
How to Use 12V Zener Diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 12V Zener Diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12V Zener Diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Zener diode is a special type of semiconductor diode that permits current to flow not only from its anode to its cathode, but also in the reverse direction when the Zener voltage is reached. The 12V Zener diode is designed to maintain a stable voltage of 12 volts across its terminals, making it an essential component in voltage regulation and overvoltage protection circuits. Common applications include power supply stabilization, voltage reference in measurement devices, and protection of sensitive electronics from voltage spikes.
Explore Projects Built with 12V Zener Diode
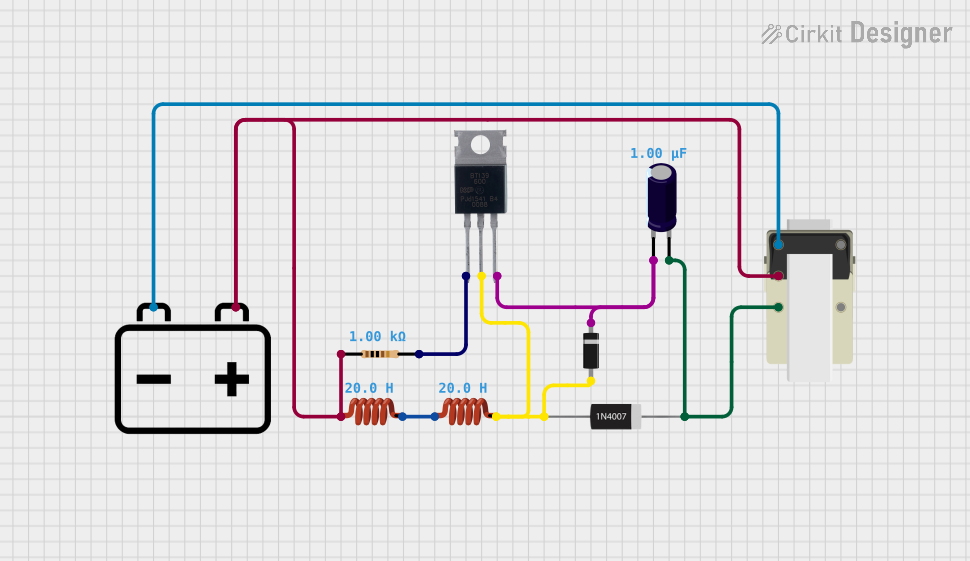
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer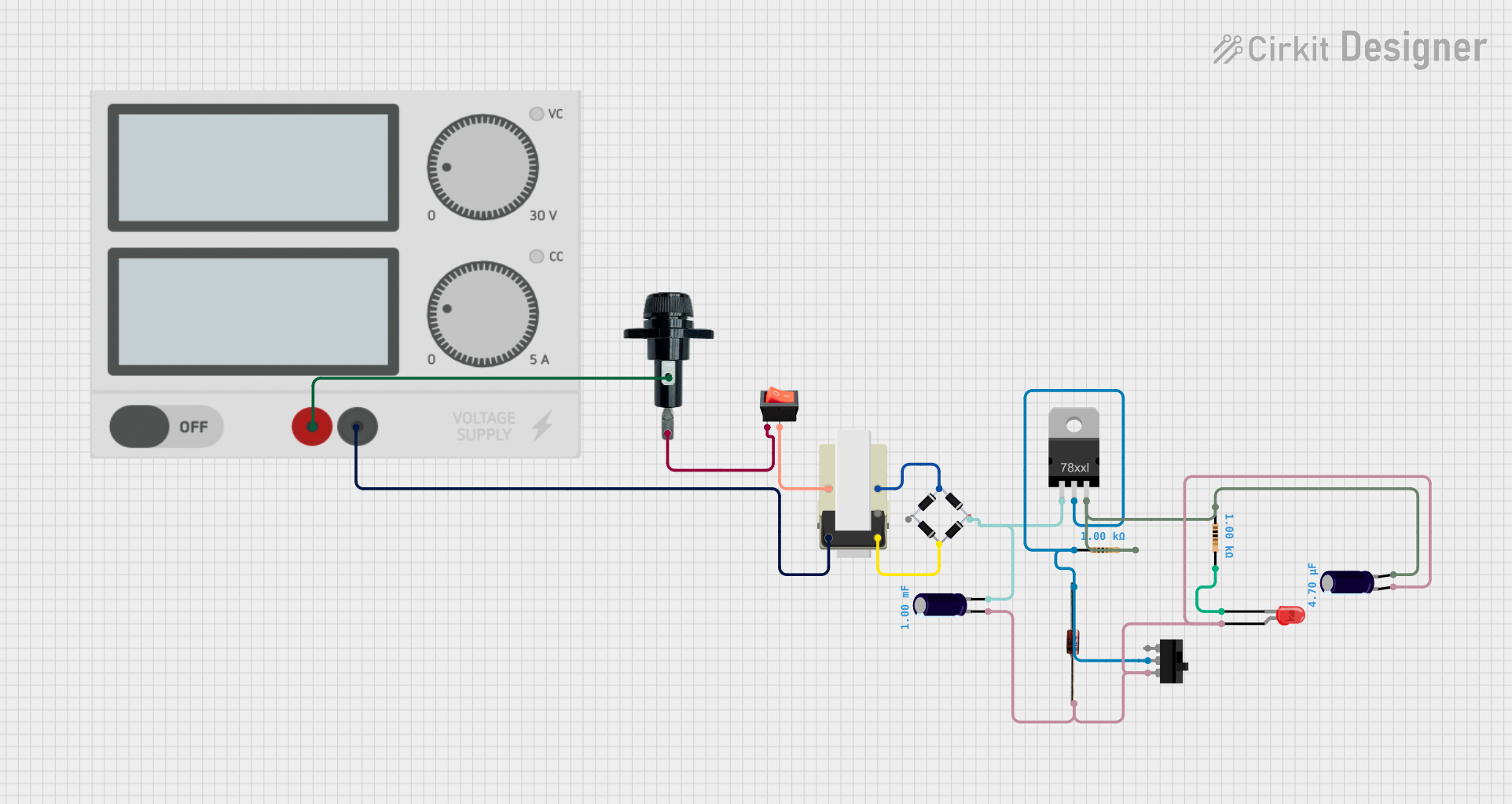
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer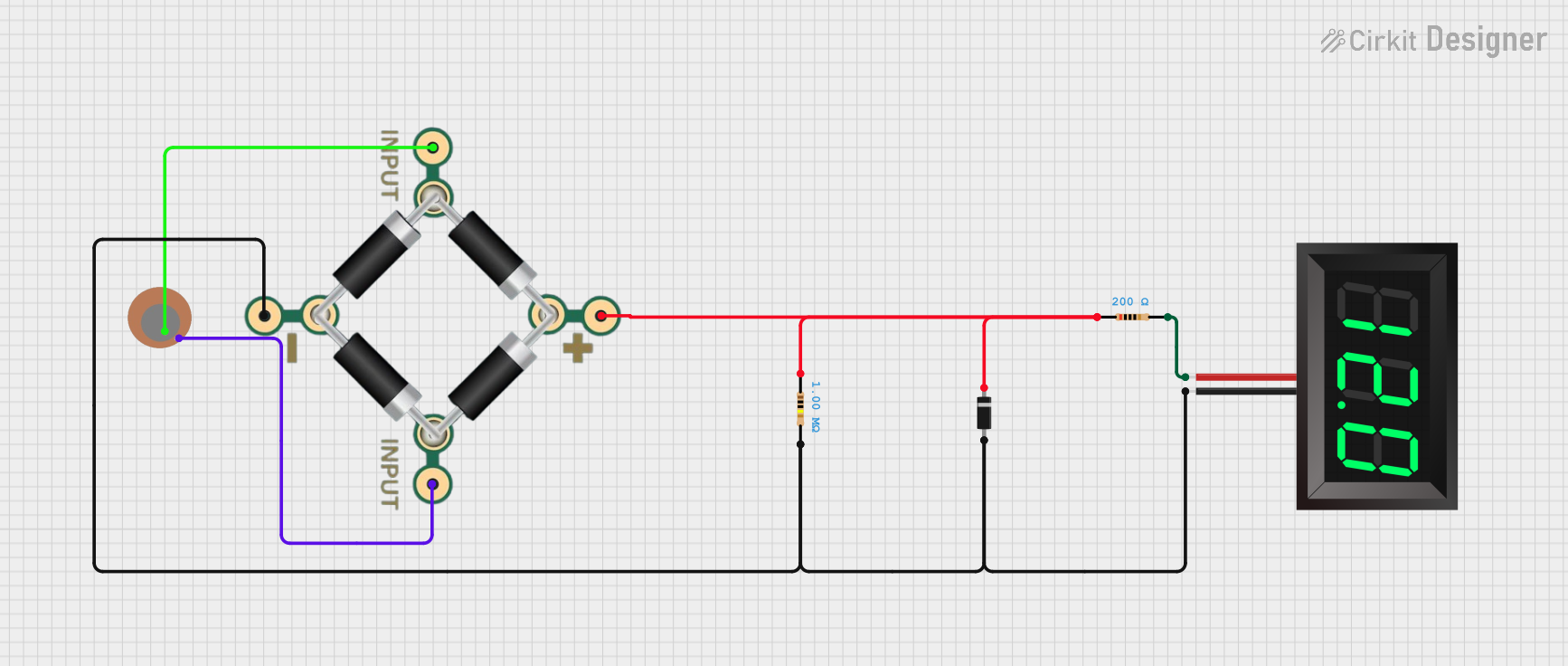
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12V Zener Diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Nominal Zener Voltage (Vz): 12V
- Test Current (Izt): Specified by manufacturer (e.g., 20mA)
- Maximum Zener Impedance (Zzt): Specified by manufacturer (e.g., 5 Ohms)
- Maximum Reverse Current (Ir): Specified at a certain voltage (e.g., 5µA at 1V)
- Power Dissipation (Pd): Typically 0.5W to 1W (higher power ratings available)
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Anode | The terminal to connect to the lower potential side in forward bias |
| 2 | Cathode | The terminal to connect to the higher potential side; marked by a band on the diode |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Voltage Regulation:
- Connect the cathode of the Zener diode to the positive side of the circuit where voltage regulation is needed.
- Connect the anode to the ground or the negative side of the circuit.
- Place a current limiting resistor in series with the Zener diode to prevent excessive current flow.
Overvoltage Protection:
- Place the Zener diode across the load or parallel to the sensitive component.
- Ensure the Zener diode's breakdown voltage is slightly above the normal operating voltage of the circuit.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a current limiting resistor to protect the Zener diode from high current that can cause overheating and damage.
- The power rating of the Zener diode should be chosen based on the maximum power it will dissipate in the circuit.
- For precise voltage regulation, select a Zener diode with a low dynamic impedance and test current close to the operating current.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Excessive Heat: This may be due to overcurrent. Check the series resistor and ensure it is of the correct value.
- Voltage Not Regulated: Ensure the Zener diode is not under the minimum current required for regulation (Izt). Also, check for any open or short circuits.
Solutions and Tips
- Use a heat sink if the Zener diode is expected to dissipate significant power.
- Verify the orientation of the Zener diode in the circuit; reversing it will prevent it from functioning properly.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 12V Zener diode in a 5V circuit? A: Yes, but it will not regulate the voltage unless the supply voltage exceeds 12V.
Q: What happens if the current exceeds the maximum rating of the Zener diode? A: The diode may become damaged due to overheating. Always use a current limiting resistor.
Q: How do I choose the right current limiting resistor? A: Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's law: R = (Vsupply - Vzener) / Iz, where Iz is the desired current through the Zener diode.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
// Example code to demonstrate the use of a 12V Zener diode for overvoltage protection
// with an Arduino UNO. This code assumes a hypothetical sensor input that may experience
// voltage spikes.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Sensor connected to A0 pin
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor value
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the serial monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next read
}
// Note: Connect the Zener diode across the sensor output and ground with the cathode
// (marked side) to the sensor output and the anode to the ground. This will protect
// the Arduino input from voltage spikes above 12V.
Remember to keep the Zener diode's orientation correct, and ensure that the sensor output does not exceed the Arduino's maximum voltage rating (5V) under normal operating conditions. The Zener diode will clamp the voltage during spikes, protecting the microcontroller's input pin.