
How to Use BMS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
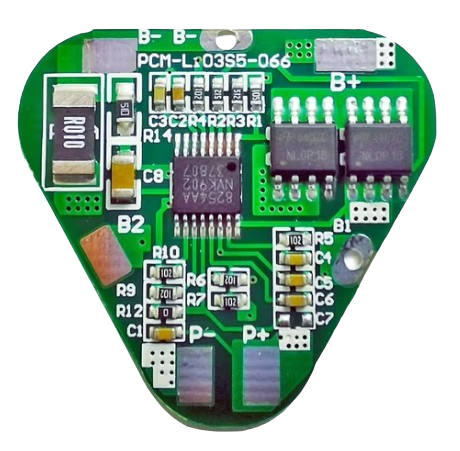
 Design with BMS in Cirkit Designer
Design with BMS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system designed to manage rechargeable batteries. It monitors the battery's state, calculates secondary data (e.g., charge level, health), reports this data, and controls the battery's operating environment. The BMS ensures safe operation, optimizes performance, and extends the battery's lifespan.
Explore Projects Built with BMS
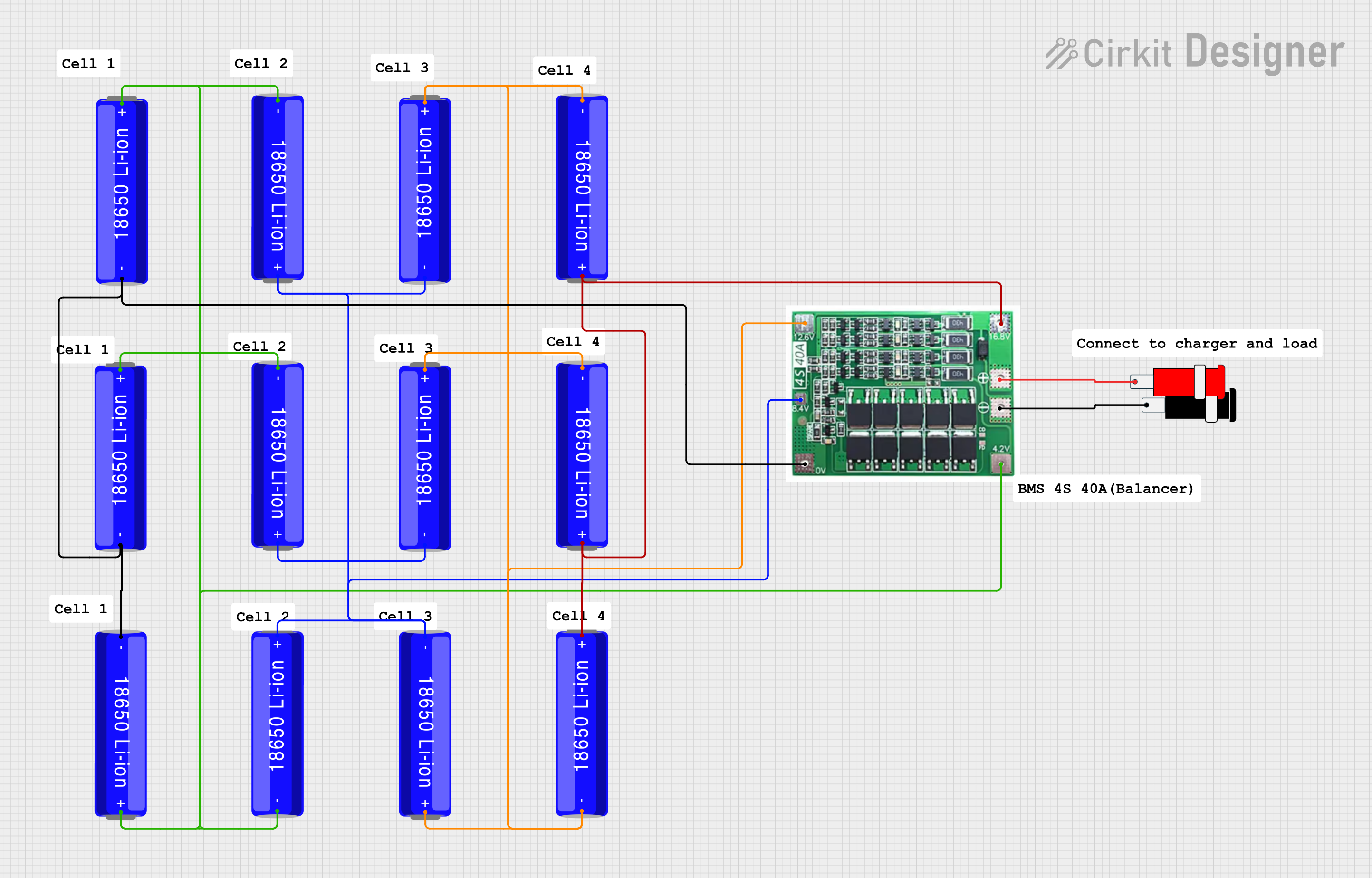
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer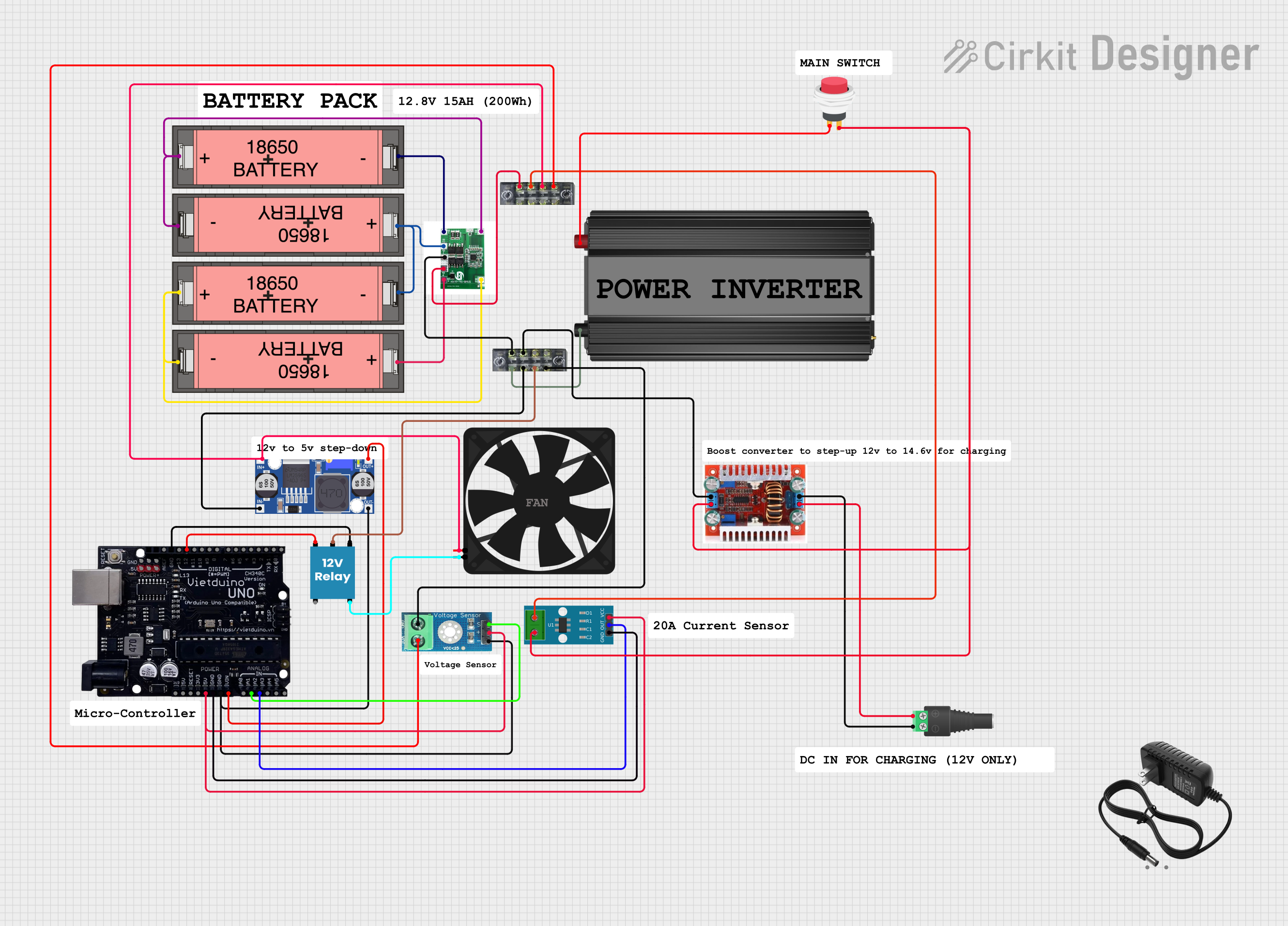
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer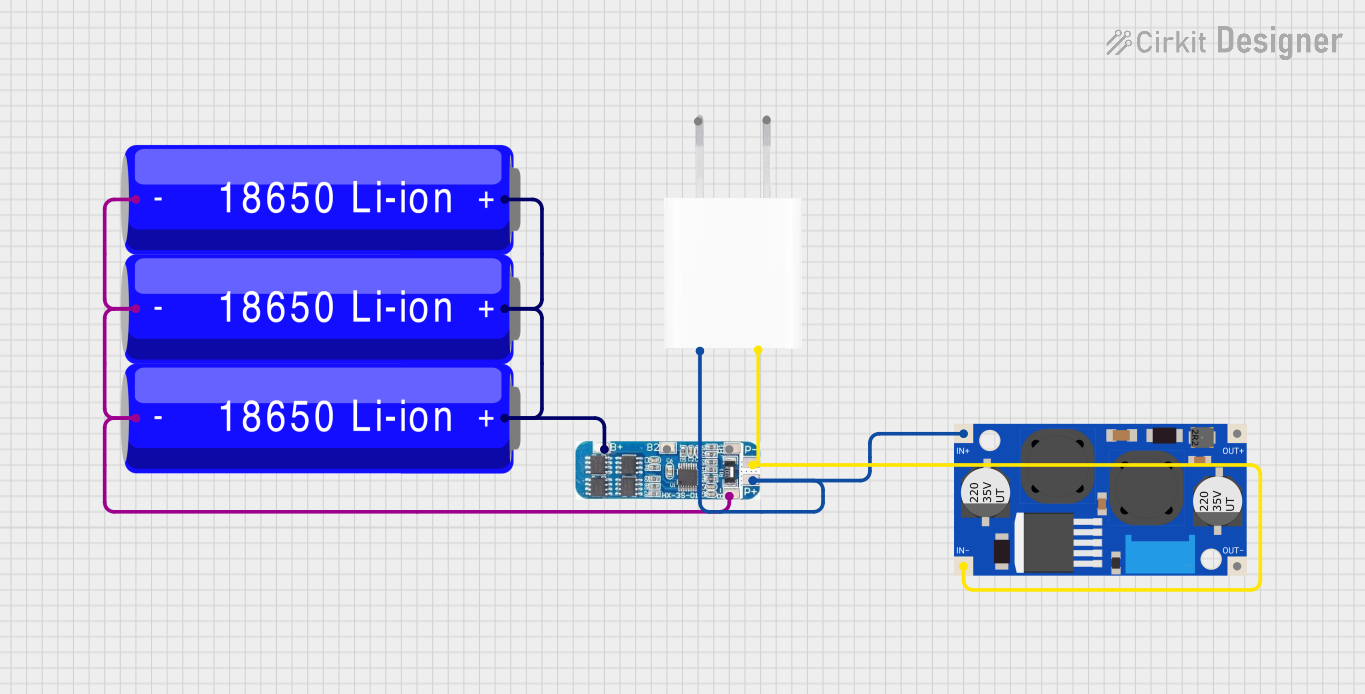
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BMS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs)
- Renewable energy storage systems (e.g., solar and wind power)
- Consumer electronics (e.g., laptops, smartphones, power banks)
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Industrial and medical equipment requiring battery backup
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Manufacturer: BMS
- Part ID: BMS
- Input Voltage Range: 3.7V to 60V (depending on battery configuration)
- Supported Battery Types: Lithium-ion (Li-ion), Lithium Polymer (LiPo), Lead-acid, etc.
- Cell Configuration: 1S to 16S (1 to 16 cells in series)
- Overcharge Protection Voltage: Configurable (e.g., 4.2V per cell for Li-ion)
- Over-discharge Protection Voltage: Configurable (e.g., 2.5V per cell for Li-ion)
- Maximum Discharge Current: 10A to 200A (varies by model)
- Temperature Monitoring: -40°C to 85°C
- Communication Protocols: I2C, UART, CAN (varies by model)
- Balancing Method: Passive or active cell balancing
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration may vary depending on the specific BMS model. Below is a general example for a typical BMS:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| B+ | Battery positive terminal |
| B- | Battery negative terminal |
| P+ | Load/charger positive terminal |
| P- | Load/charger negative terminal |
| C+ | Charger positive terminal (if separate from P+) |
| C- | Charger negative terminal (if separate from P-) |
| T1, T2 | Temperature sensor inputs |
| BAL1, BAL2… | Balancing pins for individual cells (e.g., BAL1 for Cell 1, BAL2 for Cell 2) |
| COMM | Communication interface (e.g., I2C, UART, or CAN) |
| GND | Ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Battery Pack:
- Connect the battery pack's positive terminal to the B+ pin and the negative terminal to the B- pin.
- Ensure the battery pack matches the BMS's supported cell configuration (e.g., 4S for 4 cells in series).
Connect the Load and Charger:
- Connect the load's positive and negative terminals to P+ and P-, respectively.
- If the charger has separate terminals, connect them to C+ and C-.
Temperature Sensors:
- Attach the temperature sensors (e.g., thermistors) to the T1 and T2 pins.
- Place the sensors near the battery cells for accurate temperature monitoring.
Balancing Connections:
- For each cell in the battery pack, connect the balancing wires to the corresponding BAL pins (e.g., BAL1 for Cell 1).
Communication Interface:
- If the BMS supports communication, connect the COMM pin to a microcontroller or monitoring system (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the BMS is compatible with the battery chemistry and configuration.
- Wiring: Use appropriate wire gauges to handle the maximum current without overheating.
- Cooling: Provide adequate cooling for high-current applications to prevent overheating.
- Firmware Configuration: If the BMS has configurable settings, use the manufacturer's software to set parameters like overcharge/over-discharge thresholds.
- Testing: Test the BMS with a small load before full-scale deployment to verify proper operation.
Example: Connecting a BMS to an Arduino UNO
If the BMS supports I2C communication, you can use the following Arduino code to read battery data:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define BMS_I2C_ADDRESS 0x10 // Replace with the BMS's I2C address
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication for debugging
Serial.println("BMS Communication Initialized");
}
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(BMS_I2C_ADDRESS); // Start communication with BMS
Wire.write(0x01); // Request battery voltage (example command)
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10); // Wait for the BMS to process the request
Wire.requestFrom(BMS_I2C_ADDRESS, 2); // Request 2 bytes of data
if (Wire.available() == 2) {
int voltage = Wire.read() << 8 | Wire.read(); // Combine two bytes into an integer
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage / 1000.0); // Convert millivolts to volts
Serial.println(" V");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read data from BMS");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
BMS Not Powering On:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient battery voltage.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the battery voltage is within the BMS's operating range.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current or poor cooling.
- Solution: Use a heatsink or fan for cooling and ensure the load does not exceed the BMS's current rating.
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Charger not connected properly or overcharge protection activated.
- Solution: Verify charger connections and check the BMS's overcharge settings.
Communication Failure:
- Cause: Incorrect I2C address or wiring.
- Solution: Confirm the BMS's I2C address and ensure proper SDA/SCL connections.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the BMS with a different battery chemistry?
- A: Only if the BMS supports that chemistry. Check the manufacturer's specifications.
Q: How do I reset the BMS after a fault?
- A: Disconnect the load and charger, then reconnect the battery to reset the system.
Q: Does the BMS support active cell balancing?
- A: Some models do. Refer to the technical specifications for details.
Q: Can I monitor the battery remotely?
- A: Yes, if the BMS supports communication protocols like CAN or UART, you can integrate it with a monitoring system.