
How to Use LM35 Temperature Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with LM35 Temperature Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with LM35 Temperature Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The LM35 is a precision temperature sensor manufactured by National Semiconductor. It provides an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in degrees Celsius. Unlike many other temperature sensors, the LM35 does not require any external calibration or trimming, making it highly accurate and easy to use. Its low output impedance and linear output make it ideal for interfacing with analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) in microcontrollers.
Explore Projects Built with LM35 Temperature Sensor
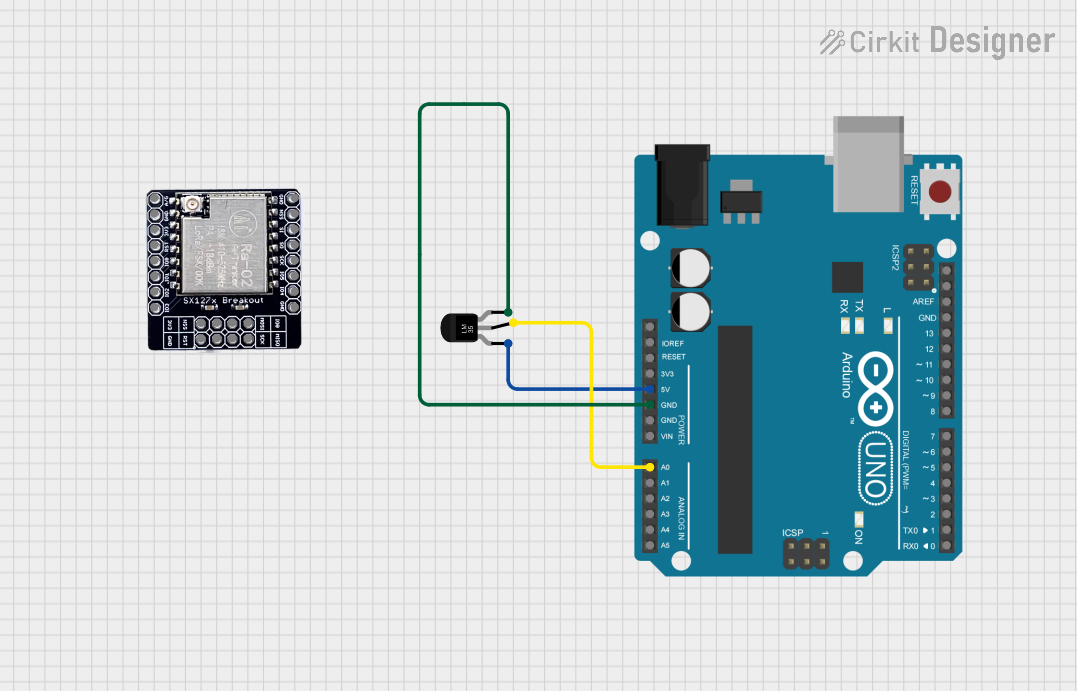
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer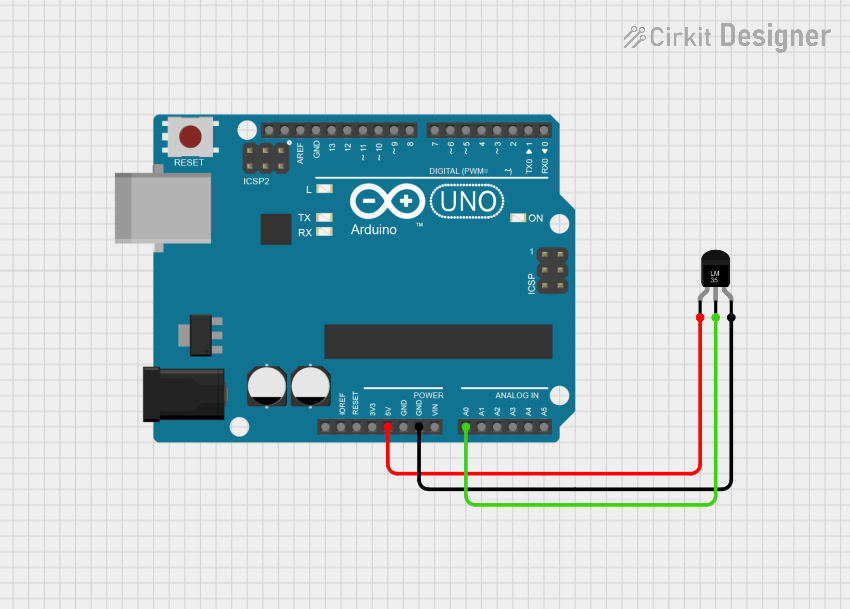
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer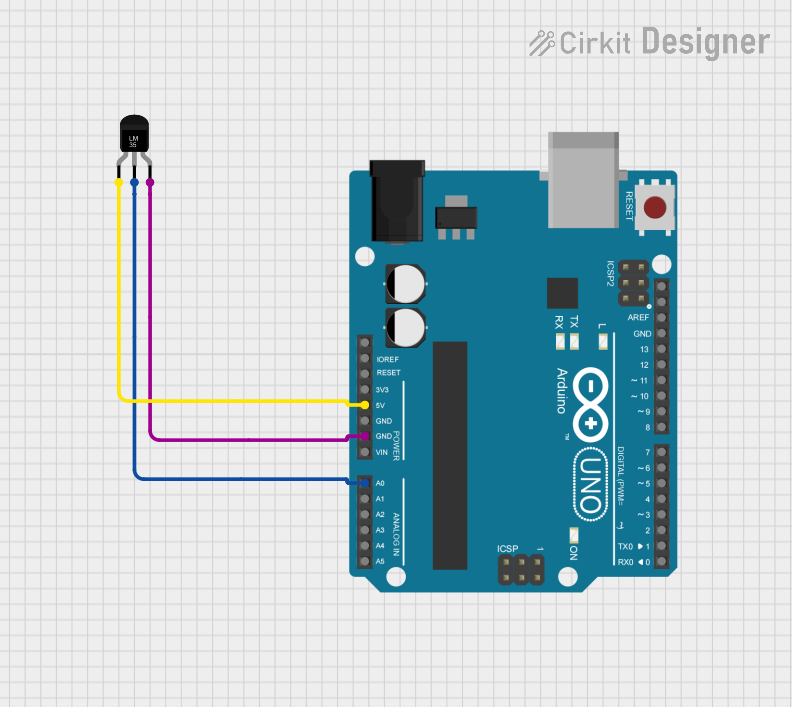
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer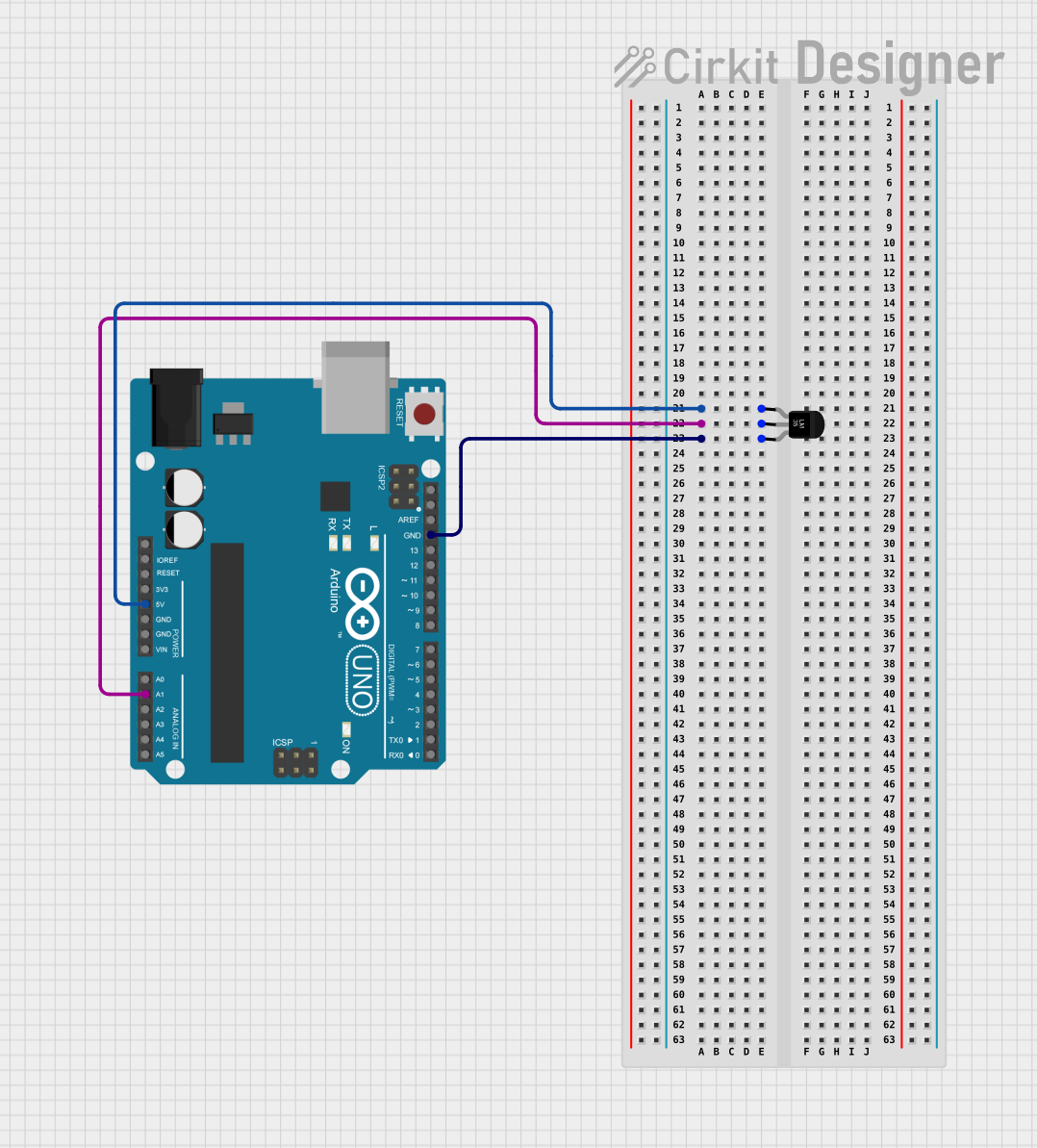
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LM35 Temperature Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Temperature monitoring in HVAC systems
- Industrial process control
- Environmental monitoring
- Consumer electronics (e.g., thermostats, appliances)
- Medical devices for temperature measurement
- Data logging systems
Technical Specifications
The LM35 is designed for a wide range of applications and offers the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | National Semiconductor |
| Part ID | LM35 |
| Temperature Range | -55°C to +150°C |
| Output Voltage | 10 mV/°C |
| Accuracy | ±0.5°C (at 25°C) |
| Supply Voltage Range | 4V to 30V |
| Supply Current | 60 µA (typical) |
| Output Impedance | 0.1 Ω (typical) |
| Response Time | 1 second (typical) |
| Package Options | TO-92, SOIC-8, TO-220 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The LM35 is available in multiple package types, such as TO-92, SOIC-8, and TO-220. Below is the pin configuration for the TO-92 package, which is the most commonly used.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | V+ | Positive supply voltage (4V to 30V) |
| 2 | VOUT | Analog output voltage proportional to temperature |
| 3 | GND | Ground (0V reference) |
Usage Instructions
The LM35 is straightforward to use in a circuit. It outputs an analog voltage that corresponds to the temperature in Celsius, with a scale factor of 10 mV/°C. For example, at 25°C, the output voltage will be 250 mV.
Connecting the LM35 to a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the V+ pin to a DC voltage source between 4V and 30V.
- Ground: Connect the GND pin to the ground of the circuit.
- Output: Connect the VOUT pin to an ADC input of a microcontroller or to a voltmeter for direct measurement.
Important Considerations
- Bypass Capacitor: Place a 0.1 µF capacitor between the V+ and GND pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
- Wiring Length: Keep the wiring between the LM35 and the microcontroller short to minimize noise and voltage drops.
- Thermal Coupling: Ensure good thermal contact between the LM35 and the surface being measured for accurate readings.
- Output Impedance: The LM35 has a low output impedance, so it can directly drive most ADC inputs without additional buffering.
Example: Interfacing LM35 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and read temperature data from the LM35 using an Arduino UNO.
Circuit Diagram
- V+: Connect to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- GND: Connect to the Arduino's GND pin.
- VOUT: Connect to the Arduino's analog input pin (e.g., A0).
Arduino Code
// LM35 Temperature Sensor Example with Arduino UNO
// Reads temperature in Celsius and prints it to the Serial Monitor
const int lm35Pin = A0; // Analog pin connected to LM35 VOUT
float temperatureC; // Variable to store temperature in Celsius
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(lm35Pin); // Read analog value from LM35
// Convert the analog value to voltage (5V reference, 10-bit ADC)
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Convert voltage to temperature in Celsius (10 mV/°C scale factor)
temperatureC = voltage * 100.0;
// Print the temperature to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperatureC);
Serial.println(" °C");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Best Practices
- Use a stable power supply to ensure accurate readings.
- Avoid placing the LM35 near heat sources or in direct sunlight, as this can affect the measurement.
- If measuring temperatures below 0°C, use a pull-down resistor on the output pin to ensure proper operation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage
- Ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range (4V to 30V).
- Verify that the connections to the V+, VOUT, and GND pins are correct.
Inaccurate Temperature Readings
- Check for noise in the power supply and add a bypass capacitor (0.1 µF) between V+ and GND.
- Ensure the LM35 is thermally coupled to the surface being measured.
- Verify that the ADC reference voltage matches the actual supply voltage.
Fluctuating Output
- Minimize wiring length to reduce noise.
- Use shielded cables if the LM35 is far from the microcontroller.
FAQs
Q: Can the LM35 measure negative temperatures?
A: Yes, the LM35 can measure temperatures below 0°C, but the output voltage will be negative. To read negative temperatures, use a negative voltage reference or a dual-supply configuration.
Q: What is the maximum distance between the LM35 and the microcontroller?
A: The LM35 can drive long cables, but for best results, keep the distance under 1 meter. For longer distances, use shielded cables or an operational amplifier as a buffer.
Q: Can the LM35 be used in a waterproof environment?
A: The LM35 itself is not waterproof. To use it in such environments, encase it in a waterproof housing while ensuring good thermal conductivity.
Q: How do I measure Fahrenheit instead of Celsius?
A: Convert the Celsius reading to Fahrenheit using the formula:
F = (C × 9/5) + 32. This can be implemented in the Arduino code.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the LM35 temperature sensor in a variety of applications.