
How to Use traic dual channel: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with traic dual channel in Cirkit Designer
Design with traic dual channel in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) dual channel is a semiconductor device designed for controlling AC power. It is capable of switching and regulating power in both directions, making it highly versatile for alternating current applications. The dual channel feature allows independent control of two separate loads, which is particularly useful in scenarios requiring multi-load management.
Explore Projects Built with traic dual channel
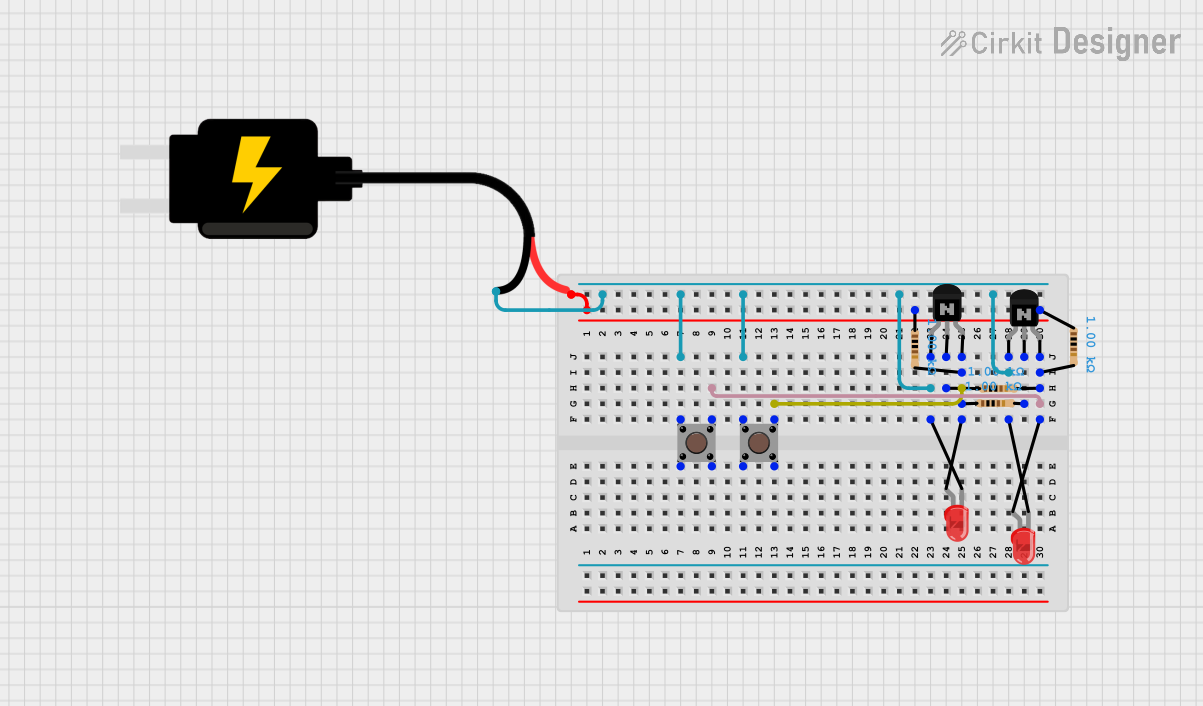
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer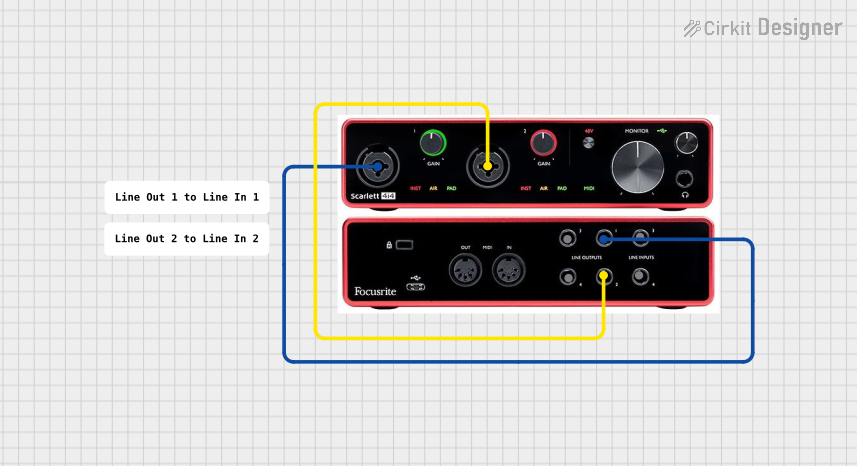
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer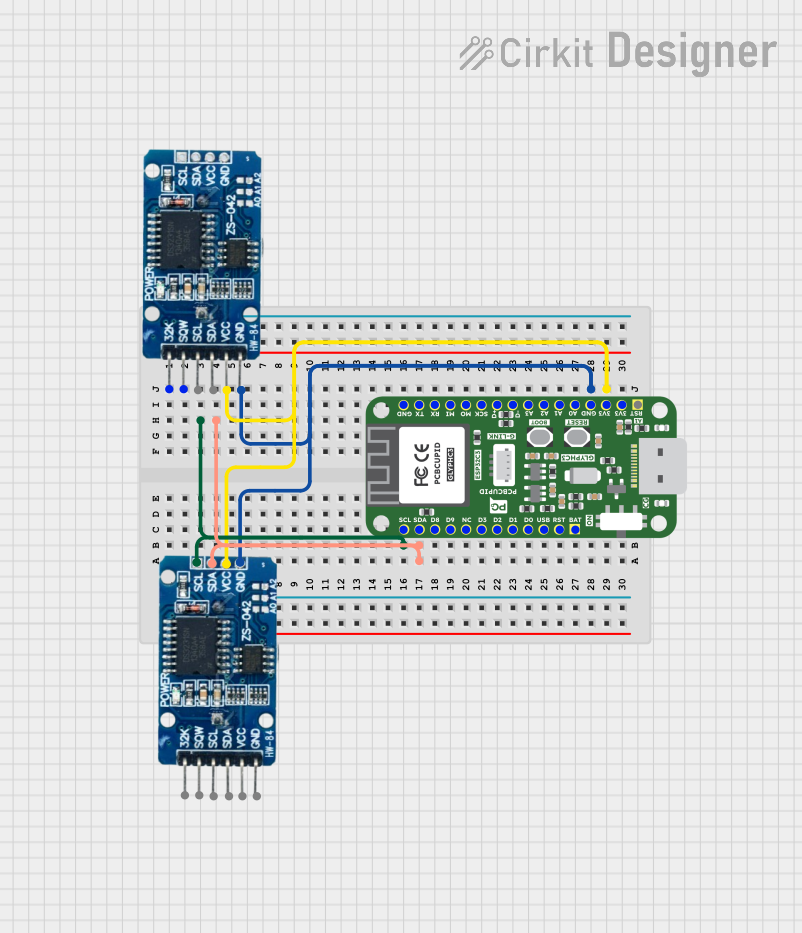
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer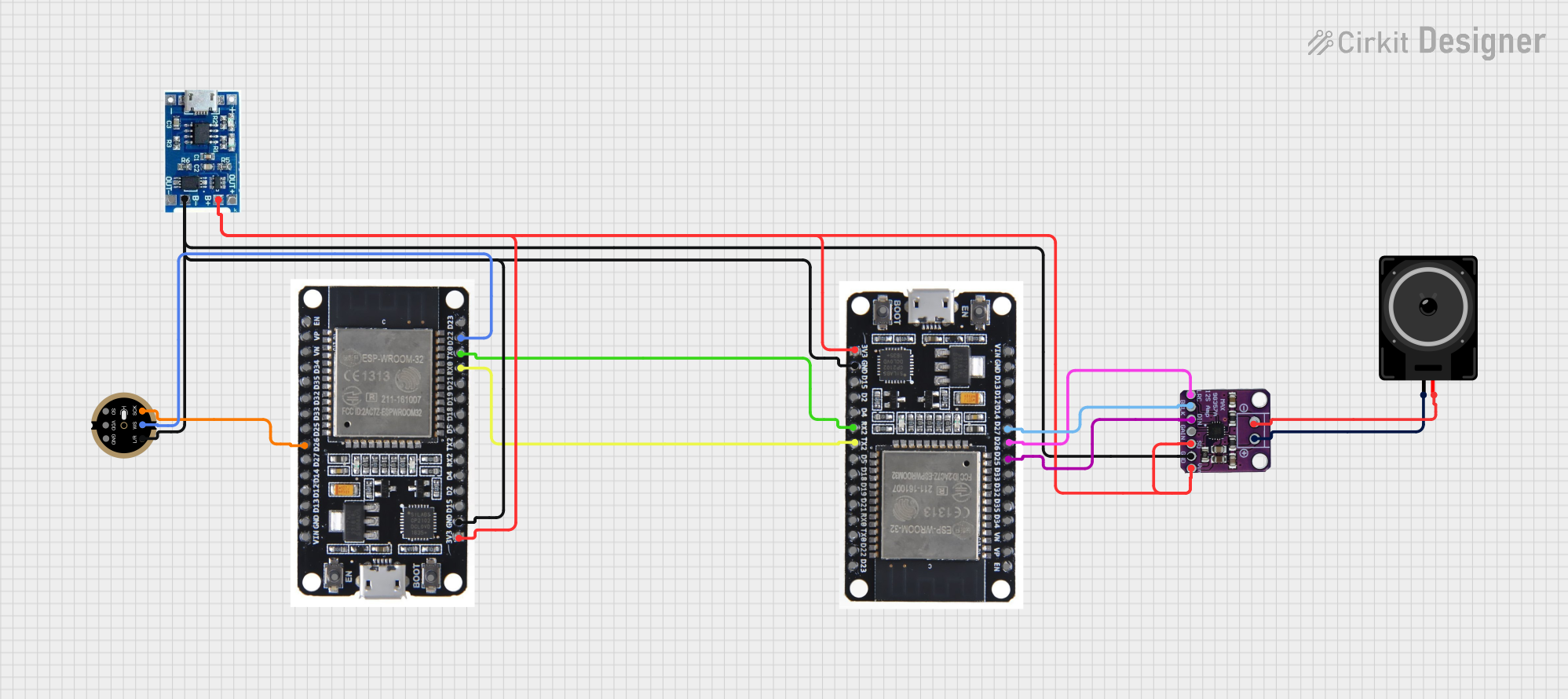
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with traic dual channel

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Light dimmers for residential and commercial lighting systems
- Motor speed control in fans, pumps, and industrial machinery
- Heating systems such as electric ovens and water heaters
- Phase control in AC circuits
- Home automation systems for controlling multiple devices
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical TRIAC dual channel:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Voltage (VDRM) | 600V - 800V (varies by model) |
| Maximum Current (IT) | 4A - 16A (per channel) |
| Gate Trigger Voltage (VGT) | 1.5V - 2.5V |
| Gate Trigger Current (IGT) | 10mA - 50mA |
| Holding Current (IH) | 5mA - 25mA |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C |
| Isolation Voltage (between channels) | 1500V |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TRIAC dual channel typically comes in a multi-pin package. Below is an example pinout for a common configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MT1 (Channel 1) | Main Terminal 1 for Channel 1 |
| 2 | MT2 (Channel 1) | Main Terminal 2 for Channel 1 |
| 3 | G1 | Gate for Channel 1 |
| 4 | MT1 (Channel 2) | Main Terminal 1 for Channel 2 |
| 5 | MT2 (Channel 2) | Main Terminal 2 for Channel 2 |
| 6 | G2 | Gate for Channel 2 |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the TRIAC is connected to an AC power source within its voltage and current ratings.
- Gate Control: Use a low-power control signal (e.g., from a microcontroller or optoisolator) to trigger the gate (G1 or G2) of the desired channel.
- Load Connection: Connect the load between MT1 and MT2 of the respective channel. Ensure the load does not exceed the TRIAC's current rating.
- Snubber Circuit: For inductive loads (e.g., motors), include a snubber circuit (a resistor-capacitor network) across MT1 and MT2 to prevent voltage spikes.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: Use an appropriate heatsink to manage heat generated during operation, especially for high-current loads.
- Isolation: If controlling the TRIAC with a microcontroller, use an optoisolator to protect the low-voltage control circuit from high-voltage AC.
- Gate Resistor: Include a resistor in series with the gate to limit the gate current and prevent damage.
- Zero-Crossing Detection: For smoother operation in light dimming or motor control, consider using a zero-crossing detection circuit.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control one channel of a TRIAC dual channel using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the TRIAC gate
const int triacGatePin = 9;
void setup() {
pinMode(triacGatePin, OUTPUT); // Set the TRIAC gate pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(triacGatePin, HIGH); // Trigger the TRIAC gate
delay(10); // Keep the gate on for 10ms (adjust as needed)
digitalWrite(triacGatePin, LOW); // Turn off the gate
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before triggering again
}
Note: The above code assumes a simple on/off control. For phase control (e.g., dimming), you would need to synchronize the gate signal with the AC mains zero-crossing point.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
TRIAC Does Not Turn On
- Cause: Insufficient gate current.
- Solution: Check the gate resistor value and ensure the control signal provides enough current to trigger the gate.
TRIAC Stays On
- Cause: Load current is above the holding current threshold.
- Solution: Ensure the load is within the TRIAC's rated current range.
Excessive Heat
- Cause: High current load or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Use a heatsink and ensure proper ventilation.
Noise or Flickering in Load
- Cause: Inductive load without a snubber circuit.
- Solution: Add a snubber circuit across MT1 and MT2.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a TRIAC dual channel for DC loads?
A: No, TRIACs are designed for AC loads. They rely on the alternating nature of AC to turn off (commutate).
Q: How do I control both channels independently?
A: Use separate control signals for G1 and G2. Ensure the control circuit is isolated from the AC side.
Q: What happens if I exceed the maximum voltage or current ratings?
A: Exceeding the ratings can permanently damage the TRIAC or cause it to fail catastrophically. Always operate within the specified limits.
Q: Do I need a heatsink for low-power applications?
A: For low-power loads, a heatsink may not be necessary. However, monitor the TRIAC's temperature during operation to ensure it stays within safe limits.