
How to Use SBUS Reciever: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
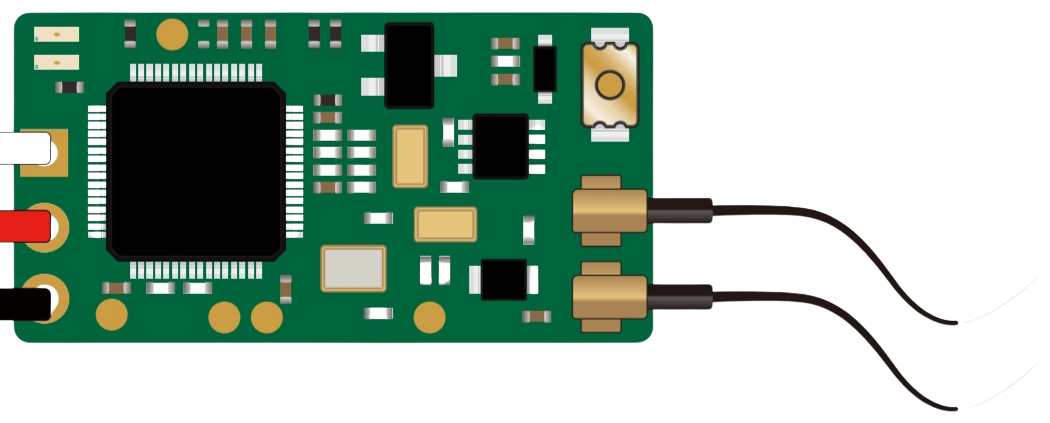
 Design with SBUS Reciever in Cirkit Designer
Design with SBUS Reciever in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SBUS Receiver is a device designed to receive signals from a transmitter using the SBUS protocol. This protocol is widely used in remote control systems for model aircraft, drones, and other RC (radio-controlled) applications. The SBUS protocol allows for the transmission of multiple control channels (up to 16 or more) over a single signal wire, providing low-latency communication and efficient use of resources.
Explore Projects Built with SBUS Reciever
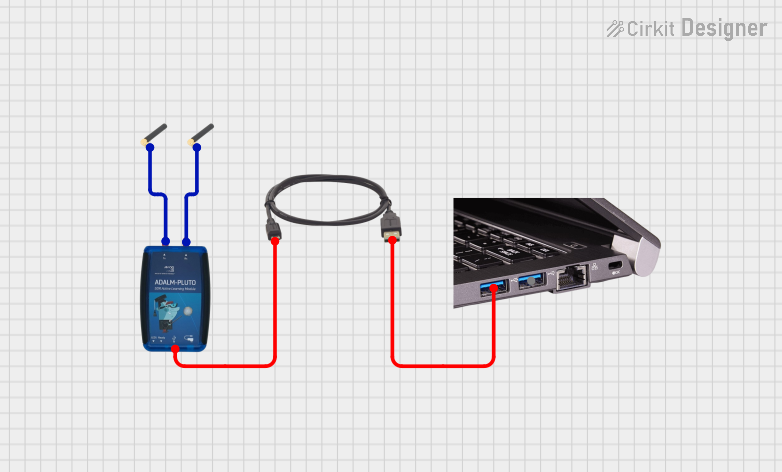
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer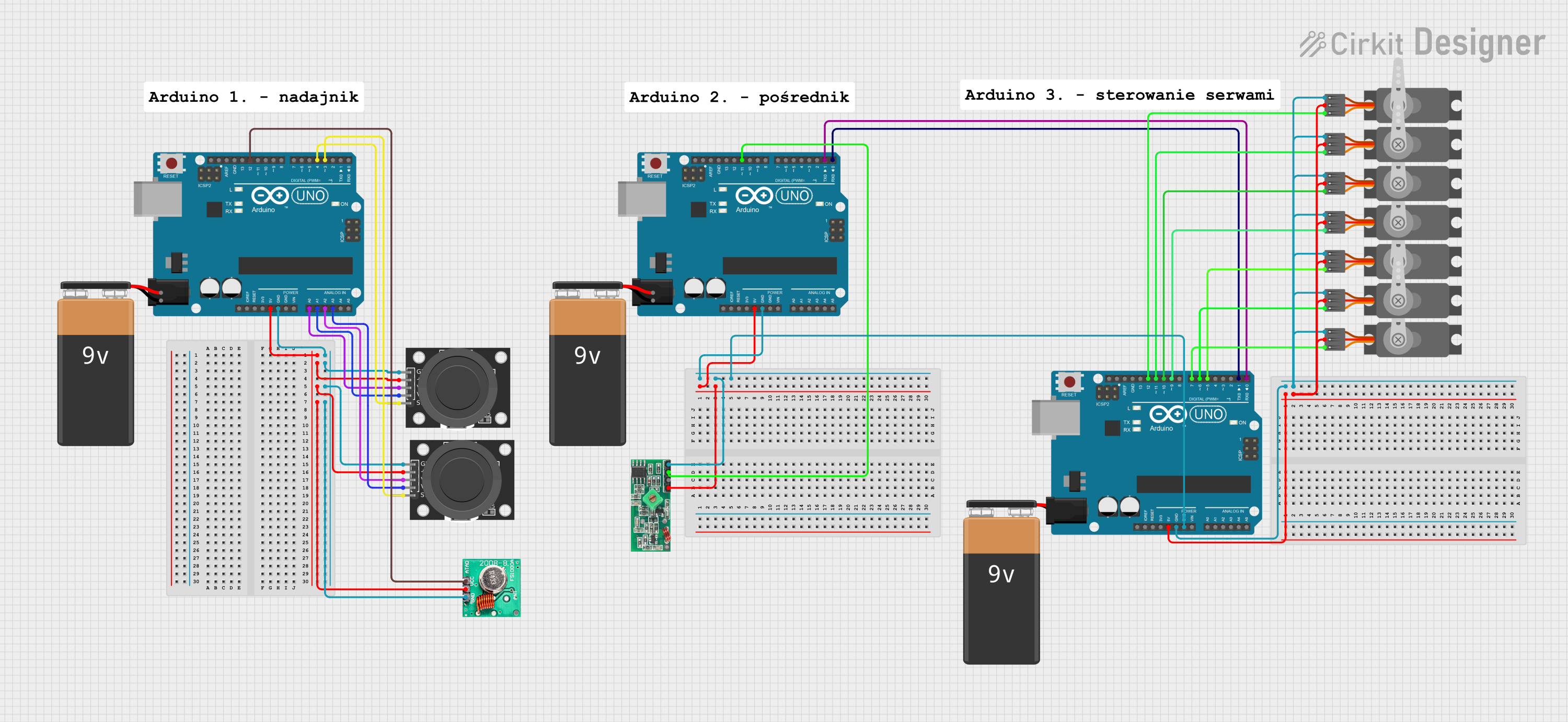
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer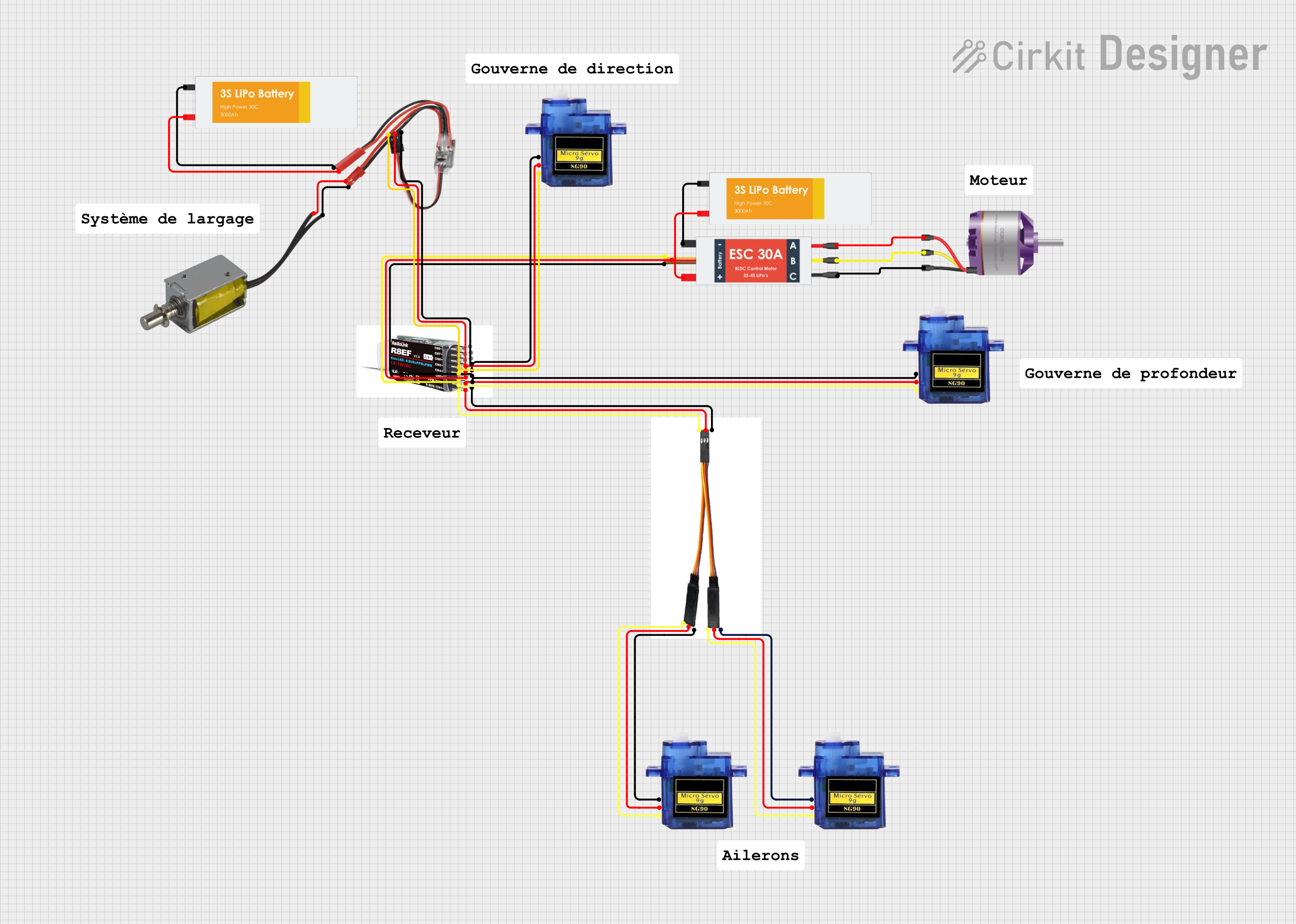
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SBUS Reciever

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Remote control of drones, quadcopters, and RC planes
- Model cars and boats
- Robotics and automation systems requiring multi-channel control
- Integration with flight controllers and microcontrollers for advanced control systems
Technical Specifications
The SBUS Receiver is designed to work seamlessly with SBUS-compatible transmitters and flight controllers. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Protocol | SBUS |
| Number of Channels | Up to 16 |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5.0V |
| Signal Output | Inverted Serial (UART) |
| Communication Speed | 100,000 baud (fixed) |
| Latency | ~3ms |
| Connector Type | 3-pin (Signal, VCC, GND) |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 25x15mm) |
| Weight | Typically <10g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Signal | SBUS signal output (inverted UART) |
| VCC | Power input (3.3V to 5.0V) |
| GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the SBUS Receiver in a Circuit
Connect the Receiver to a Power Source:
- Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5.0V power source. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the
Connect the Signal Pin:
- Connect the
Signalpin to the SBUS input of your flight controller or microcontroller. - Ensure that the microcontroller or flight controller supports inverted UART signals. If not, use an inverter circuit or software-based signal inversion.
- Connect the
Bind the Receiver to the Transmitter:
- Follow the specific binding procedure for your SBUS receiver and transmitter. This typically involves pressing a bind button on the receiver while powering it on.
Configure the Flight Controller or Microcontroller:
- Set the communication protocol to SBUS in your flight controller or microcontroller software.
- Ensure the baud rate is set to 100,000.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Signal Inversion: SBUS uses an inverted UART signal. If your microcontroller does not support inverted signals, you may need to use a hardware inverter or configure software-based inversion.
- Power Supply: Ensure the receiver is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5.0V). Exceeding this range may damage the receiver.
- Antenna Placement: For optimal signal reception, position the receiver's antenna away from sources of interference, such as motors or ESCs (Electronic Speed Controllers).
- Failsafe Configuration: Configure the failsafe settings on your transmitter to ensure safe operation in case of signal loss.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
To use the SBUS Receiver with an Arduino UNO, you will need to invert the SBUS signal. This can be done using a hardware inverter or by modifying the Arduino's UART library. Below is an example code snippet for reading SBUS data:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define the SBUS signal pin
#define SBUS_PIN 10
// Create a SoftwareSerial object for SBUS communication
SoftwareSerial sbusSerial(SBUS_PIN, -1); // RX pin, no TX pin
void setup() {
// Initialize the serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize the SBUS communication at 100,000 baud
sbusSerial.begin(100000);
Serial.println("SBUS Receiver Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the SBUS receiver
if (sbusSerial.available()) {
// Read and print the incoming SBUS data
uint8_t sbusData = sbusSerial.read();
Serial.print("SBUS Data: ");
Serial.println(sbusData, HEX);
}
}
Note: The above code assumes the use of a hardware inverter for the SBUS signal. If you are using a software-based inversion library, modify the code accordingly.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Signal from the Receiver:
- Ensure the receiver is properly bound to the transmitter.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.3V to 5.0V).
- Check the signal connection and ensure it is connected to the correct pin on the flight controller or microcontroller.
Data Corruption or Unreadable Data:
- Confirm that the baud rate is set to 100,000 in your microcontroller or flight controller software.
- Ensure the SBUS signal is properly inverted if required by your hardware.
Intermittent Signal Loss:
- Check the antenna placement and ensure it is not obstructed or too close to sources of interference.
- Verify that the transmitter and receiver are within the specified range.
Failsafe Not Working:
- Configure the failsafe settings on your transmitter to ensure proper behavior in case of signal loss.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the SBUS Receiver with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the SBUS Receiver operates within a voltage range of 3.3V to 5.0V, making it compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers.
Q: Do I need a hardware inverter for the SBUS signal?
A: It depends on your microcontroller. Some microcontrollers support inverted UART signals natively, while others require a hardware inverter or software-based inversion.
Q: How many channels can the SBUS Receiver handle?
A: The SBUS protocol supports up to 16 channels, with some receivers offering additional channels for telemetry or auxiliary functions.
Q: Can I use the SBUS Receiver with non-SBUS transmitters?
A: No, the SBUS Receiver is specifically designed to work with SBUS-compatible transmitters.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot the SBUS Receiver in your projects.