
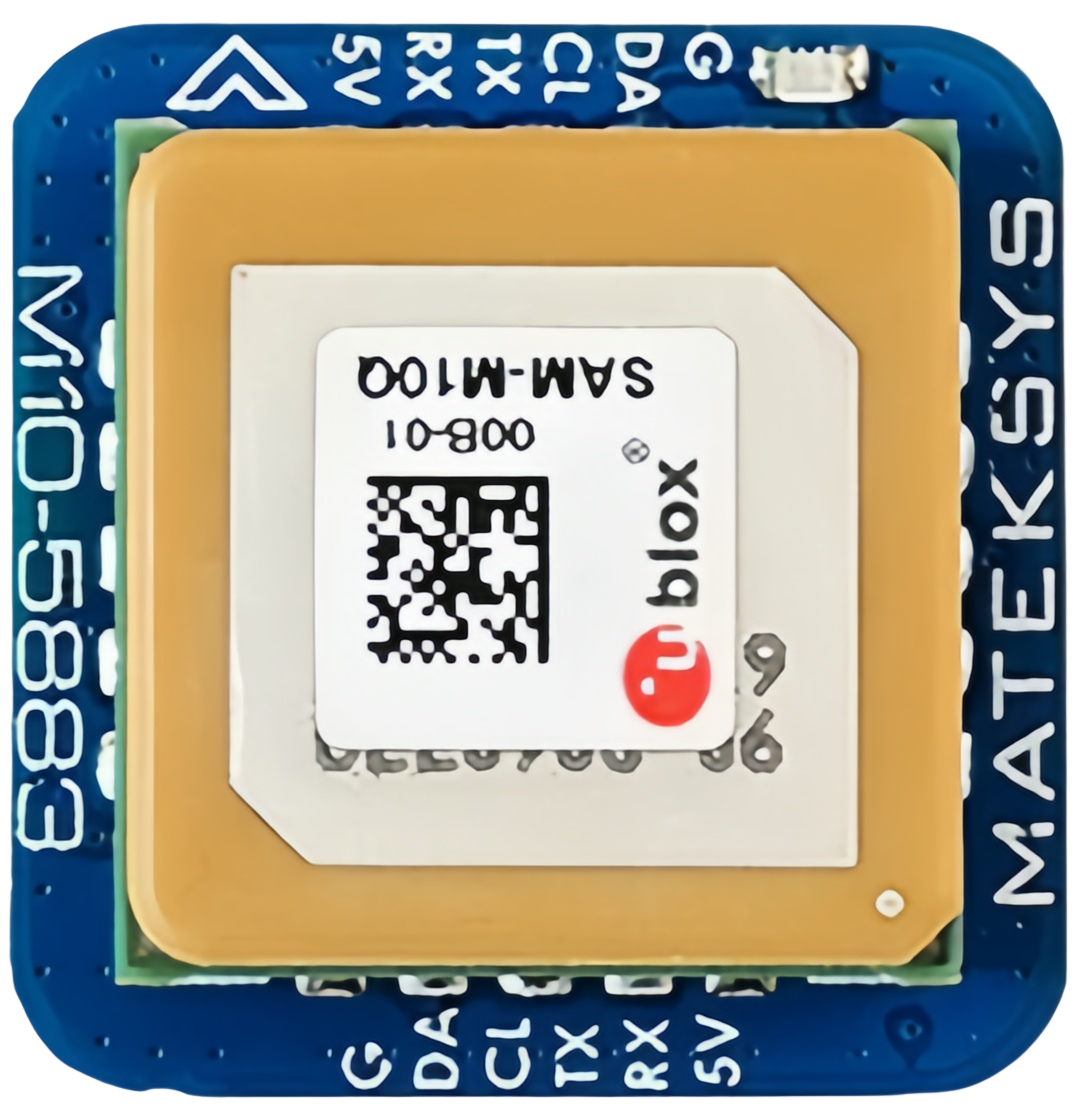
How to Use GPS Matek M10-5883: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with GPS Matek M10-5883 in Cirkit Designer
Design with GPS Matek M10-5883 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The GPS Matek M10-5883 is a high-performance GPS module designed for applications requiring precise positioning and navigation. It features a 10Hz update rate, a built-in antenna, and support for multiple GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems), including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. This module is particularly well-suited for drones, robotics, and other systems where accurate and reliable location data is critical.
Explore Projects Built with GPS Matek M10-5883
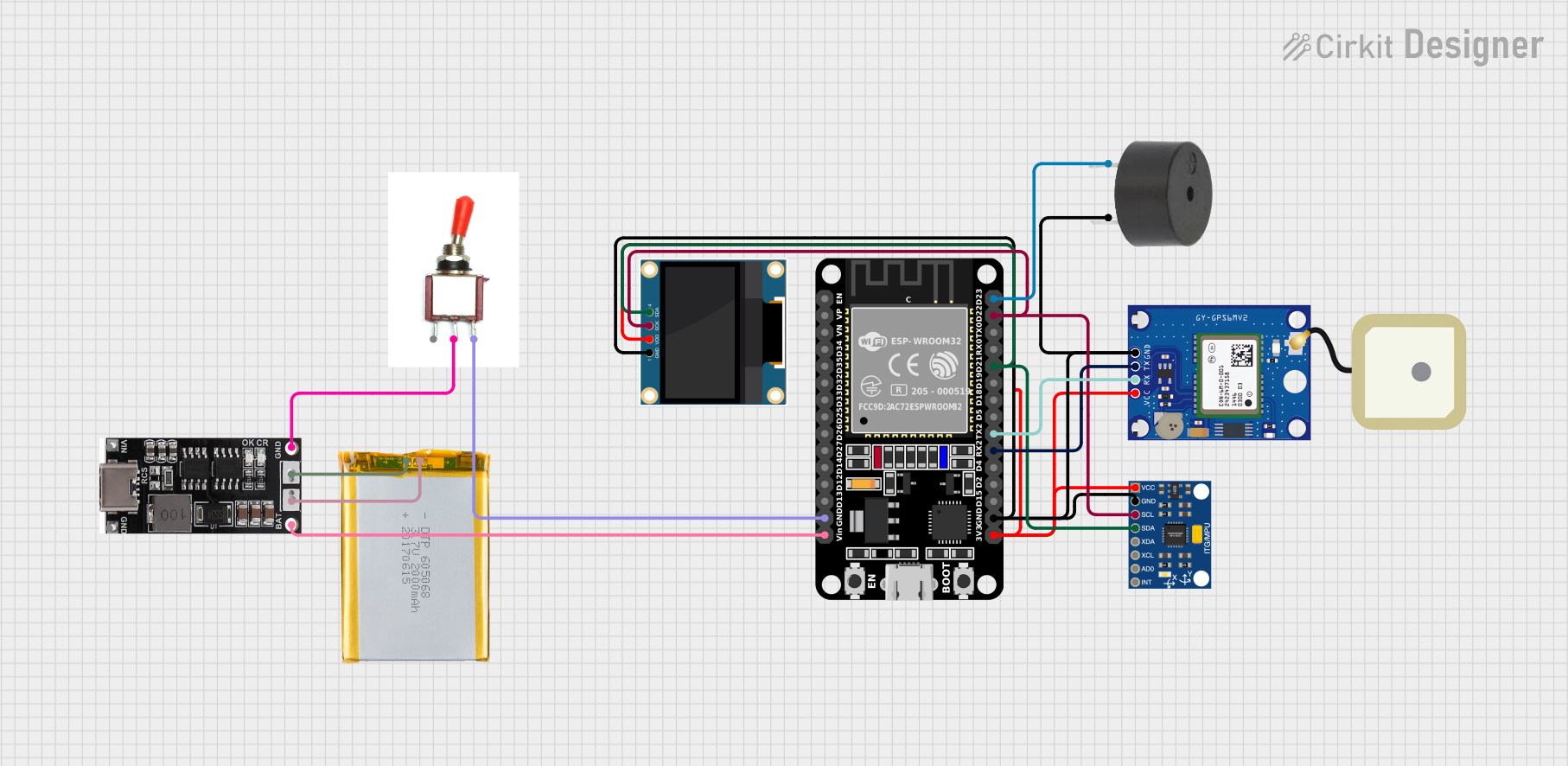
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer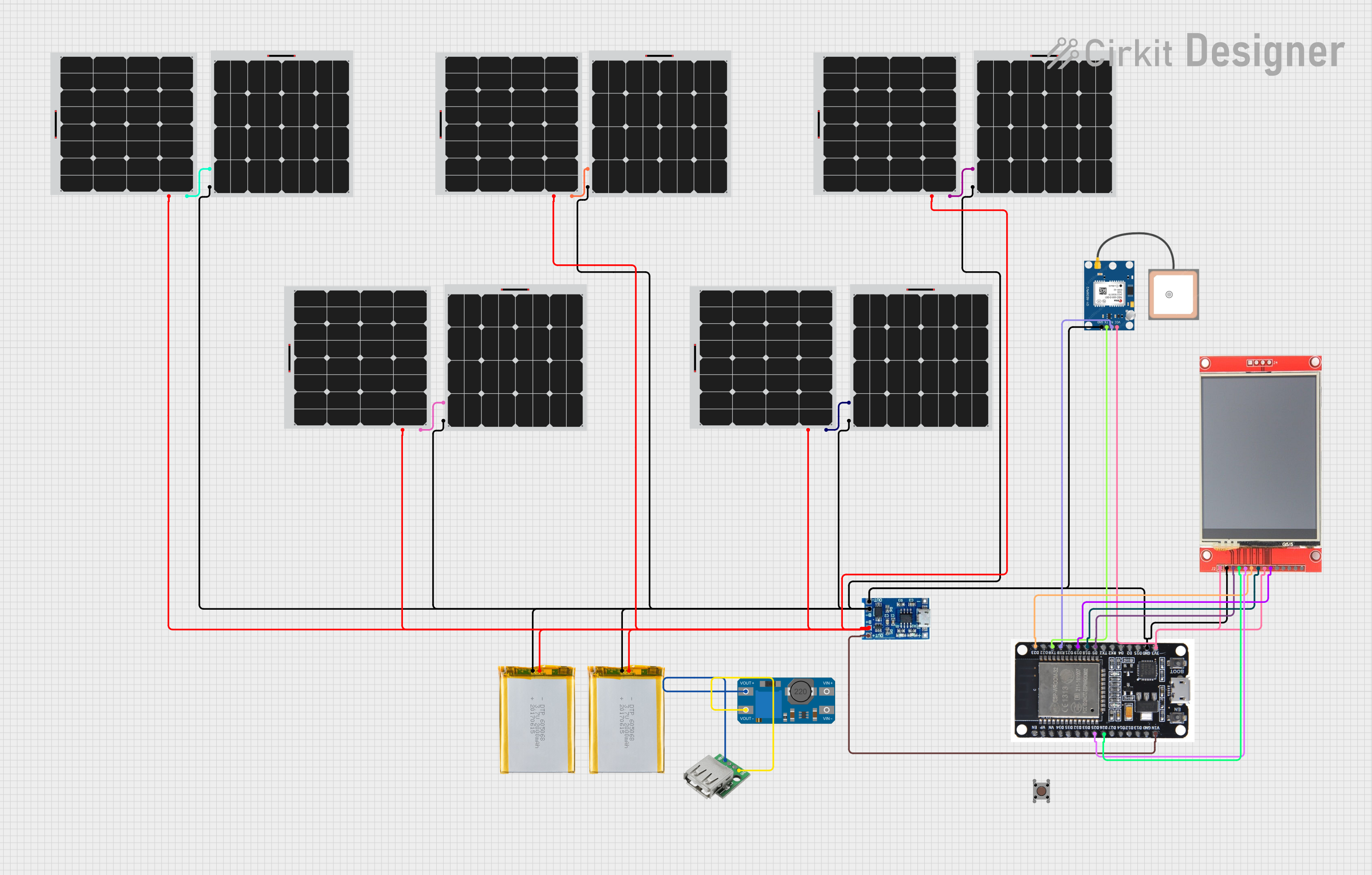
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer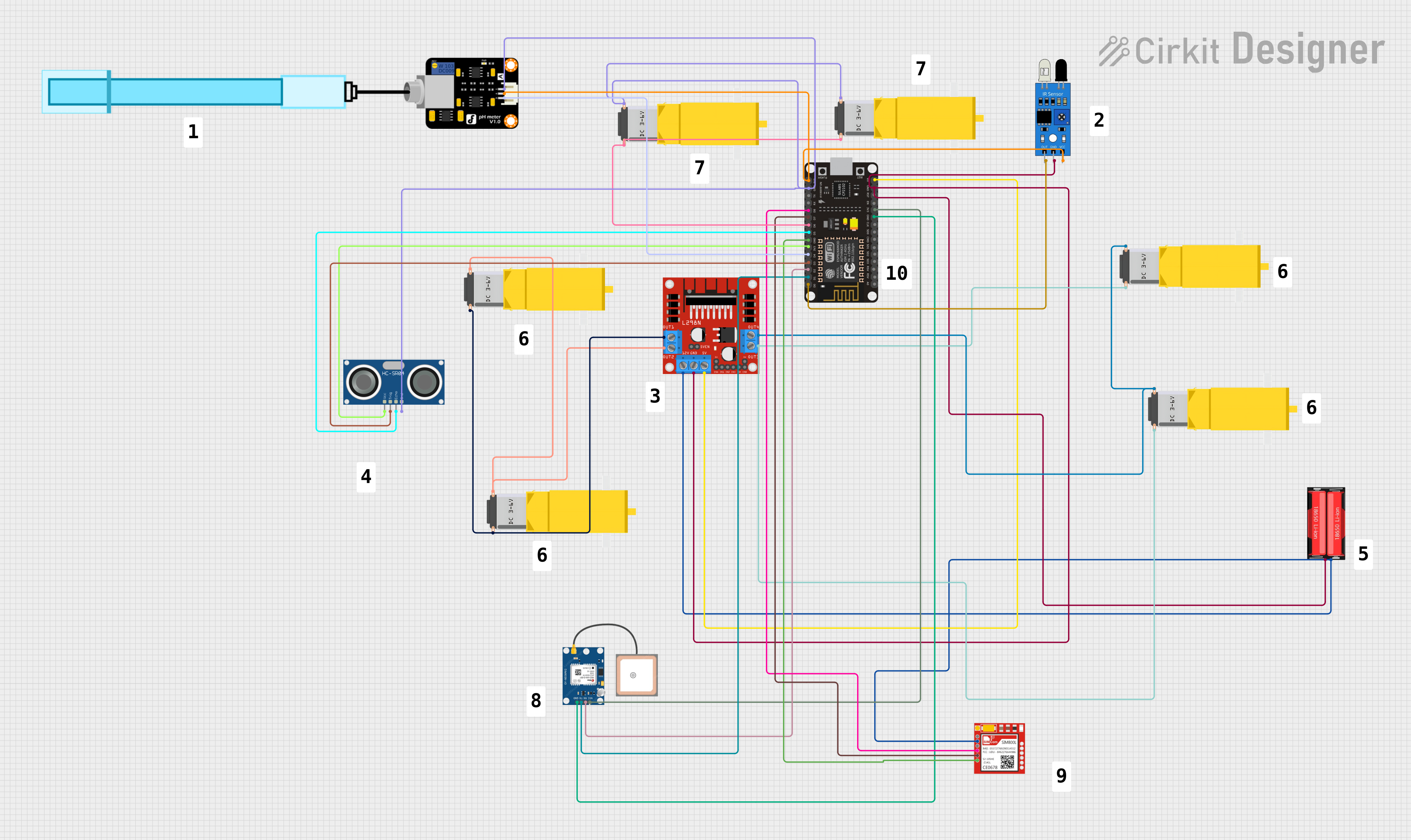
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GPS Matek M10-5883

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Autonomous drones and UAVs for navigation and waypoint tracking
- Robotics for precise localization and mapping
- Outdoor navigation systems
- Geocaching and surveying
- IoT devices requiring real-time location tracking
Technical Specifications
The GPS Matek M10-5883 module is designed to deliver high accuracy and reliability. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| GNSS Support | GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou |
| Update Rate | 10Hz |
| Position Accuracy | < 1.5m CEP |
| Sensitivity | -167 dBm (tracking), -160 dBm (cold start) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5.5V |
| Current Consumption | ~50mA |
| Communication Interface | UART (default: 9600 baud rate) |
| Built-in Antenna | Yes |
| Magnetometer | HMC5883L (3-axis digital compass) |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 25mm x 10mm |
| Weight | ~10g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The GPS Matek M10-5883 module has a standard pinout for easy integration into your projects. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power input (3.3V - 5.5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | TX | UART Transmit (data output from GPS module) |
| 4 | RX | UART Receive (data input to GPS module) |
| 5 | SDA | I2C Data line for magnetometer (HMC5883L) |
| 6 | SCL | I2C Clock line for magnetometer (HMC5883L) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the GPS Matek M10-5883 in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - Connect UART: Use the
TXandRXpins to interface with a microcontroller or computer. Ensure the baud rate is set to 9600 (default). - Magnetometer Connection: If using the HMC5883L magnetometer, connect the
SDAandSCLpins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller. - Antenna Placement: Ensure the module's built-in antenna has a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid GPS signal disruptions.
- Antenna Orientation: Place the module with the antenna facing upward and away from obstructions or sources of interference (e.g., metal surfaces, motors).
- UART Configuration: If using a different baud rate, configure it via the microcontroller or GPS software.
- Magnetometer Calibration: Calibrate the HMC5883L magnetometer before use to ensure accurate heading data.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use the GPS Matek M10-5883 with an Arduino UNO:
Wiring
| GPS Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX | D4 (via SoftwareSerial) |
| RX | D3 (via SoftwareSerial) |
| SDA | A4 |
| SCL | A5 |
Code Example
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_HMC5883_U.h>
// Create a SoftwareSerial instance for GPS communication
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(4, 3); // RX, TX
// Create an instance of the HMC5883L magnetometer
Adafruit_HMC5883_Unified mag = Adafruit_HMC5883_Unified(12345);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600);
gpsSerial.begin(9600); // GPS default baud rate
// Initialize magnetometer
if (!mag.begin()) {
Serial.println("Magnetometer not detected. Check wiring!");
while (1);
}
Serial.println("Magnetometer initialized.");
}
void loop() {
// Read GPS data
while (gpsSerial.available()) {
char c = gpsSerial.read();
Serial.print(c); // Print GPS data to Serial Monitor
}
// Read magnetometer data
sensors_event_t event;
mag.getEvent(&event);
Serial.print("Magnetometer Heading (X, Y, Z): ");
Serial.print(event.magnetic.x);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.print(event.magnetic.y);
Serial.print(", ");
Serial.println(event.magnetic.z);
delay(1000); // Delay for readability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No GPS Fix:
- Ensure the module has a clear view of the sky.
- Wait for a few minutes for the first fix (cold start).
- Check the power supply for stability.
No Data Output:
- Verify the UART connections (TX and RX).
- Ensure the baud rate matches the module's default (9600).
Magnetometer Not Detected:
- Check the I2C connections (SDA and SCL).
- Ensure pull-up resistors are present on the I2C lines if required.
Inaccurate Magnetometer Readings:
- Perform a calibration routine for the HMC5883L.
- Avoid placing the module near magnetic or metallic objects.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the GPS Matek M10-5883 indoors?
A: While the module may work indoors near windows, it is designed for outdoor use where it can receive satellite signals without obstruction.
Q: How do I change the GPS update rate?
A: The update rate can be configured using specific commands sent via UART. Refer to the module's datasheet for details.
Q: Is the module compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the module supports both 3.3V and 5V logic levels.
Q: Can I use the magnetometer without the GPS?
A: Yes, the HMC5883L magnetometer can be used independently via the I2C interface.