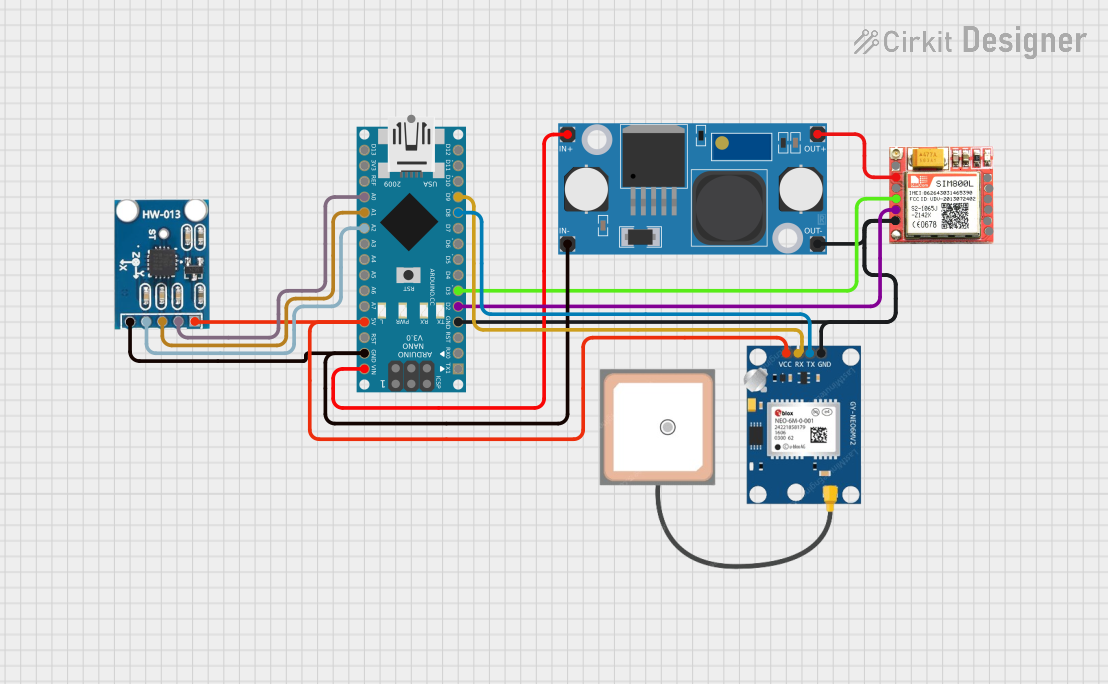
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer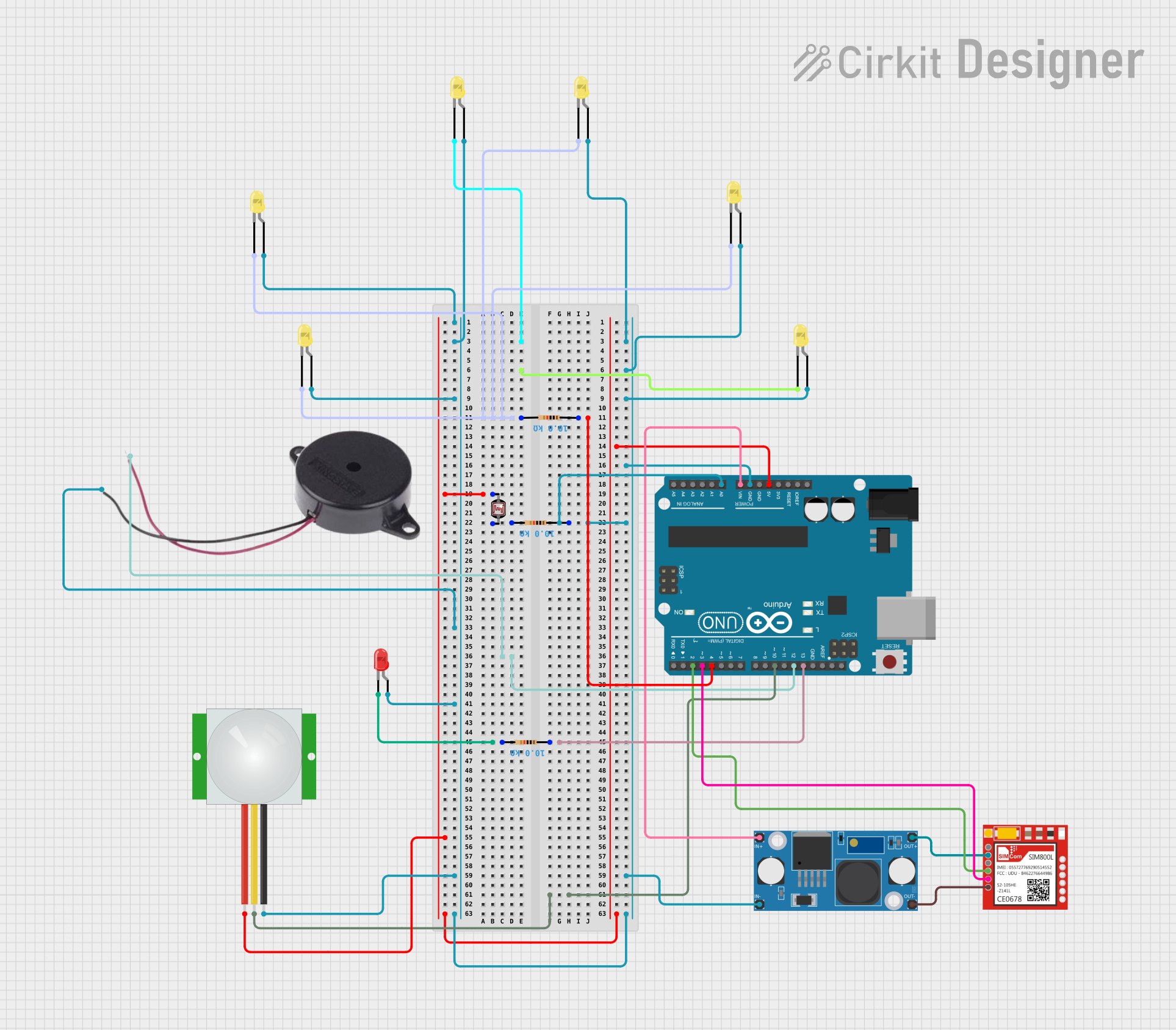
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with lm2596

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers and sensors in embedded systems
- Battery charging circuits
- Voltage regulation in industrial equipment
- DC-DC converters for automotive applications
- Power supplies for LED drivers and communication devices
Technical Specifications
The LM2596 is available in both adjustable and fixed output voltage versions. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.5V to 40V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.23V to 37V (adjustable) |
| Fixed Output Voltages | 3.3V, 5V, 12V |
| Maximum Output Current | 3A |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The LM2596 is typically available in a 5-pin TO-220 or TO-263 package. Below is the pinout description:
TO-220/TO-263 Pinout
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage pin. Connect to the unregulated DC input voltage. |
| 2 | Output | Regulated output voltage pin. Connect to the load. |
| 3 | Ground (GND) | Ground pin. Connect to the circuit ground. |
| 4 | Feedback | Feedback pin. Used to set the output voltage (for adjustable versions). |
| 5 | ON/OFF | Enable pin. Pull low to disable the regulator; pull high to enable it. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the LM2596 in a Circuit
- Input Voltage: Connect the input voltage (VIN) to the LM2596's VIN pin. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (4.5V to 40V).
- Output Voltage: For fixed versions, the output voltage is pre-set (e.g., 5V). For adjustable versions, connect a resistor divider to the Feedback pin to set the desired output voltage.
- Capacitors: Add input and output capacitors to stabilize the circuit. Typically, a 100µF capacitor is used on the input, and a 220µF capacitor is used on the output.
- Inductor: Select an appropriate inductor value based on the desired output voltage and current. A typical value is 33µH.
- Enable Pin: Connect the ON/OFF pin to a high logic level to enable the regulator. Pull it low to disable the output.
Example Circuit
Below is a basic circuit for using the LM2596 adjustable version:
VIN (12V) ----+----[100µF Capacitor]----+----> VIN (Pin 1)
| |
[Inductor (33µH)] [GND]
| |
VOUT (Pin 2) ----[220µF Capacitor]----> Load
|
[Voltage Divider] ----> Feedback (Pin 4)
|
GND (Pin 3)
Using LM2596 with Arduino UNO
The LM2596 can be used to power an Arduino UNO by stepping down a higher voltage (e.g., 12V) to 5V. Below is an example code snippet to monitor the output voltage using the Arduino's ADC:
// Define the analog pin connected to the LM2596 output
const int voltagePin = A0;
// Reference voltage for the ADC (5V for Arduino UNO)
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0;
// Voltage divider ratio (if used to scale down the LM2596 output voltage)
const float dividerRatio = 2.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int adcValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the ADC value
float outputVoltage = (adcValue * referenceVoltage / 1023.0) * dividerRatio;
// Print the output voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("LM2596 Output Voltage: ");
Serial.print(outputVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: The LM2596 can generate heat under high current loads. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Input Voltage: Ensure the input voltage is at least 3V higher than the desired output voltage for proper regulation.
- Ripple Reduction: Use low-ESR capacitors to minimize output voltage ripple.
- Inductor Selection: Choose an inductor with a current rating higher than the maximum load current to avoid saturation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Check if the ON/OFF pin is properly connected to a high logic level.
- Verify the input voltage is within the specified range.
- Inspect the circuit for loose connections or soldering issues.
Output Voltage is Unstable:
- Ensure the input and output capacitors are of the correct value and low ESR.
- Check for proper grounding and minimize noise in the circuit.
Excessive Heat:
- Verify that the load current does not exceed 3A.
- Use a heatsink or improve airflow around the LM2596.
Incorrect Output Voltage:
- For adjustable versions, check the resistor divider values connected to the Feedback pin.
- Ensure the input voltage is at least 3V higher than the desired output voltage.
FAQs
Q: Can the LM2596 be used for battery charging?
A: Yes, the LM2596 can be used in battery charging circuits, but additional circuitry (e.g., current limiting) may be required for safe operation.
Q: What is the maximum efficiency of the LM2596?
A: The LM2596 can achieve an efficiency of up to 90%, depending on the input voltage, output voltage, and load conditions.
Q: Can I use the LM2596 to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the LM2596 can step down a higher voltage (e.g., 12V) to 5V to power a Raspberry Pi. Ensure the current rating meets the Raspberry Pi's requirements.
Q: Is the LM2596 suitable for audio applications?
A: The LM2596 may introduce switching noise, which can affect audio circuits. Use additional filtering to reduce noise if necessary.