
How to Use DPDT Switch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DPDT Switch in Cirkit Designer
Design with DPDT Switch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) switch is an electrical switch designed to control two separate circuits simultaneously. It features two input terminals and can connect each input to one of two output terminals, enabling versatile control and functionality. DPDT switches are commonly used in applications requiring polarity reversal, motor control, or switching between two power sources.
Explore Projects Built with DPDT Switch
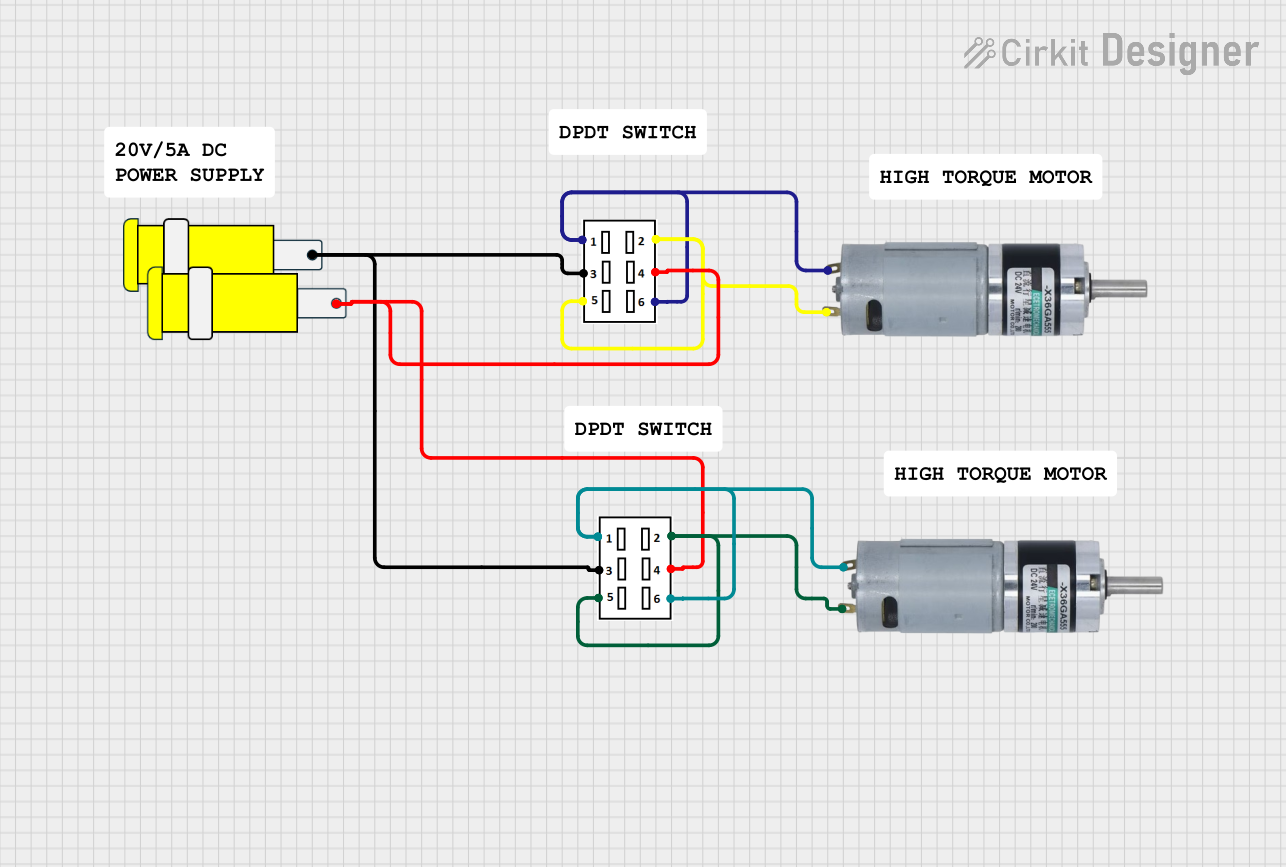
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer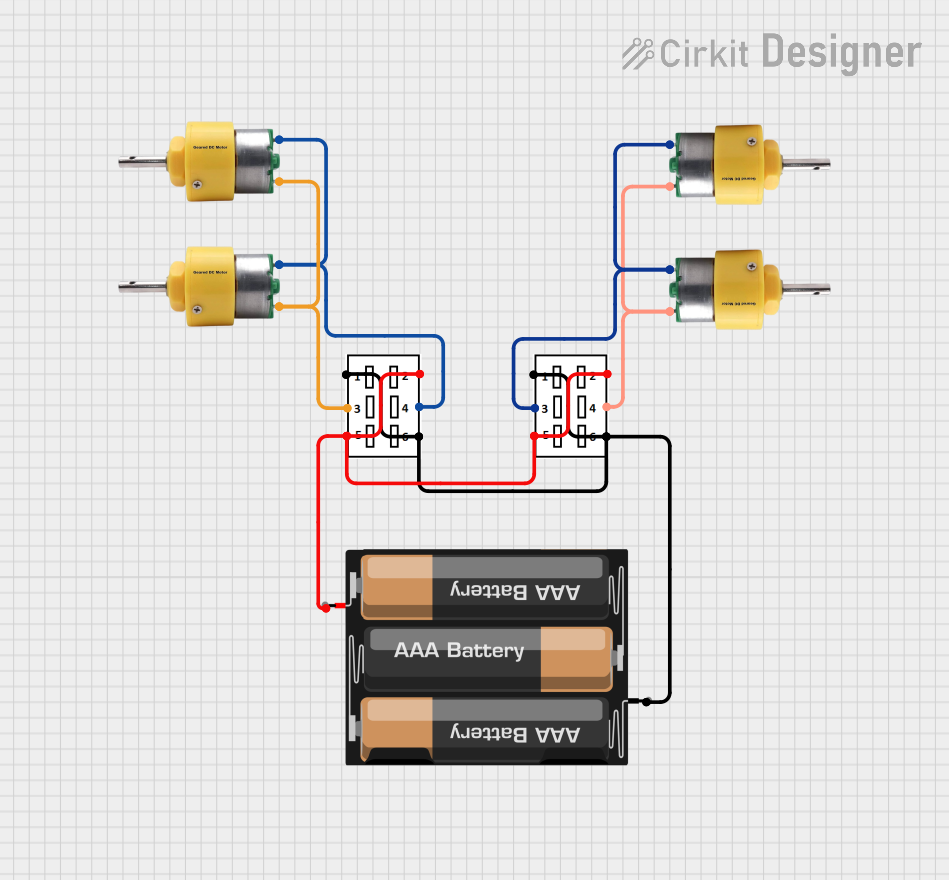
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer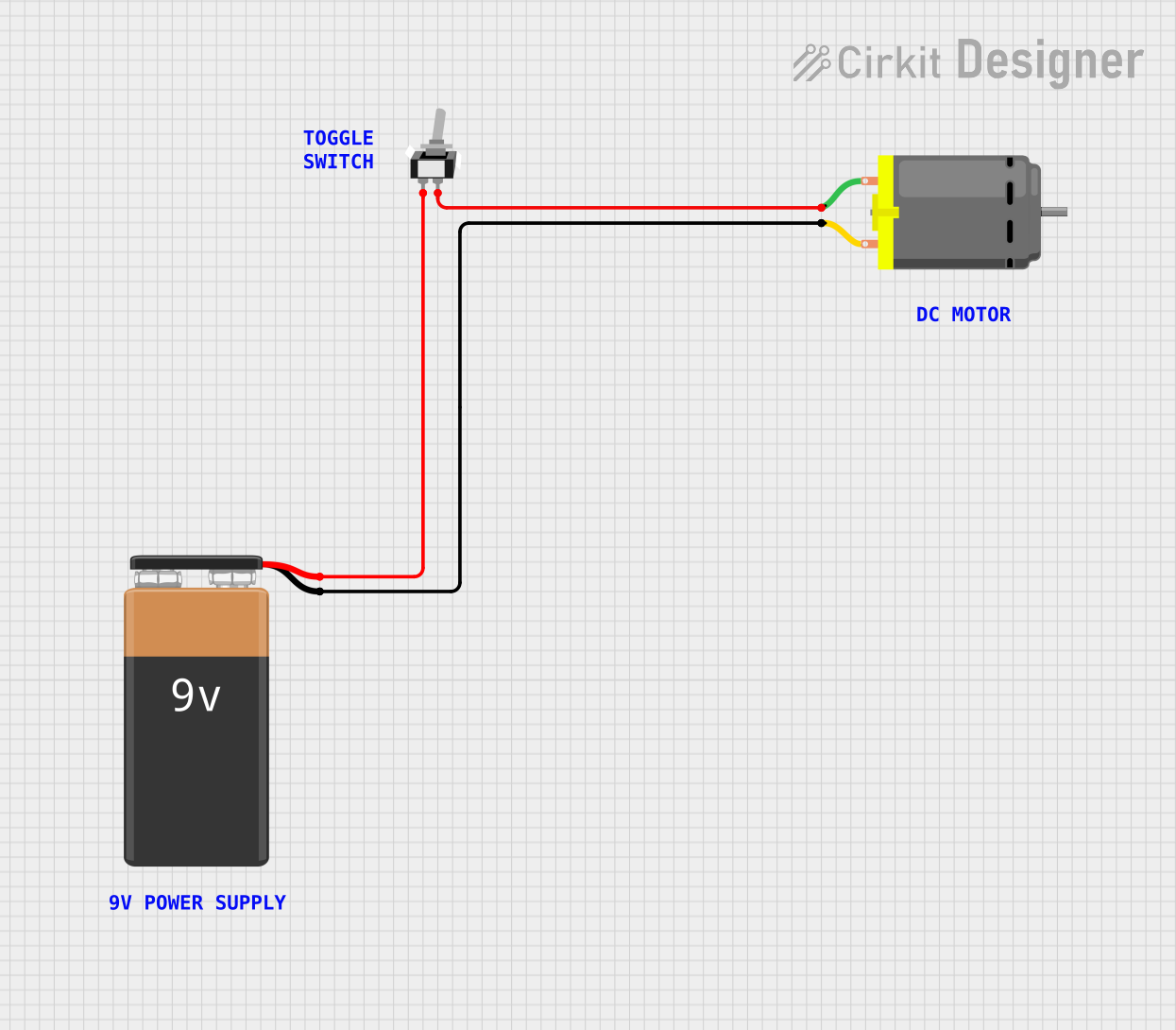
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DPDT Switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Polarity reversal for DC motors
- Switching between two power sources or circuits
- Audio signal routing
- Controlling two independent circuits with a single switch
- Robotics and automation systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a standard DPDT switch:
Key Technical Details
- Switch Type: Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT)
- Number of Poles: 2
- Number of Throws: 2
- Voltage Rating: Typically 12V to 250V (varies by model)
- Current Rating: Typically 2A to 15A (varies by model)
- Contact Material: Silver alloy or copper (varies by model)
- Actuation Type: Toggle, slide, or rocker
- Mounting Style: Panel mount or PCB mount
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
A DPDT switch typically has six terminals. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin Number | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input 1 (Pole 1) | First input terminal for the first circuit. |
| 2 | Output 1A | First output terminal for the first circuit (connected to Input 1 in one state). |
| 3 | Output 1B | Second output terminal for the first circuit (connected to Input 1 in another state). |
| 4 | Input 2 (Pole 2) | Second input terminal for the second circuit. |
| 5 | Output 2A | First output terminal for the second circuit (connected to Input 2 in one state). |
| 6 | Output 2B | Second output terminal for the second circuit (connected to Input 2 in another state). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the DPDT Switch in a Circuit
- Identify the Terminals: Locate the six terminals on the switch. Refer to the pin configuration table above to understand their functions.
- Connect the Inputs: Connect the two input terminals (Pin 1 and Pin 4) to the power sources or circuits you want to control.
- Connect the Outputs: Connect the output terminals (Pins 2, 3, 5, and 6) to the devices or circuits you want to control.
- Switch Operation: Toggle the switch to change the connection state:
- In one position, Input 1 connects to Output 1A, and Input 2 connects to Output 2A.
- In the other position, Input 1 connects to Output 1B, and Input 2 connects to Output 2B.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the switch's voltage and current ratings match your circuit requirements to avoid damage.
- Debouncing: Mechanical switches may produce noise or "bouncing" when toggled. Use a debouncing circuit or software if precise switching is required.
- Mounting: Securely mount the switch to prevent accidental toggling or damage.
- Polarity Reversal: For DC motor control, connect the DPDT switch in an H-bridge configuration to reverse the motor's direction.
Example: Using a DPDT Switch with an Arduino UNO
A DPDT switch can be used to control the direction of a DC motor. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code:
Circuit Description
- Connect the DPDT switch to the motor and power supply in an H-bridge configuration.
- Use the Arduino to control the motor's speed via a PWM signal.
Arduino Code
// Example code to control a DC motor using a DPDT switch and Arduino UNO
const int motorPin1 = 9; // PWM pin for motor control (connected to one side of DPDT)
const int motorPin2 = 10; // PWM pin for motor control (connected to the other side of DPDT)
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin1, OUTPUT); // Set motorPin1 as output
pinMode(motorPin2, OUTPUT); // Set motorPin2 as output
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor in one direction
analogWrite(motorPin1, 255); // Full speed on motorPin1
analogWrite(motorPin2, 0); // No speed on motorPin2
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(motorPin1, 0); // No speed on motorPin1
analogWrite(motorPin2, 0); // No speed on motorPin2
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
// Rotate motor in the opposite direction
analogWrite(motorPin1, 0); // No speed on motorPin1
analogWrite(motorPin2, 255); // Full speed on motorPin2
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Stop the motor
analogWrite(motorPin1, 0); // No speed on motorPin1
analogWrite(motorPin2, 0); // No speed on motorPin2
delay(1000); // Pause for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Switch Doesn't Work:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Switch Overheats:
- Cause: Exceeding the voltage or current rating.
- Solution: Verify that the switch's ratings match your circuit requirements.
Motor Doesn't Reverse:
- Cause: Incorrect H-bridge wiring.
- Solution: Ensure the DPDT switch is wired correctly for polarity reversal.
Noise or Flickering:
- Cause: Switch bouncing or poor contact.
- Solution: Use a debouncing circuit or software to eliminate noise.
FAQs
Q: Can a DPDT switch be used for AC circuits?
A: Yes, as long as the switch's voltage and current ratings are suitable for the AC circuit.Q: What is the difference between DPDT and SPDT switches?
A: A DPDT switch controls two circuits simultaneously, while an SPDT switch controls only one circuit.Q: Can I use a DPDT switch to control LEDs?
A: Yes, you can use a DPDT switch to toggle between two sets of LEDs or change their polarity.Q: How do I mount a DPDT switch?
A: Most DPDT switches are designed for panel or PCB mounting. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for secure installation.