
How to Use ESP32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
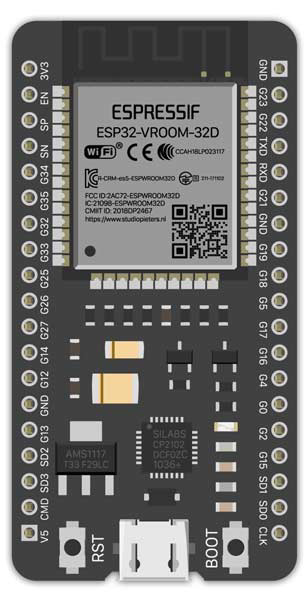
 Design with ESP32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32 is a powerful, low-cost microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) applications and embedded systems. Developed by Espressif Systems, the ESP32 is widely used in smart home devices, wearable electronics, industrial automation, and more. Its dual-core processor, extensive GPIO options, and support for various communication protocols make it a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of projects.
Common applications of the ESP32 include:
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wireless sensor networks
- Wearable technology
- Robotics and industrial control systems
- Audio streaming and Bluetooth-enabled devices
Explore Projects Built with ESP32
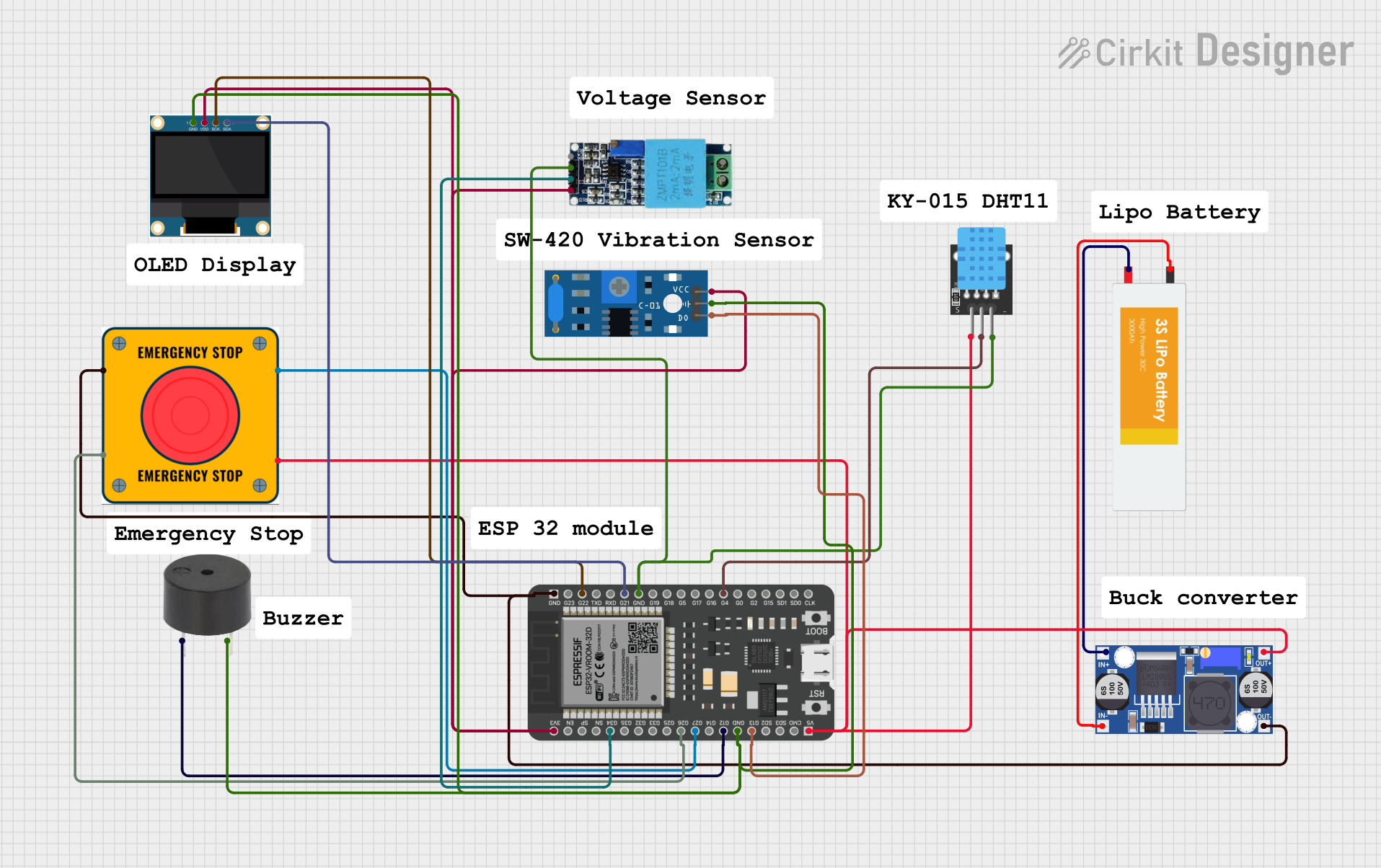
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer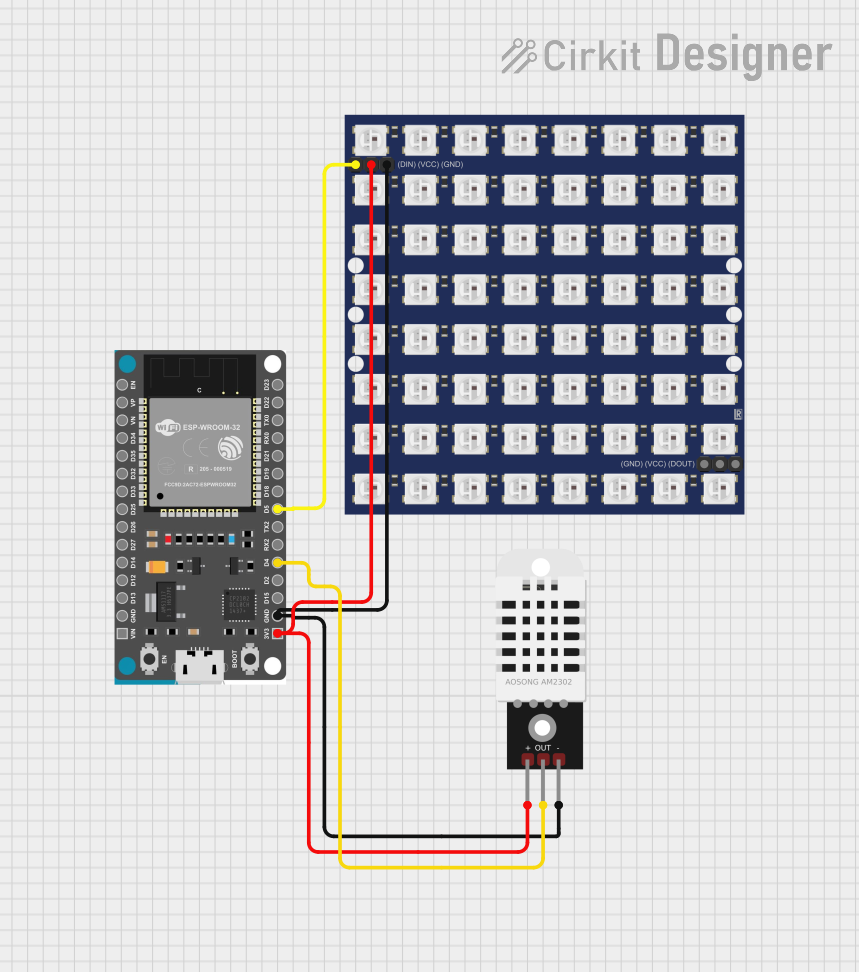
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer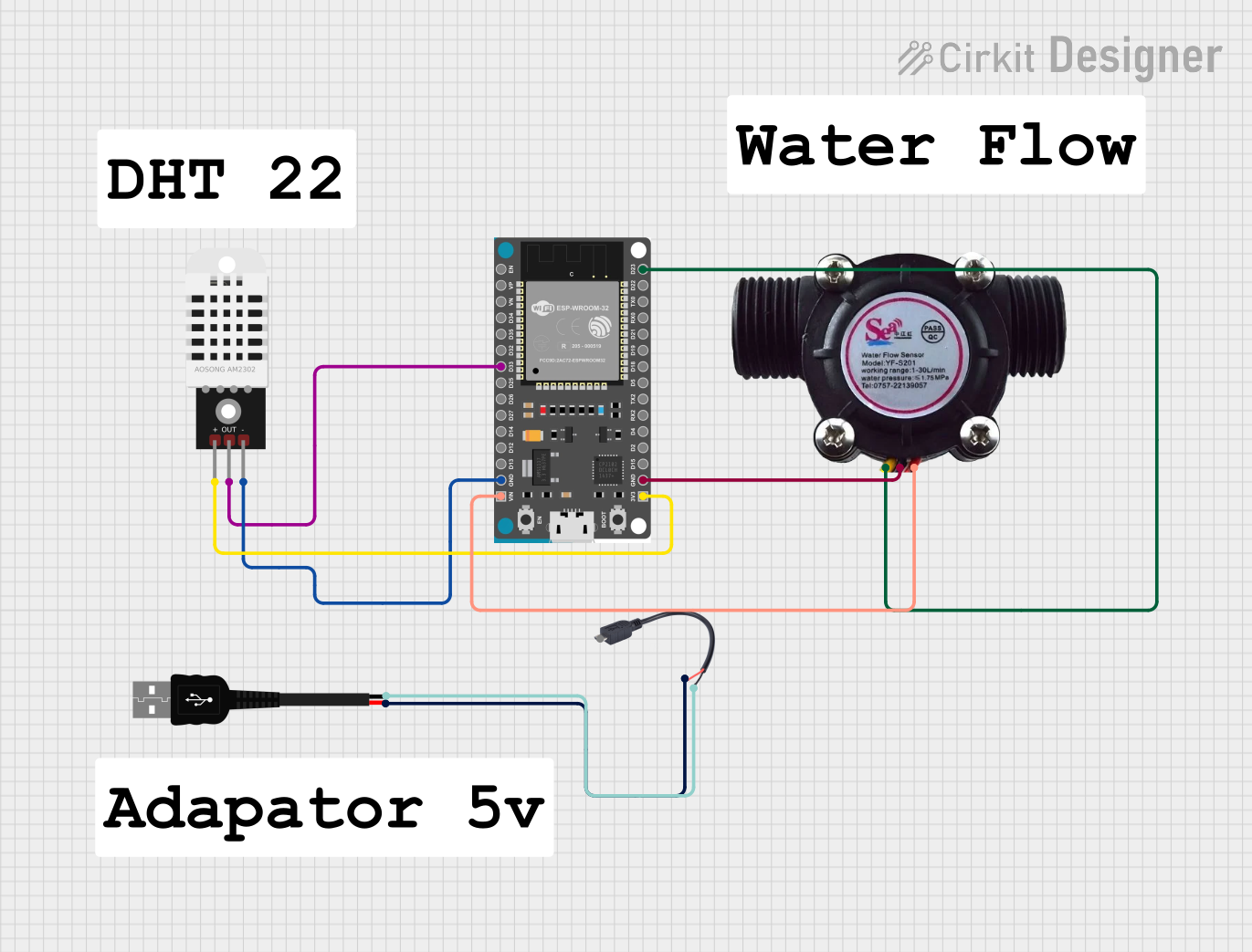
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The ESP32 is packed with features that make it a standout microcontroller for modern applications. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
- Processor: Dual-core Xtensa® 32-bit LX6 microprocessor
- Clock Speed: Up to 240 MHz
- RAM: 520 KB SRAM
- Flash Memory: Typically 4 MB (varies by module)
- Wi-Fi: 802.11 b/g/n (2.4 GHz)
- Bluetooth: v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- GPIO Pins: 34 (multipurpose, including ADC, DAC, PWM, I2C, SPI, UART)
- ADC Channels: 18 (12-bit resolution)
- DAC Channels: 2 (8-bit resolution)
- Power Consumption: Ultra-low power consumption with multiple power modes
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32 has a variety of pins for different functionalities. Below is a table summarizing the key pins and their descriptions:
| Pin Name | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO0 | Input/Output, Boot Mode Selection | Used for general I/O or to select boot mode during startup. |
| GPIO2 | Input/Output, ADC, DAC | General-purpose I/O, supports ADC and DAC functionality. |
| GPIO12 | Input/Output, ADC, Touch Sensor | General-purpose I/O, supports ADC and capacitive touch sensing. |
| GPIO13 | Input/Output, ADC, Touch Sensor | General-purpose I/O, supports ADC and capacitive touch sensing. |
| GPIO15 | Input/Output, ADC, PWM | General-purpose I/O, supports ADC and PWM functionality. |
| EN | Enable | Active-high pin to enable or reset the chip. |
| 3V3 | Power | Provides 3.3V power output. |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection. |
| TX0 (GPIO1) | UART Transmit | UART0 transmit pin for serial communication. |
| RX0 (GPIO3) | UART Receive | UART0 receive pin for serial communication. |
For a complete pinout, refer to the ESP32 datasheet or module-specific documentation.
Usage Instructions
The ESP32 is highly versatile and can be used in a variety of circuits. Below are the steps to get started with the ESP32:
Setting Up the ESP32 with Arduino IDE
Install the ESP32 Board Package:
- Open the Arduino IDE.
- Go to
File > Preferences. - In the "Additional Board Manager URLs" field, add the following URL:
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json - Go to
Tools > Board > Boards Manager, search for "ESP32," and install the package.
Connect the ESP32 to Your Computer:
- Use a USB cable to connect the ESP32 to your computer.
- Select the correct board and port in the Arduino IDE:
Tools > Board > ESP32 Dev ModuleTools > Port > [Your ESP32 Port]
Upload a Test Sketch:
- Use the following example code to test the ESP32:
// Blink example for ESP32
// This code blinks the built-in LED on the ESP32 board.
#define LED_PIN 2 // Built-in LED is usually connected to GPIO2
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
- Upload the Code:
- Click the upload button in the Arduino IDE.
- If the upload fails, press and hold the "BOOT" button on the ESP32 while uploading.
Important Considerations
- Power Supply: Ensure the ESP32 is powered with a stable 3.3V source. Avoid exceeding the voltage limit to prevent damage.
- Boot Mode: Some ESP32 modules require pressing the "BOOT" button during programming.
- GPIO Limitations: Certain GPIO pins have specific functions or restrictions (e.g., GPIO0 is used for boot mode selection).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Upload Fails with Timeout Error:
- Solution: Press and hold the "BOOT" button on the ESP32 while uploading the code.
ESP32 Not Detected by Computer:
- Solution: Ensure the USB cable is data-capable (not just for charging). Check the drivers for the USB-to-serial chip (e.g., CP2102 or CH340).
Wi-Fi Connection Issues:
- Solution: Double-check the SSID and password in your code. Ensure the Wi-Fi network is 2.4 GHz, as the ESP32 does not support 5 GHz networks.
Random Resets or Instability:
- Solution: Verify the power supply. Use a capacitor to stabilize the power if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP32 run on 5V?
- A: No, the ESP32 operates at 3.3V. Applying 5V to its GPIO pins can damage the chip.
Q: How do I use the ESP32's Bluetooth functionality?
- A: The ESP32 supports both Bluetooth Classic and BLE. Use the
BluetoothSerialorBLElibraries in the Arduino IDE to implement Bluetooth features.
- A: The ESP32 supports both Bluetooth Classic and BLE. Use the
Q: Can I use the ESP32 for battery-powered projects?
- A: Yes, the ESP32 has ultra-low-power modes, making it suitable for battery-powered applications. Use the deep sleep mode to conserve power.
This documentation provides a comprehensive overview of the ESP32, helping you get started with this versatile microcontroller. For more advanced features, refer to the official Espressif documentation.