
How to Use PIXHAWK 2.4.8 DRONE CONTROLLER: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with PIXHAWK 2.4.8 DRONE CONTROLLER in Cirkit Designer
Design with PIXHAWK 2.4.8 DRONE CONTROLLER in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PIXHAWK 2.4.8 Drone Controller is a versatile and powerful flight control hardware designed for drones and UAVs. It features advanced autopilot capabilities, support for a wide range of sensors, and compatibility with multiple software platforms such as PX4 and ArduPilot. This controller is widely used in both hobbyist and professional drone applications due to its reliability, flexibility, and robust performance.
Explore Projects Built with PIXHAWK 2.4.8 DRONE CONTROLLER
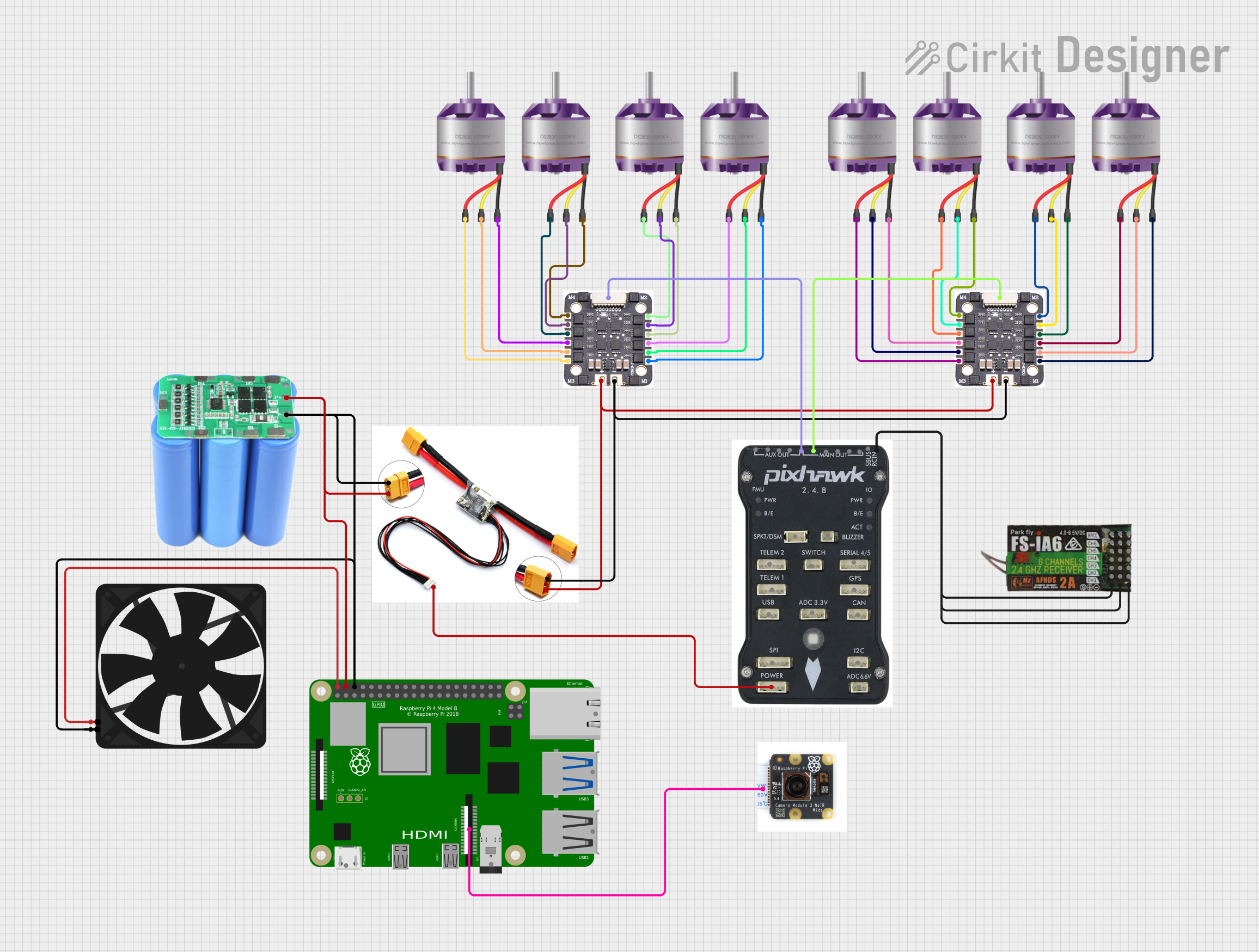
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer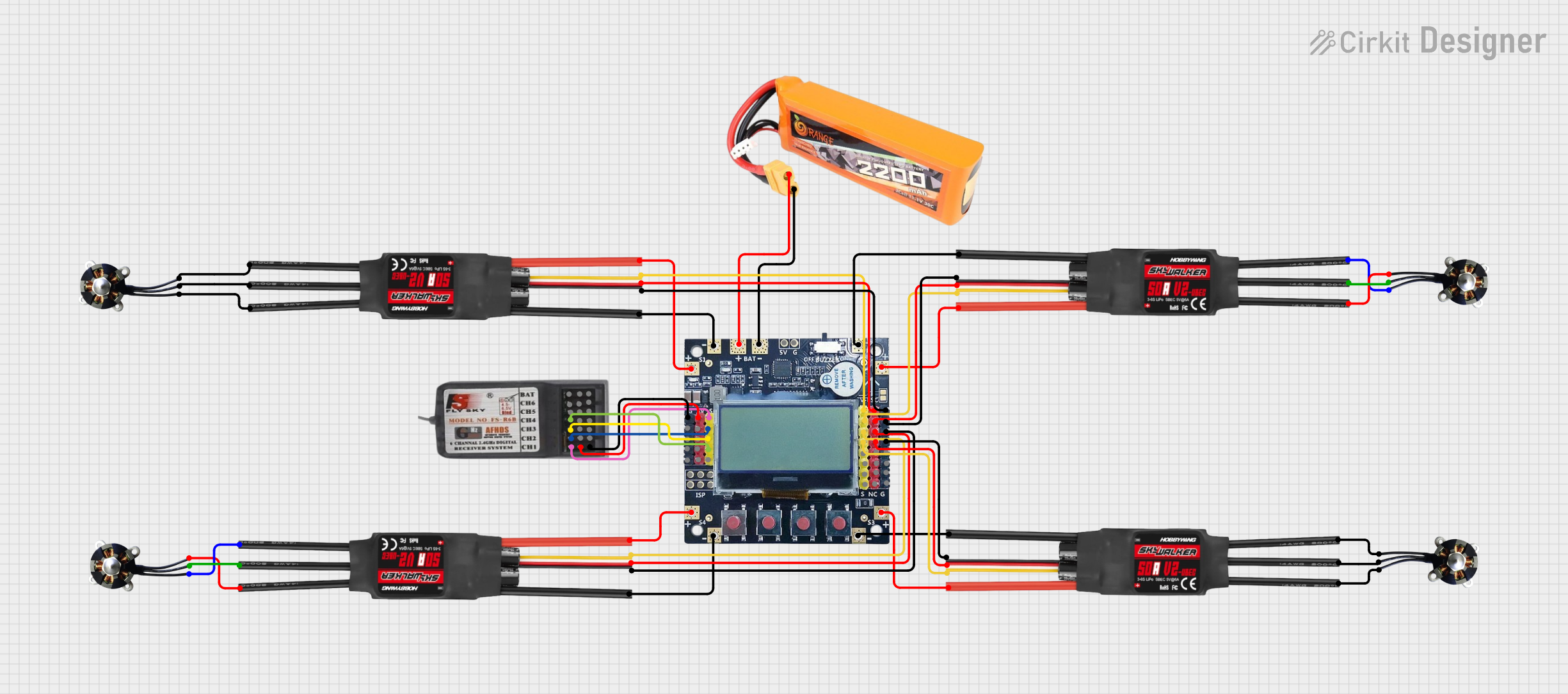
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer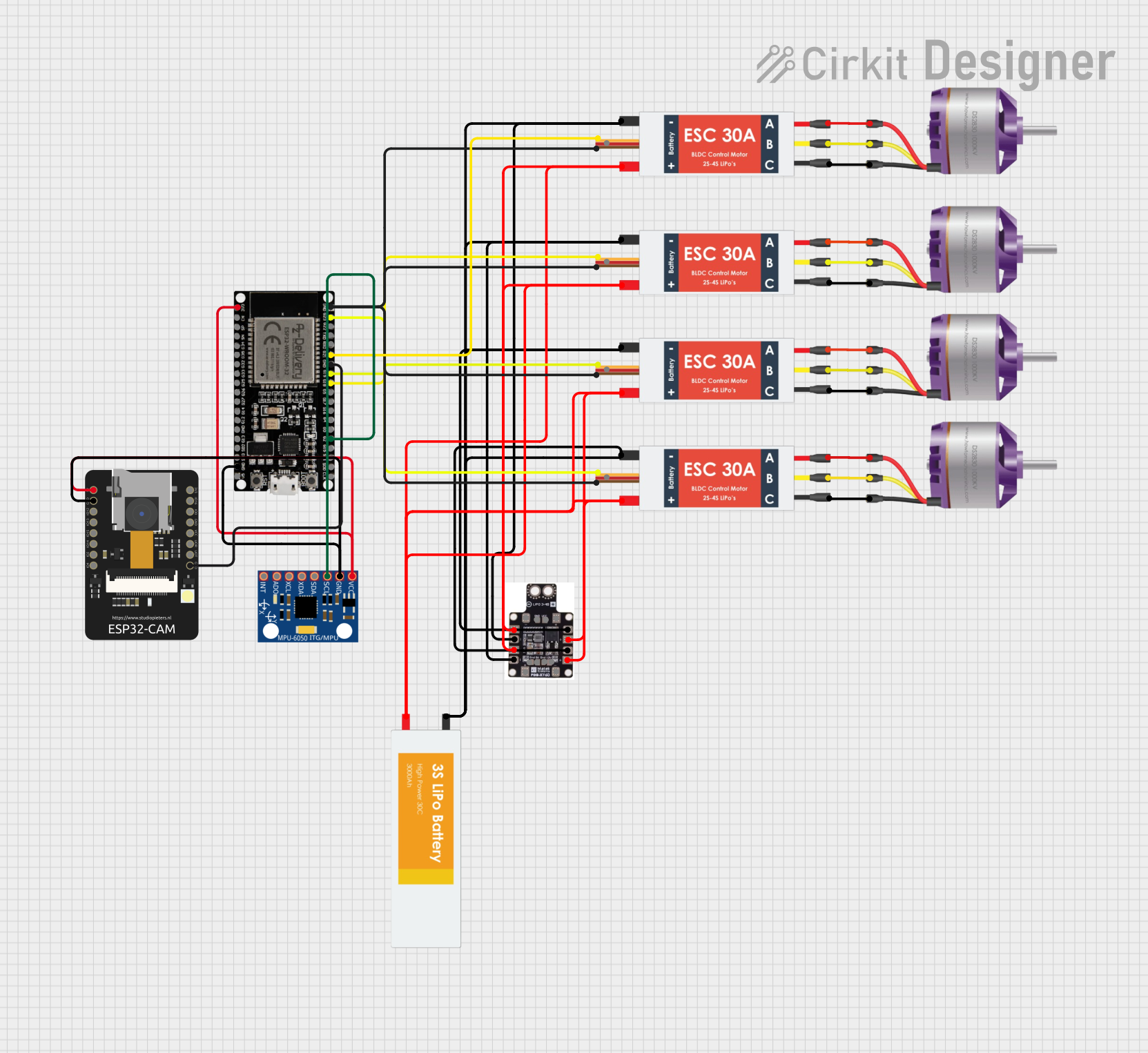
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PIXHAWK 2.4.8 DRONE CONTROLLER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Autonomous drone navigation and control
- Aerial photography and videography
- Agricultural monitoring and surveying
- Search and rescue operations
- Research and development of UAV systems
- Industrial inspections and mapping
Technical Specifications
The PIXHAWK 2.4.8 is equipped with high-performance hardware and a variety of interfaces to support complex drone operations. Below are the key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Processor: 32-bit STM32F427 Cortex-M4, 168 MHz, with FPU
- IMU Sensors:
- MPU6000 (3-axis accelerometer and gyroscope)
- LSM303D (3-axis magnetometer)
- MS5611 (barometer)
- Flash Memory: 2 MB
- RAM: 256 KB
- Input Voltage: 4.8V to 5.4V
- Power Consumption: ~280 mA at 5V
- Interfaces:
- 14 PWM/Servo outputs
- 5 UART ports
- I2C, SPI, CAN, and ADC ports
- Dimensions: 81.5 mm x 50 mm x 15.5 mm
- Weight: ~38 grams
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PIXHAWK 2.4.8 features multiple connectors for peripherals and power. Below is a summary of the key pin configurations:
Power Input
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Power (+) | Positive voltage input (4.8V-5.4V) |
| Power (-) | Ground connection |
PWM/Servo Outputs
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PWM1 - PWM14 | Outputs for motor ESCs or servos |
| GND | Ground connection |
Communication Ports
| Port Name | Description |
|---|---|
| UART1 - UART5 | Serial communication ports |
| I2C | Interface for external sensors |
| SPI | High-speed sensor interface |
| CAN | Communication for UAVCAN devices |
Auxiliary Ports
| Port Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter inputs |
| GPS | GPS module connection |
| Telemetry 1/2 | Telemetry data transmission |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the PIXHAWK 2.4.8 in a Circuit
Powering the Controller:
- Connect a power module to the power input pins. Ensure the voltage is within the range of 4.8V to 5.4V.
- Alternatively, power the controller via USB for configuration purposes.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Attach ESCs or servos to the PWM output pins.
- Connect sensors (e.g., GPS, barometer, or magnetometer) to the appropriate ports (I2C, SPI, or UART).
Software Setup:
- Install a compatible flight control software such as PX4 or ArduPilot.
- Use a ground control station (e.g., QGroundControl or Mission Planner) to configure the controller.
Calibrating Sensors:
- Perform sensor calibration (e.g., accelerometer, gyroscope, and compass) using the ground control software.
- Follow the on-screen instructions for proper calibration.
Testing:
- Conduct a pre-flight check to ensure all connections are secure and the system is functioning correctly.
- Test motor outputs and verify sensor readings before flight.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a stable power source to avoid voltage fluctuations that may affect performance.
- Ensure proper vibration damping for the controller to improve sensor accuracy.
- Regularly update the firmware to benefit from the latest features and bug fixes.
- Use a GPS module with a built-in compass for better navigation accuracy.
- Perform a failsafe configuration to handle communication loss or low battery scenarios.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The PIXHAWK 2.4.8 can communicate with an Arduino UNO via UART. Below is an example code snippet for reading telemetry data:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for communication with PIXHAWK
SoftwareSerial pixhawkSerial(10, 11); // RX = pin 10, TX = pin 11
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging via Serial Monitor
pixhawkSerial.begin(57600); // Communication with PIXHAWK
Serial.println("Starting communication with PIXHAWK...");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from PIXHAWK
if (pixhawkSerial.available()) {
// Read and print data from PIXHAWK
char data = pixhawkSerial.read();
Serial.print(data);
}
}
Note: Ensure the UART port on the PIXHAWK is configured for telemetry output.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: The controller does not power on.
- Solution: Verify the power module connection and ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (4.8V-5.4V).
Issue: Motors do not respond to commands.
- Solution: Check the PWM connections and ensure the ESCs are properly calibrated. Verify motor outputs in the ground control software.
Issue: GPS module is not detected.
- Solution: Ensure the GPS is connected to the correct port and the wiring is secure. Check the software configuration for GPS settings.
Issue: Unstable flight or poor performance.
- Solution: Perform sensor calibration and ensure proper vibration isolation. Verify the PID tuning parameters in the flight control software.
FAQs
Q: Can the PIXHAWK 2.4.8 be used with fixed-wing aircraft?
- A: Yes, the controller supports fixed-wing, multirotor, and VTOL configurations.
Q: What software platforms are compatible with the PIXHAWK 2.4.8?
- A: The controller is compatible with PX4, ArduPilot, and other open-source autopilot software.
Q: How do I update the firmware?
- A: Use a ground control station like QGroundControl or Mission Planner to download and install the latest firmware.
Q: Is the PIXHAWK 2.4.8 waterproof?
- A: No, the controller is not waterproof. Use a protective enclosure for outdoor applications in wet conditions.