
How to Use TB6560 Stepper Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
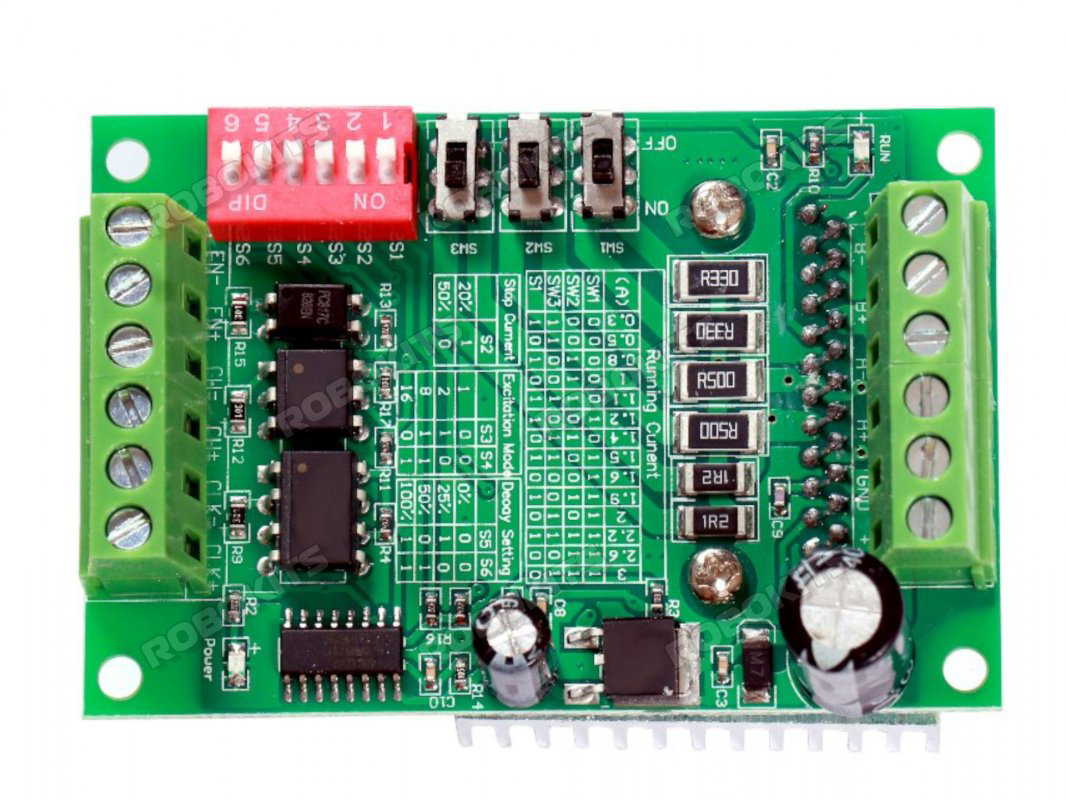
 Design with TB6560 Stepper Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB6560 Stepper Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6560 is a microstepping driver designed for controlling bipolar stepper motors with high precision. It supports multiple microstepping resolutions and adjustable current settings, making it ideal for applications requiring precise movement and positioning. With a maximum current capacity of 3A per phase, the TB6560 is commonly used in CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics, and other motion control systems.
Explore Projects Built with TB6560 Stepper Motor Driver
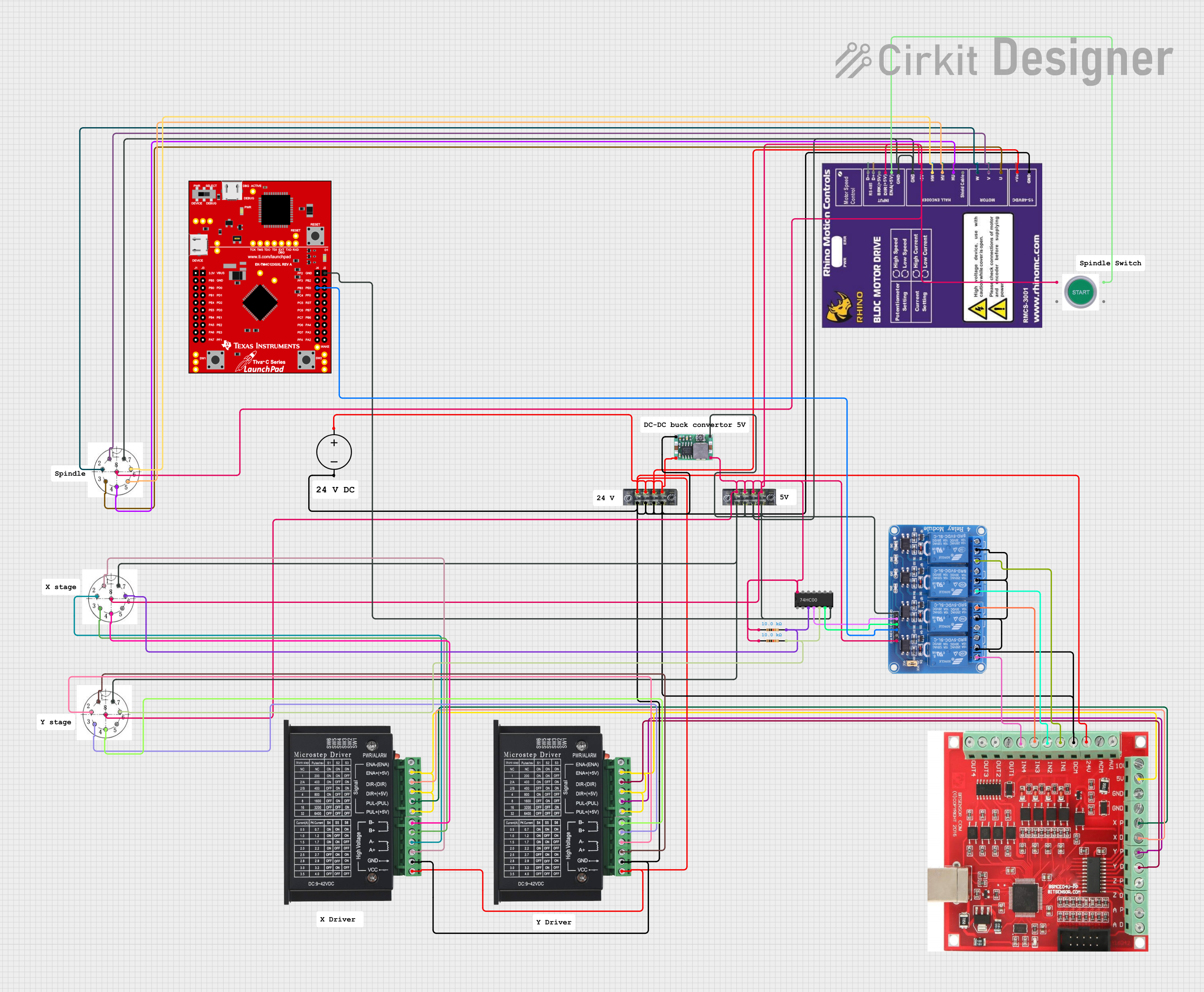
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer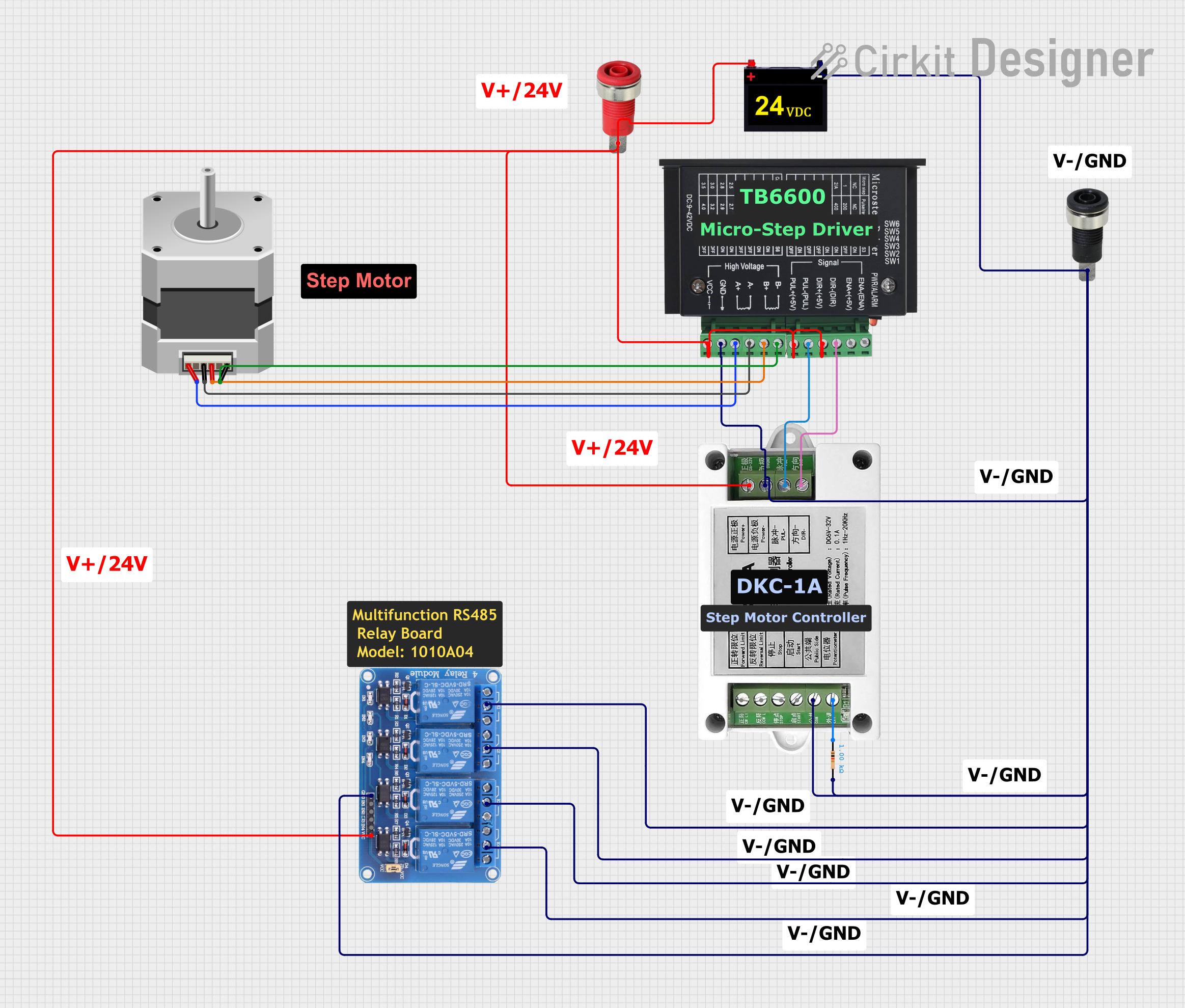
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer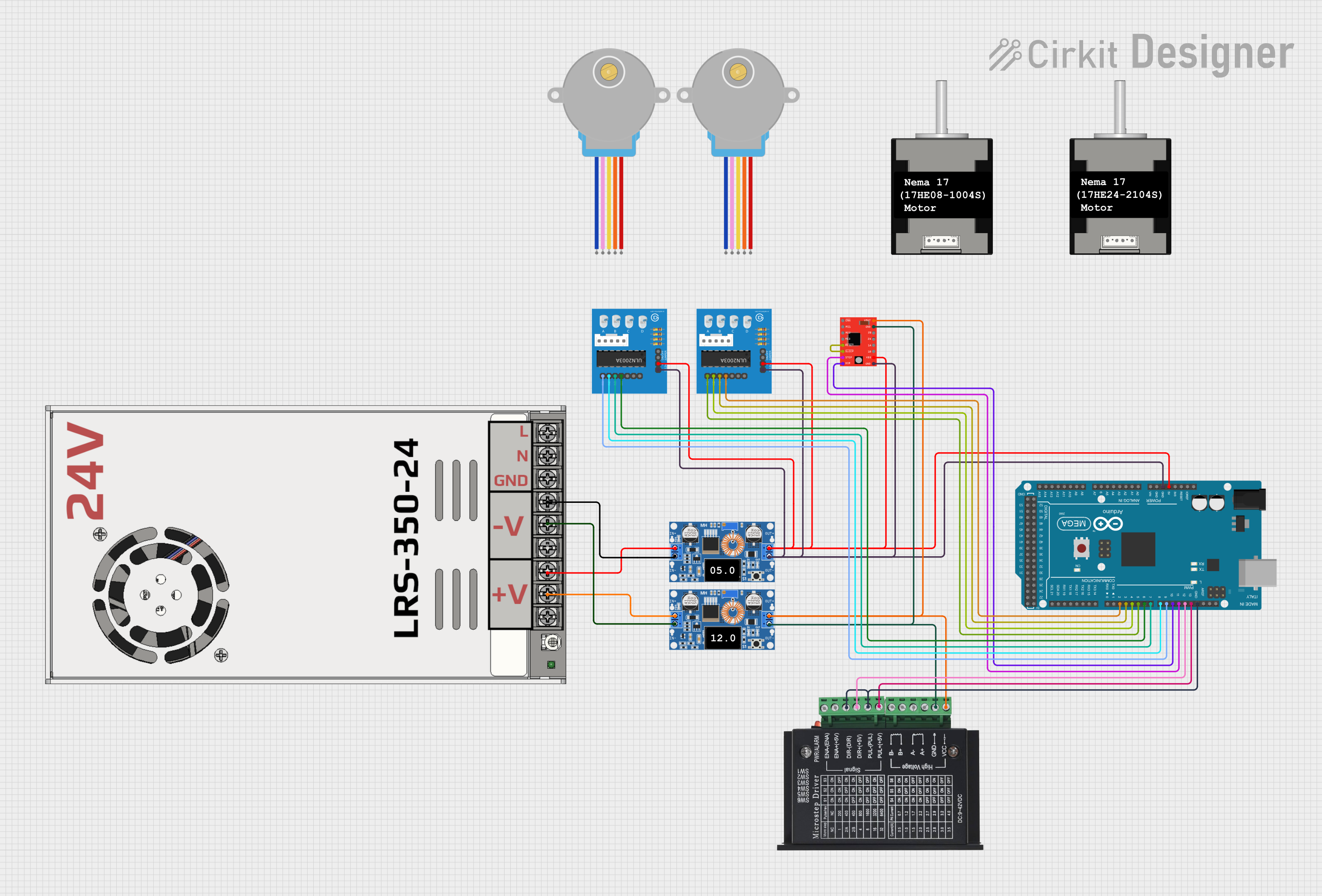
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer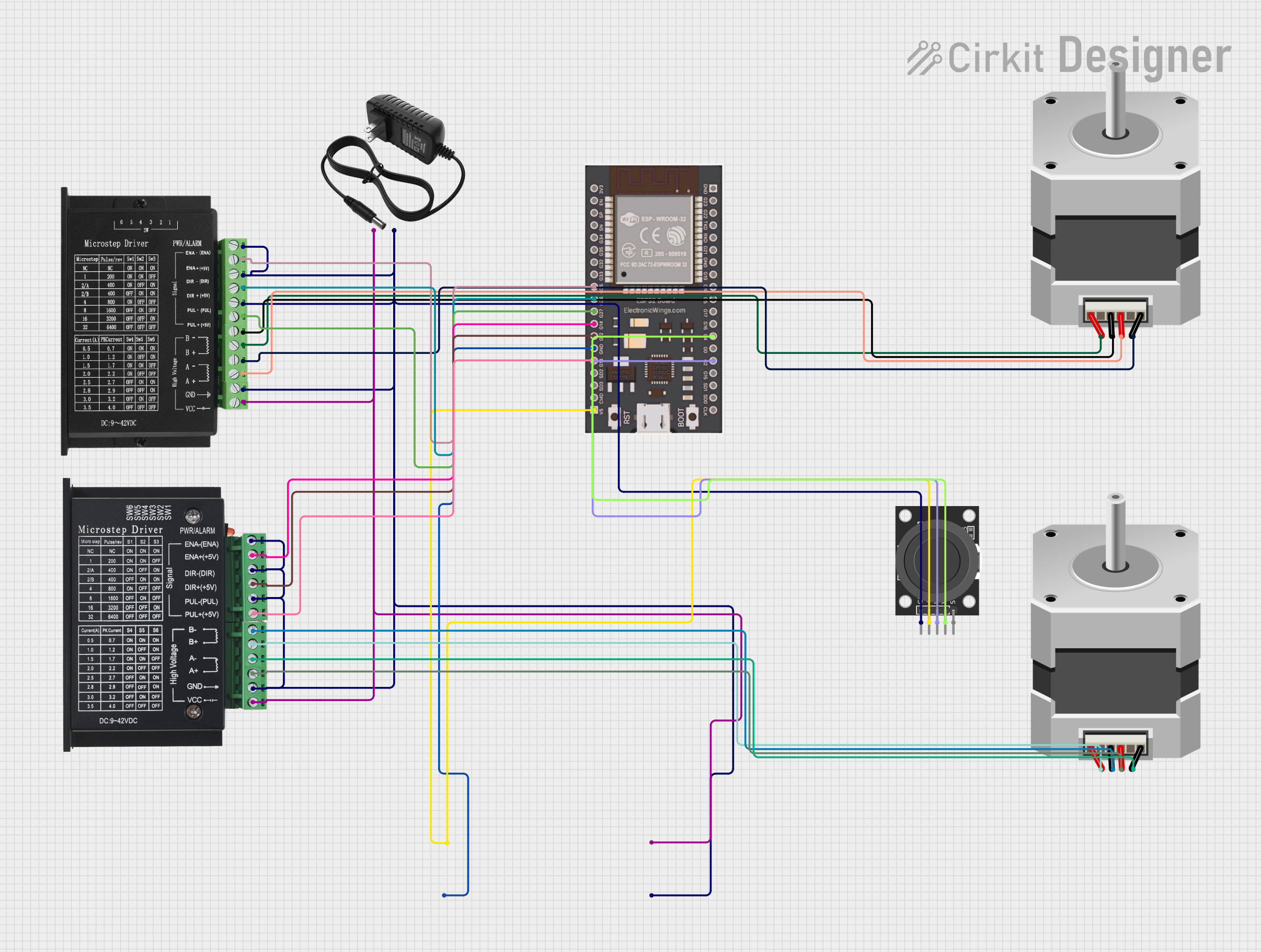
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB6560 Stepper Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- CNC machines for precise cutting and engraving
- 3D printers for accurate layer positioning
- Robotics for controlled movement
- Automated machinery and conveyor systems
Technical Specifications
The TB6560 stepper motor driver offers robust performance and flexibility. Below are its key technical details:
Key Specifications:
- Input Voltage: 10V to 35V DC
- Output Current: Up to 3A per phase (adjustable)
- Microstepping Modes: Full step, 1/2 step, 1/8 step, 1/16 step
- Control Signal Voltage: 3.3V to 5V logic compatible
- Step Frequency: Up to 15kHz
- Overcurrent Protection: Built-in
- Overheat Protection: Built-in
- Motor Type: Bipolar stepper motors
Pin Configuration and Descriptions:
The TB6560 driver typically has the following pinout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ENA- | Enable signal (active low). Disables the driver when pulled high. |
| DIR- | Direction control signal. Determines the rotation direction of the motor. |
| PUL- | Pulse signal. Each pulse moves the motor one step (or microstep). |
| GND | Ground connection for control signals. |
| VCC | Power supply for control signals (3.3V or 5V). |
| Motor A+ | Positive terminal of motor coil A. |
| Motor A- | Negative terminal of motor coil A. |
| Motor B+ | Positive terminal of motor coil B. |
| Motor B- | Negative terminal of motor coil B. |
| Power + | Positive terminal for motor power supply (10V to 35V DC). |
| Power - | Negative terminal for motor power supply (ground). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TB6560 in a Circuit:
- Power Supply: Connect a DC power supply (10V to 35V) to the
Power +andPower -terminals. Ensure the voltage matches the motor's requirements. - Motor Connection: Connect the stepper motor's coils to the
Motor A+,Motor A-,Motor B+, andMotor B-terminals. Verify the wiring matches the motor's datasheet. - Control Signals: Connect the
ENA-,DIR-, andPUL-pins to a microcontroller or control board (e.g., Arduino UNO). Use theGNDandVCCpins to provide a common ground and logic voltage. - Microstepping Settings: Adjust the DIP switches on the driver to set the desired microstepping mode and current limit. Refer to the TB6560 datasheet for switch configurations.
- Enable the Driver: Pull the
ENA-pin low to enable the driver. Send pulses to thePUL-pin to move the motor.
Important Considerations:
- Current Settings: Set the current limit to match the motor's rated current to avoid overheating or damaging the motor.
- Cooling: Ensure proper heat dissipation for the TB6560 driver, as it can get hot during operation. Use a heatsink or fan if necessary.
- Signal Voltage: Ensure the control signals are within the 3.3V to 5V range to avoid damaging the driver.
Example Code for Arduino UNO:
Below is an example of how to control a stepper motor using the TB6560 and an Arduino UNO:
// Define control pins for the TB6560 driver
const int dirPin = 2; // Direction control pin
const int stepPin = 3; // Step pulse pin
const int enPin = 4; // Enable pin
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enPin, OUTPUT);
// Enable the driver
digitalWrite(enPin, LOW); // Pull ENA- low to enable the driver
}
void loop() {
// Set motor direction
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH); // Set direction to clockwise
// Generate step pulses
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { // Move 200 steps (1 revolution for a 1.8° motor)
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH); // Send a high pulse
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW); // Send a low pulse
delayMicroseconds(500); // Wait 500 microseconds
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before changing direction
// Change direction
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW); // Set direction to counterclockwise
// Generate step pulses
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { // Move 200 steps in the opposite direction
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions:
Motor Not Moving:
- Check the power supply voltage and current rating.
- Verify the motor wiring matches the datasheet.
- Ensure the
ENA-pin is pulled low to enable the driver.
Motor Vibrates but Doesn't Rotate:
- Check the microstepping settings on the DIP switches.
- Verify the pulse signal frequency is within the driver's range.
Driver Overheating:
- Ensure the current limit is set correctly for the motor.
- Add a heatsink or fan to improve cooling.
Inconsistent Motor Movement:
- Check for loose connections in the wiring.
- Ensure the control signals are clean and free of noise.
FAQs:
Can the TB6560 drive unipolar stepper motors? No, the TB6560 is designed for bipolar stepper motors only.
What is the maximum step frequency supported? The TB6560 supports step frequencies up to 15kHz.
Can I use a 12V power supply with the TB6560? Yes, the TB6560 works with power supplies ranging from 10V to 35V. Ensure the motor is compatible with the chosen voltage.
How do I set the microstepping mode? Use the DIP switches on the driver to configure the microstepping mode. Refer to the TB6560 datasheet for detailed settings.