
How to Use Raspberry pi zero w: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
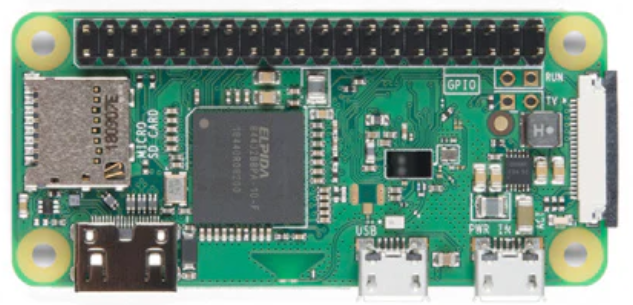
 Design with Raspberry pi zero w in Cirkit Designer
Design with Raspberry pi zero w in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Raspberry Pi Zero W is a compact, low-cost single-board computer with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. It is designed for a variety of DIY electronics projects and educational purposes. Despite its small size, the Raspberry Pi Zero W is a powerful tool that can be used in numerous applications, including home automation, robotics, and IoT (Internet of Things) projects.
Explore Projects Built with Raspberry pi zero w
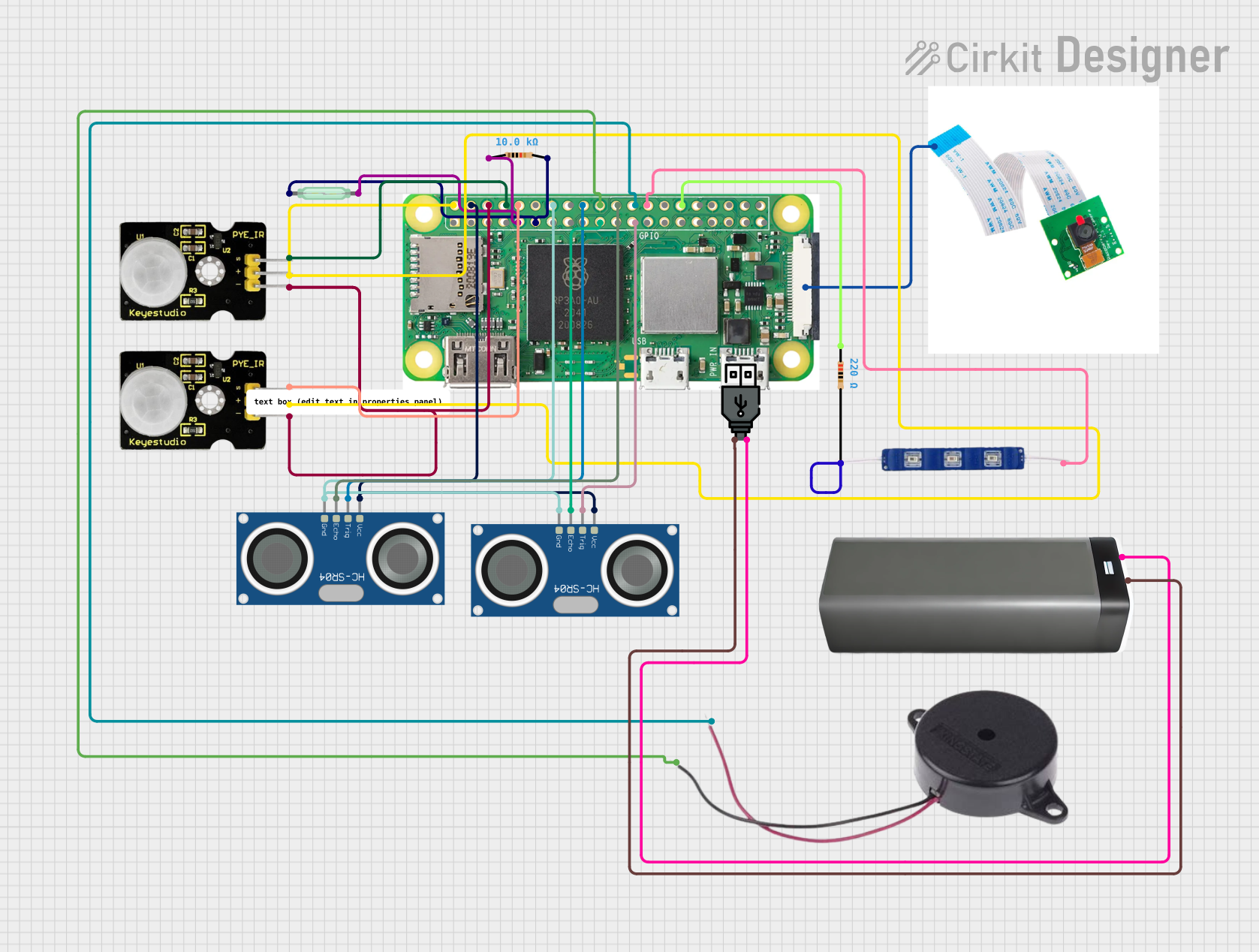
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer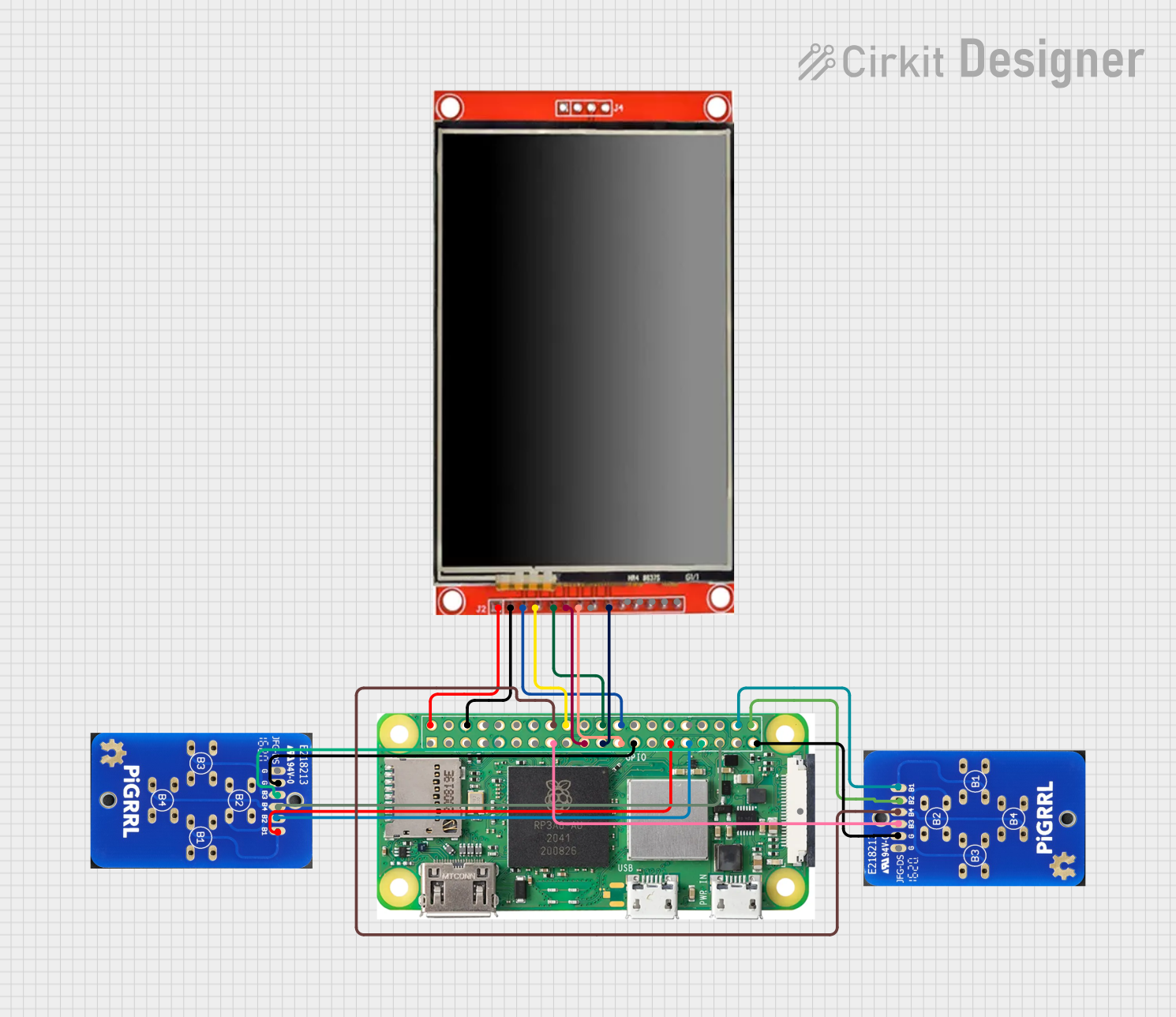
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer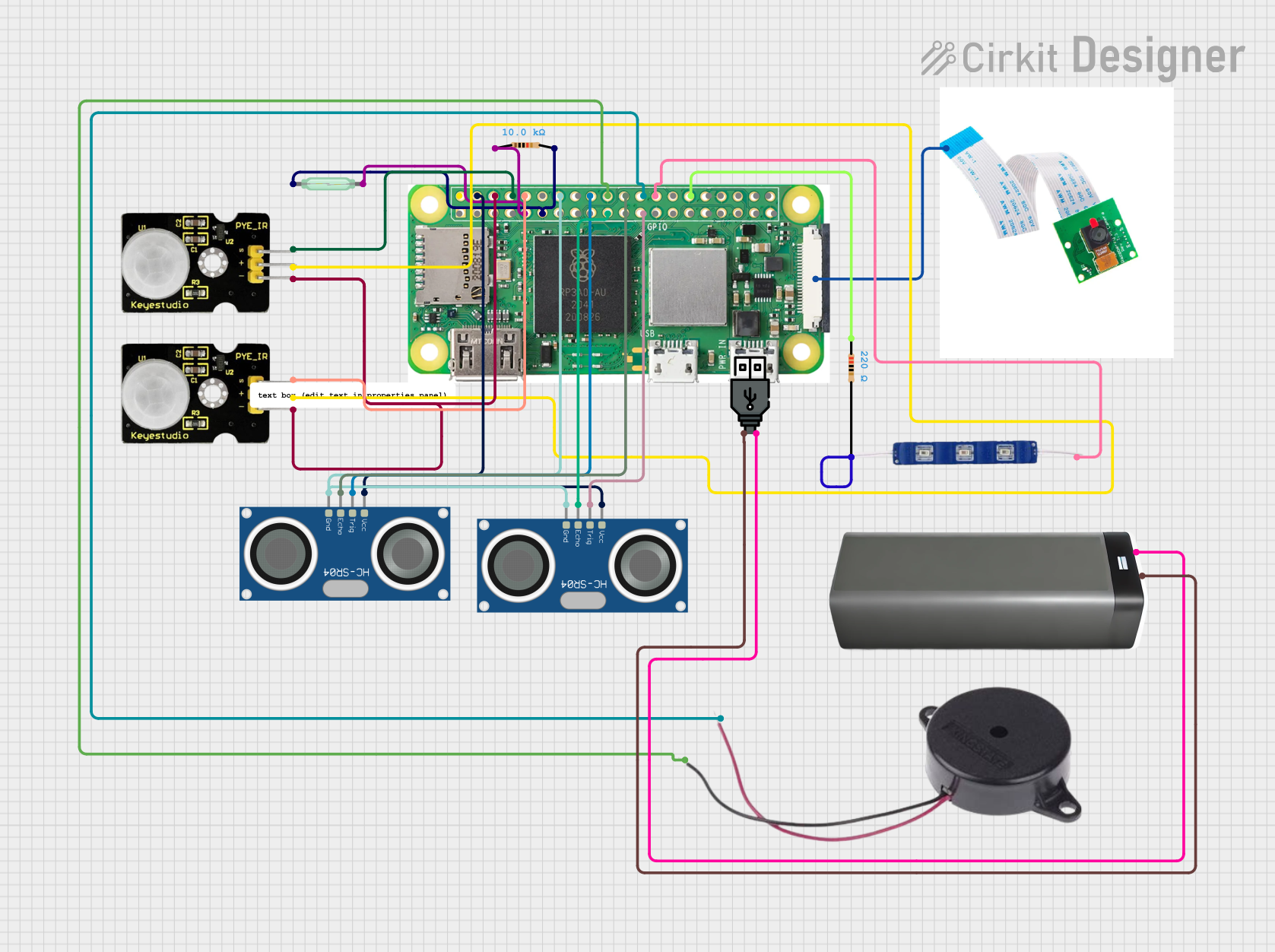
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer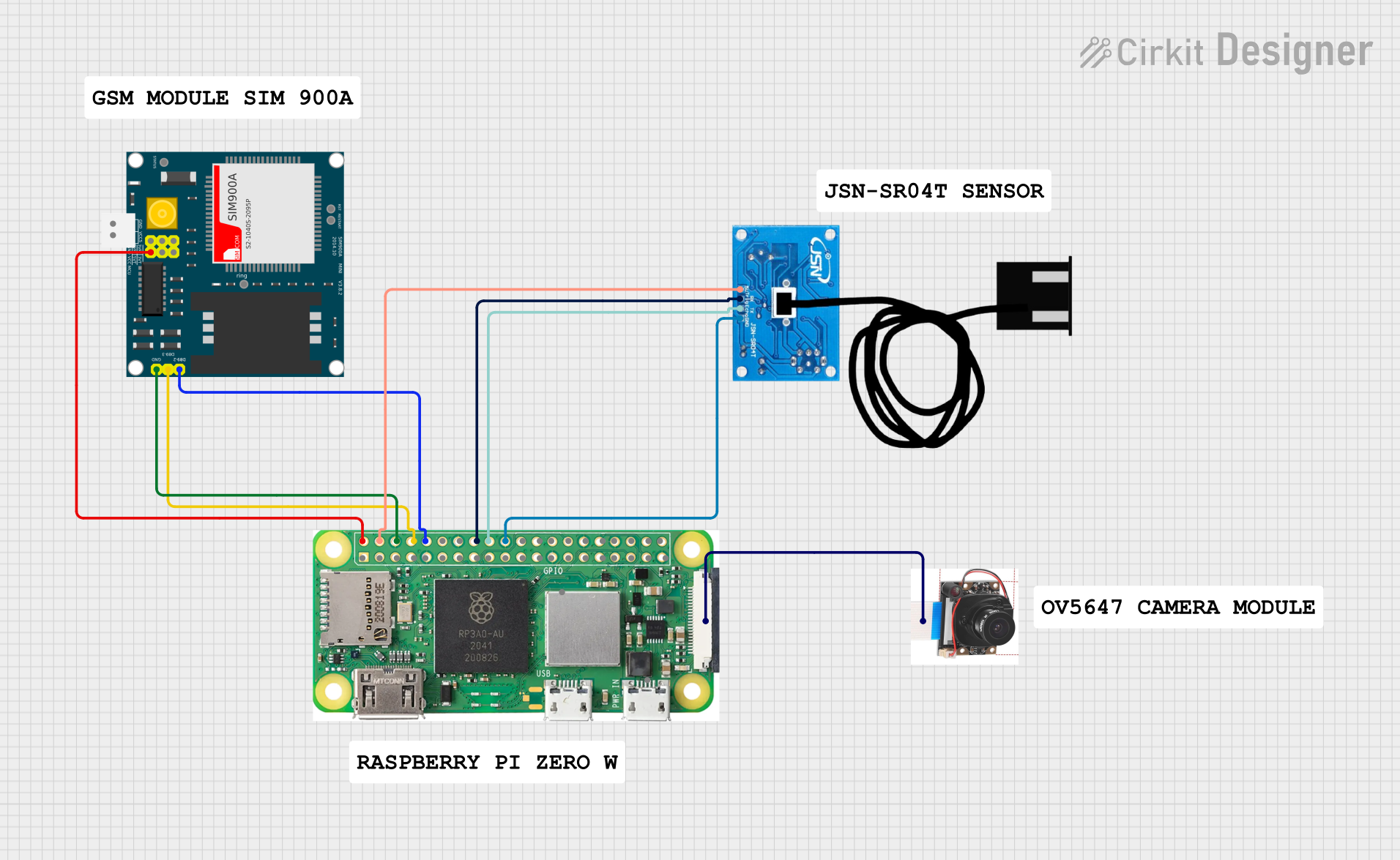
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Raspberry pi zero w

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2835, 1GHz ARM11 core |
| Memory | 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM |
| Wireless | 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.1, BLE |
| GPIO | 40-pin header, unpopulated |
| Ports | Mini HDMI, Micro USB OTG, Micro USB power |
| Storage | MicroSD card slot |
| Video Output | Mini HDMI, Composite video via GPIO |
| Audio Output | HDMI, PWM audio via GPIO |
| Power Supply | 5V, via Micro USB |
| Dimensions | 65mm x 30mm x 5mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Raspberry Pi Zero W has a 40-pin GPIO header, which is unpopulated by default. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V | Power | 3.3V power supply |
| 2 | 5V | Power | 5V power supply |
| 3 | GPIO2 | SDA1, I2C | Data line for I2C |
| 4 | 5V | Power | 5V power supply |
| 5 | GPIO3 | SCL1, I2C | Clock line for I2C |
| 6 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 7 | GPIO4 | GPCLK0 | General-purpose clock |
| 8 | GPIO14 | TXD0, UART | UART Transmit |
| 9 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 10 | GPIO15 | RXD0, UART | UART Receive |
| 11 | GPIO17 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 12 | GPIO18 | PCM_CLK, PWM0 | Pulse-width modulation, Clock |
| 13 | GPIO27 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 14 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 15 | GPIO22 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 16 | GPIO23 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 17 | 3.3V | Power | 3.3V power supply |
| 18 | GPIO24 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 19 | GPIO10 | SPI0_MOSI | SPI0 Master Out Slave In |
| 20 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 21 | GPIO9 | SPI0_MISO | SPI0 Master In Slave Out |
| 22 | GPIO25 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 23 | GPIO11 | SPI0_SCLK | SPI0 Clock |
| 24 | GPIO8 | SPI0_CE0_N | SPI0 Chip Enable 0 |
| 25 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 26 | GPIO7 | SPI0_CE1_N | SPI0 Chip Enable 1 |
| 27 | ID_SD | I2C ID EEPROM | I2C ID EEPROM |
| 28 | ID_SC | I2C ID EEPROM | I2C ID EEPROM |
| 29 | GPIO5 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 30 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 31 | GPIO6 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 32 | GPIO12 | PWM0 | Pulse-width modulation |
| 33 | GPIO13 | PWM1 | Pulse-width modulation |
| 34 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 35 | GPIO19 | PCM_FS | Frame Sync for PCM |
| 36 | GPIO16 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 37 | GPIO26 | General-purpose I/O | General-purpose I/O |
| 38 | GPIO20 | PCM_DIN | Data In for PCM |
| 39 | GND | Ground | Ground |
| 40 | GPIO21 | PCM_DOUT | Data Out for PCM |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Raspberry Pi Zero W in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a 5V power supply to the Micro USB power port.
- Storage: Insert a microSD card with a pre-installed operating system (e.g., Raspbian).
- Display: Connect a display via the Mini HDMI port.
- Peripherals: Connect peripherals such as a keyboard and mouse via a USB OTG adapter.
- Network: Utilize the built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth for network connectivity and peripheral connections.
- GPIO: Use the 40-pin GPIO header for interfacing with sensors, actuators, and other electronic components.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable 5V power supply with at least 1A current rating.
- Static Electricity: Handle the board with care to avoid static electricity damage.
- Cooling: Consider passive or active cooling if running intensive applications.
- Software Updates: Regularly update the operating system and software packages for security and performance improvements.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Display Output:
- Ensure the HDMI cable is properly connected.
- Verify the display is set to the correct input source.
- Check the microSD card for a valid operating system image.
Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems:
- Verify the Wi-Fi credentials are correct.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range.
- Reboot the Raspberry Pi Zero W and try reconnecting.
Peripheral Not Recognized:
- Check the USB OTG adapter connection.
- Ensure the peripheral is compatible with the Raspberry Pi Zero W.
- Try connecting the peripheral to a different USB port.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Raspberry Pi Zero W for a headless setup? A: Yes, you can set up the Raspberry Pi Zero W to operate without a monitor, keyboard, or mouse by enabling SSH and connecting via Wi-Fi.
Q: How do I enable the GPIO pins?
A: You can enable and control the GPIO pins using the gpio command-line utility or libraries such as RPi.GPIO in Python.
Q: Can I connect the Raspberry Pi Zero W to an Arduino UNO? A: Yes, you can connect the Raspberry Pi Zero W to an Arduino UNO via the GPIO pins or using serial communication.
Example Code for GPIO Control
Here is an example of how to control an LED connected to GPIO pin 17 using Python:
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
Set up GPIO mode
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
Set up GPIO pin 17 as an output
GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT)
try: while True: GPIO.output(17, GPIO.HIGH) # Turn on LED time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second GPIO.output(17, GPIO.LOW) # Turn off LED time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second except KeyboardInterrupt: pass finally: GPIO.cleanup() # Clean up GPIO settings
This code will blink an LED connected to GPIO pin 17 on and off every second. Make sure to connect a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED to prevent damage.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the Raspberry Pi Zero W in their projects, troubleshoot common issues, and explore various applications.