
How to Use 3.7v lipo 300mAh: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 3.7v lipo 300mAh in Cirkit Designer
Design with 3.7v lipo 300mAh in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 3.7V LiPo 300mAh battery, manufactured by FITHOOD (Part ID: B0CM63V327), is a lightweight and compact lithium polymer (LiPo) battery. It features a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts and a capacity of 300 milliampere-hours (mAh). This battery is widely used in portable electronics, remote-controlled (RC) devices, wearables, and other applications requiring a high energy density in a small form factor.
Explore Projects Built with 3.7v lipo 300mAh

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer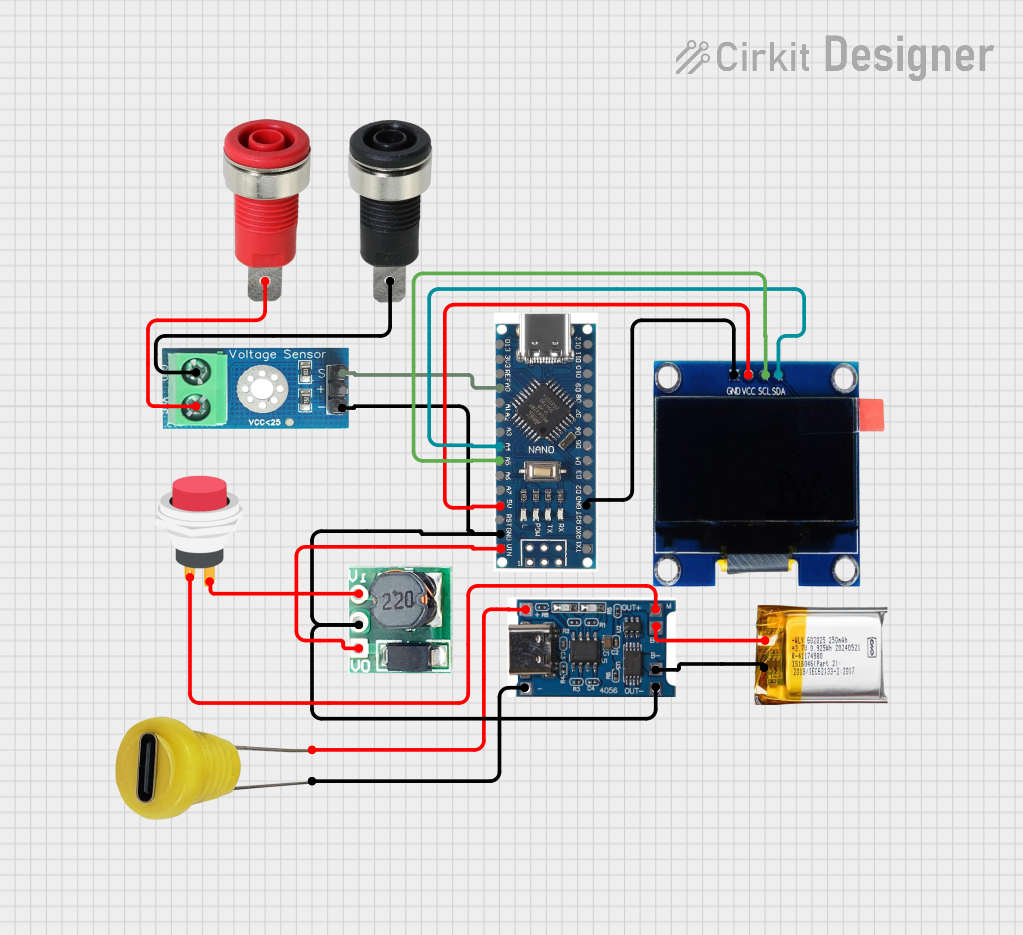
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer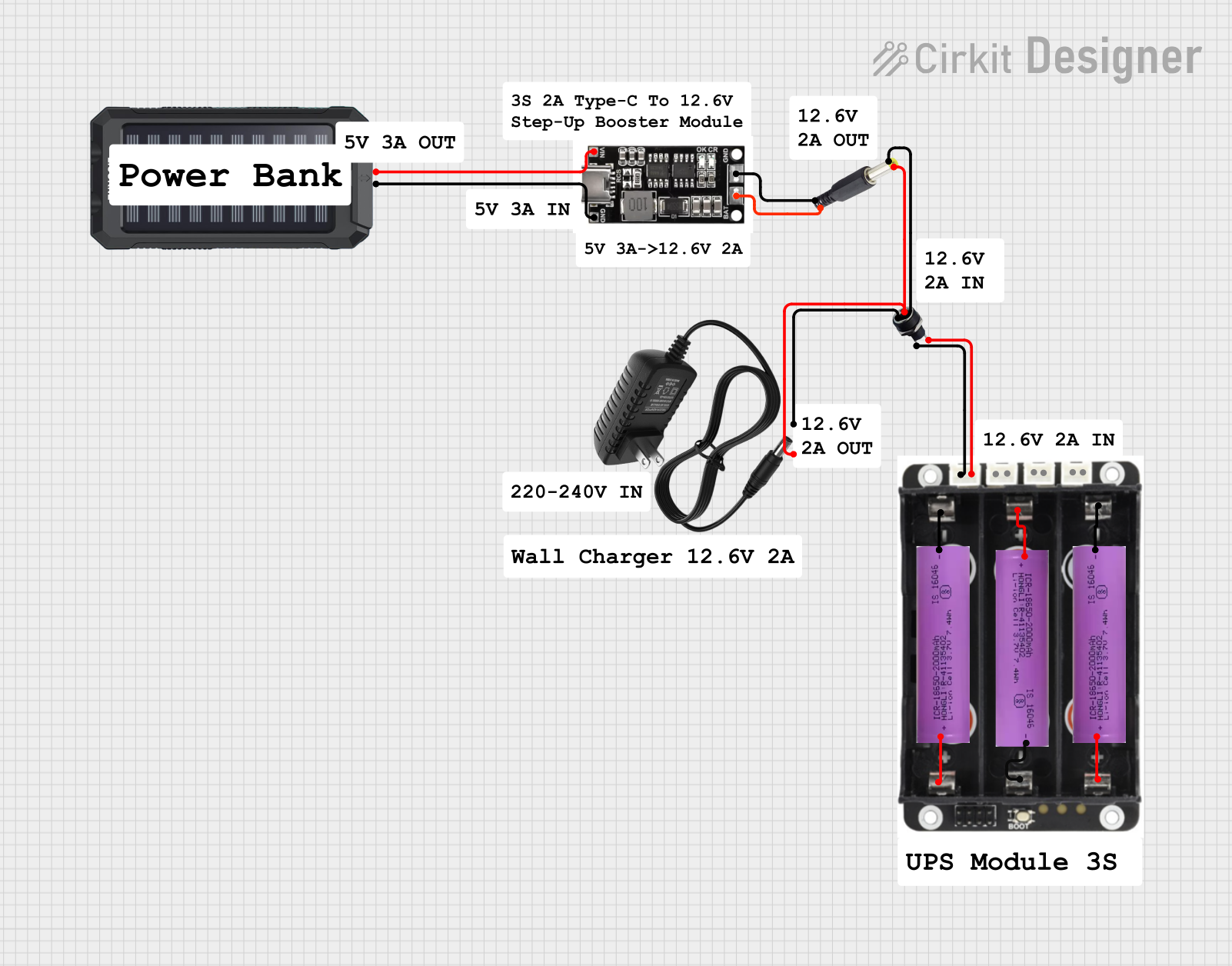
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer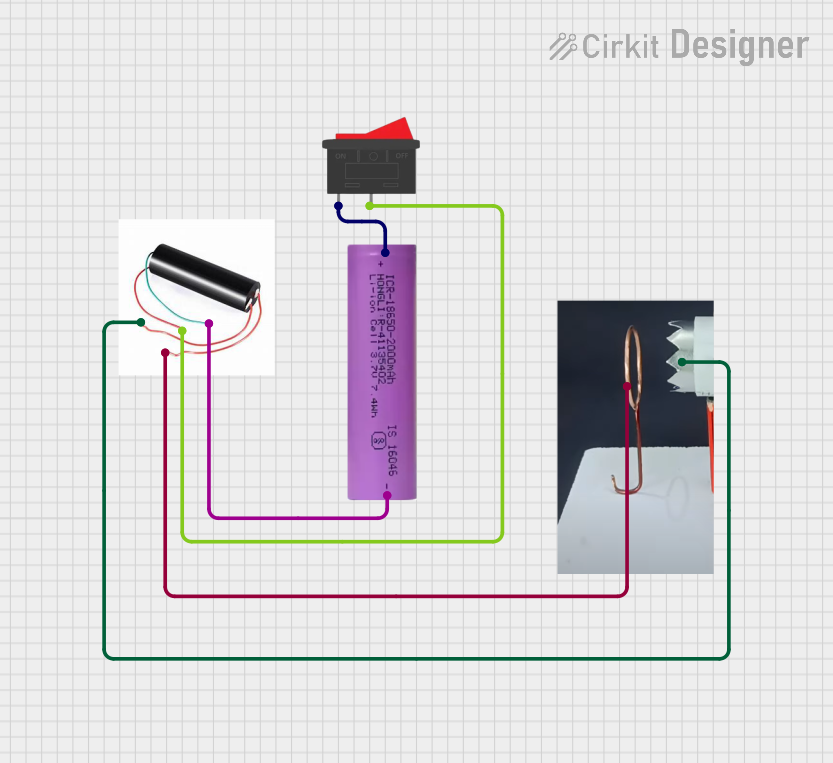
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 3.7v lipo 300mAh

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Portable electronic devices (e.g., MP3 players, fitness trackers)
- Remote-controlled drones, cars, and boats
- IoT devices and sensors
- DIY electronics projects
- Backup power for small embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the 3.7V LiPo 300mAh battery:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V |
| Capacity | 300mAh |
| Chemistry | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) |
| Maximum Charge Voltage | 4.2V |
| Discharge Cutoff Voltage | 3.0V |
| Maximum Discharge Current | 1C (300mA) |
| Recommended Charge Current | 0.5C (150mA) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | ~30mm x 20mm x 5mm |
| Weight | ~6 grams |
| Connector Type | JST 2-pin (commonly used) |
Pin Configuration
The battery typically comes with a JST 2-pin connector. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Description | Wire Color |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Terminal (+) | Red |
| 2 | Negative Terminal (-) | Black |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Battery in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the battery to your circuit using the JST 2-pin connector. Ensure the polarity matches the circuit's power input (red wire to positive, black wire to negative).
- Charging: Use a LiPo-compatible charger to charge the battery. Set the charger to a maximum charge voltage of 4.2V and a charge current of 150mA (0.5C) for optimal battery life.
- Discharging: Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum discharge current of 300mA (1C). Use a voltage cutoff circuit or battery management system (BMS) to prevent the voltage from dropping below 3.0V, which can damage the battery.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overcharging: Never charge the battery above 4.2V, as this can cause overheating or damage.
- Avoid Over-Discharging: Do not let the battery voltage drop below 3.0V to prevent permanent capacity loss.
- Temperature Range: Operate the battery within the recommended temperature range (typically 0°C to 45°C for charging and -20°C to 60°C for discharging).
- Storage: Store the battery at a partial charge (around 3.7V) in a cool, dry place if not in use for extended periods.
- Safety: Avoid puncturing, short-circuiting, or exposing the battery to fire or water.
Example: Using the Battery with an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO with the 3.7V LiPo 300mAh battery, you will need a boost converter to step up the voltage to 5V. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the battery to the input of the boost converter.
- Set the boost converter output to 5V.
- Connect the boost converter output to the Arduino UNO's 5V and GND pins.
Example Code
// Example code to blink an LED using Arduino UNO powered by a 3.7V LiPo battery
// Ensure the battery is connected via a boost converter to provide 5V to the Arduino
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Charger not compatible with LiPo batteries or incorrect settings.
- Solution: Use a LiPo-specific charger and ensure the charge voltage is set to 4.2V.
Battery Drains Quickly
- Cause: Excessive load or battery degradation.
- Solution: Ensure the load does not exceed 300mA. Replace the battery if it has degraded.
Battery Swells or Overheats
- Cause: Overcharging, over-discharging, or physical damage.
- Solution: Stop using the battery immediately. Dispose of it safely according to local regulations.
Arduino UNO Not Powering On
- Cause: Insufficient voltage or current from the battery.
- Solution: Use a boost converter to step up the voltage to 5V. Ensure the battery is fully charged.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this battery to power a 5V device directly?
A: No, the battery's nominal voltage is 3.7V. Use a boost converter to step up the voltage to 5V.
Q: How long will the battery last on a 100mA load?
A: The runtime can be estimated as 300mAh ÷ 100mA = 3 hours.
Q: Is it safe to leave the battery connected to the charger?
A: No, disconnect the battery once fully charged to prevent overcharging.
Q: Can I use this battery in parallel with another LiPo battery?
A: Yes, but ensure both batteries have the same voltage and capacity, and use a proper balancing circuit.