
How to Use Laser diode: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
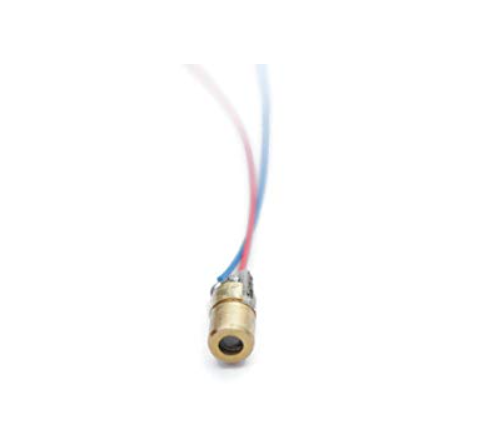

 Design with Laser diode in Cirkit Designer
Design with Laser diode in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A laser diode, manufactured by Electronic Spices, is a semiconductor device known for its ability to emit coherent light through a process called stimulated emission. Laser diodes are widely used in various applications such as fiber-optic communications, barcode readers, laser pointers, CD/DVD/Blu-ray reading and writing, laser printing, and in medical equipment.
Explore Projects Built with Laser diode
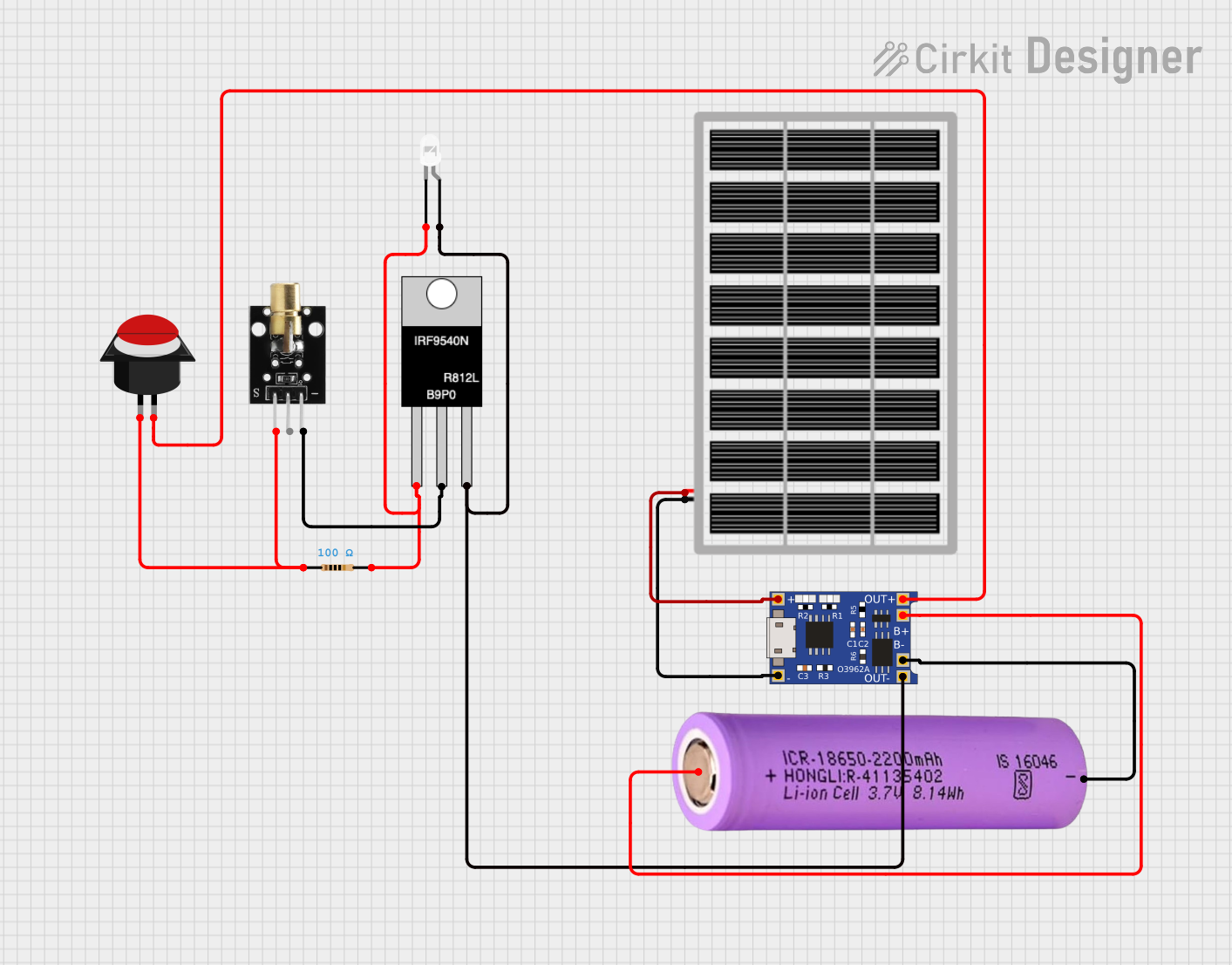
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer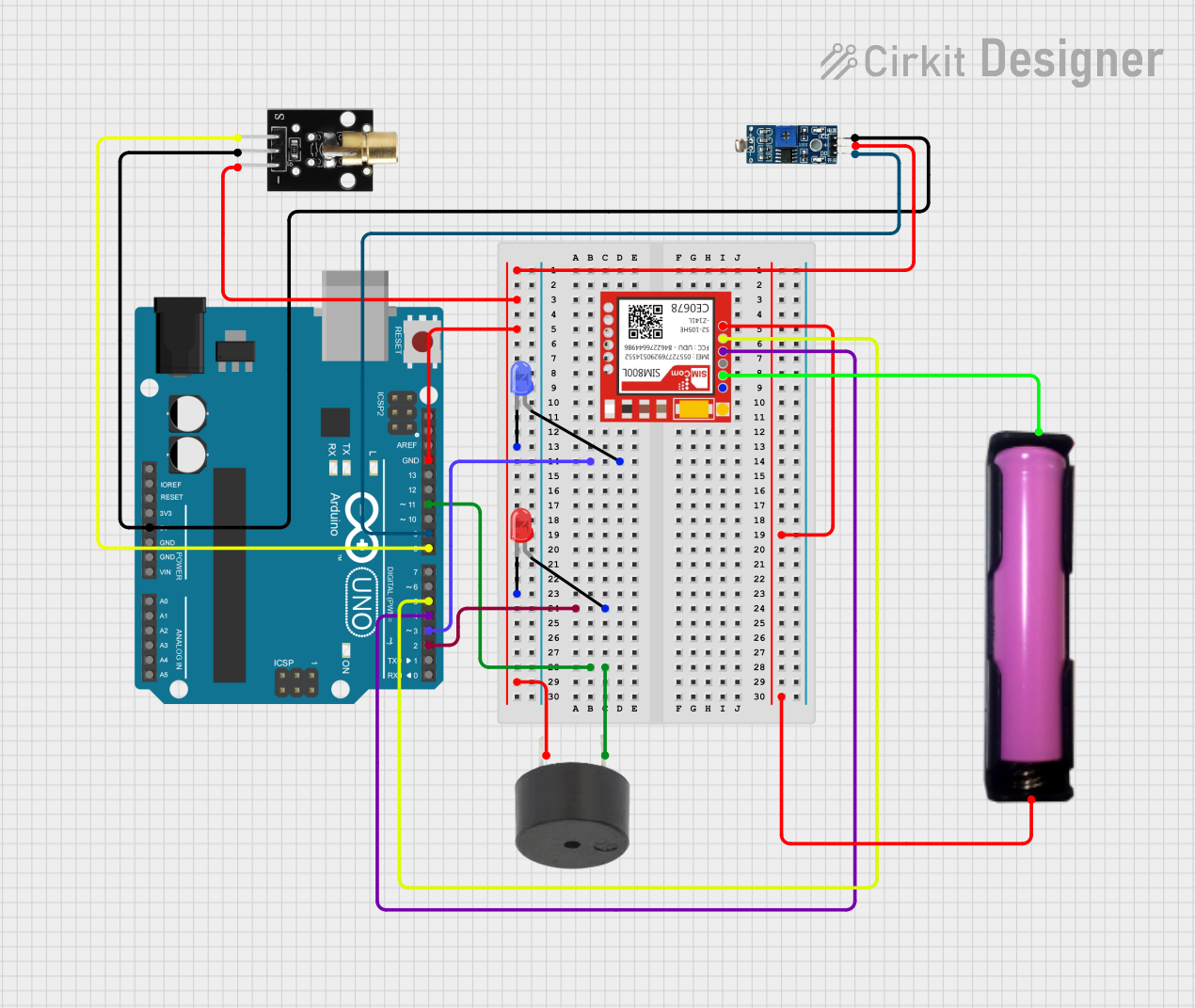
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer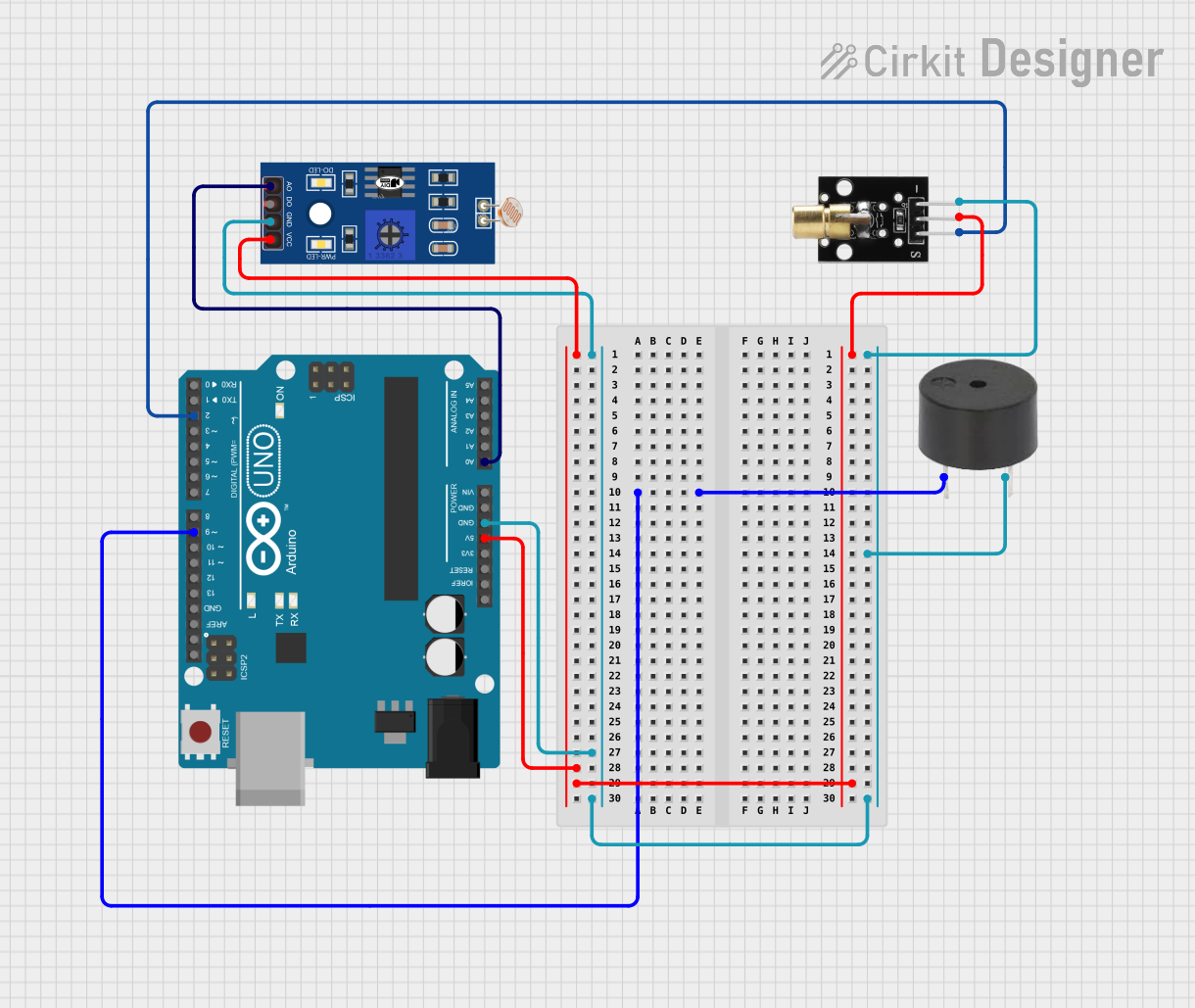
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer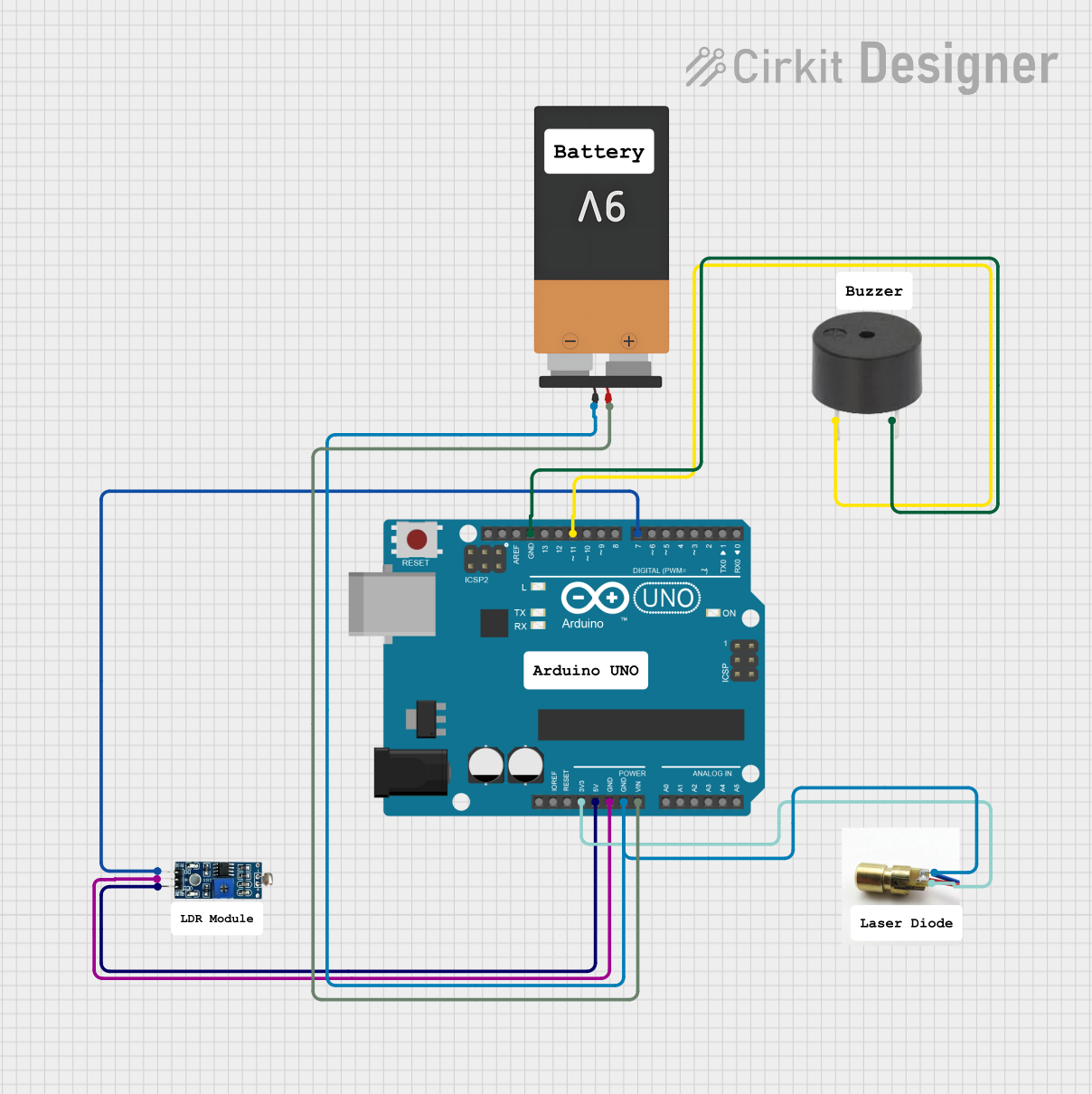
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Laser diode

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Optical communication
- Scanning and imaging devices
- Laser printing
- Medical diagnostics and treatments
- Material processing
- Consumer electronics
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: Electronic Spices
- Part ID: dblldhrlpo5
- Wavelength: Typically ranges from 400 nm to 1600 nm (varies by model)
- Output Power: Varies by model (e.g., 5 mW, 10 mW, etc.)
- Operating Voltage: Typically around 2.2V to 3.6V
- Operating Current: Depends on the model, often around 20 mA to 150 mA
- Threshold Current: The minimum current at which the diode starts to emit laser light
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to +60°C (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Anode (+) |
| 2 | Cathode (-) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply matches the operating voltage and current requirements of the laser diode.
- Current Limiting: Always use a current limiting resistor or a constant current source to prevent overdriving the diode.
- Heat Sinking: Laser diodes generate heat during operation. Use appropriate heat sinking to maintain operational temperature.
- Avoid Direct Eye Exposure: Never look directly into the laser beam or point it at others. Use appropriate safety goggles that block the specific laser wavelength.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- ESD Sensitivity: Laser diodes are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Handle with proper ESD precautions.
- Reverse Voltage: Avoid applying reverse voltage as it can damage the diode.
- Modulation: If modulation is required, ensure it is within the diode's bandwidth capabilities.
- Lifetime: Operating the diode within specified limits ensures maximum lifetime.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Dim or No Laser Emission: Check if the diode is properly powered and the current is within specified limits. Ensure the diode is not damaged.
- Overheating: Verify that the heat sinking is adequate. Reduce the operating current if necessary.
- Intermittent Operation: Check for loose connections and ensure that the power supply is stable.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a Multimeter: To check for proper voltage and current.
- Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correct.
- Replace the Diode: If the diode is damaged, it may need to be replaced.
FAQs
Q: Can I drive the laser diode directly from an Arduino pin? A: No, an Arduino pin cannot supply sufficient current and may not provide the necessary voltage. Use a driver circuit.
Q: What is the lifetime of a laser diode? A: The lifetime can vary widely based on usage, but typically tens of thousands of hours if operated within specifications.
Q: Is it safe to use a laser diode without goggles? A: No, always use safety goggles rated for the specific wavelength of the laser diode to prevent eye damage.
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to control a laser diode using an Arduino UNO. This example assumes the use of a laser diode driver circuit.
const int laserPin = 3; // Laser diode connected to digital pin 3
void setup() {
pinMode(laserPin, OUTPUT); // Set the laser pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(laserPin, HIGH); // Turn on the laser diode
delay(1000); // Keep the laser on for 1 second
digitalWrite(laserPin, LOW); // Turn off the laser diode
delay(1000); // Keep the laser off for 1 second
}
Note: The above code is a simple on-off example. Always ensure that the laser diode is driven through a proper driver circuit to regulate current and voltage as per the diode's specifications.