
How to Use 75HC165: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 75HC165 in Cirkit Designer
Design with 75HC165 in Cirkit Designer75HC165 Shift Register Documentation
1. Introduction
The 75HC165 is an 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register designed for digital data storage and manipulation. It enables the serial input of data and outputs the data in parallel format, making it a versatile component in digital electronics. This shift register is commonly used in applications where multiple digital inputs need to be read using fewer microcontroller pins, such as in microcontroller-based projects, data acquisition systems, and digital signal processing.
Common Applications:
- Expanding the number of input pins for microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Reading multiple switches or sensors
- Digital data storage and transfer
- Keypad or button matrix interfacing
- LED or display control
2. Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 75HC165:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2V to 6V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to Vcc |
| Maximum Clock Frequency | 25 MHz (at 4.5V to 5.5V Vcc) |
| Output Current (per pin) | ±6 mA |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Propagation Delay | ~20 ns (at 5V Vcc) |
| Package Types | DIP-16, SOIC-16, TSSOP-16 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 75HC165 has 16 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q7 |
Serial data output (most significant bit of the shift register). |
| 2 | CLK |
Clock input. Data is shifted on the rising edge of the clock signal. |
| 3 | CLK INH |
Clock inhibit. When HIGH, the clock is disabled, and no shifting occurs. |
| 4 | SH/LD |
Shift/Load control. LOW = Load parallel data; HIGH = Shift data. |
| 5-12 | D0-D7 |
Parallel data inputs (D0 = LSB, D7 = MSB). |
| 13 | Q7’ |
Complementary serial data output (inverted Q7). |
| 14 | SER |
Serial data input. |
| 15 | Vcc |
Positive power supply. |
| 16 | GND |
Ground (0V reference). |
3. Usage Instructions
Connecting the 75HC165 to a Microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO)
The 75HC165 can be used to read multiple digital inputs using only a few pins on a microcontroller. Below is a step-by-step guide to using the component:
Wiring the Component:
- Connect
Vccto the 5V pin of the microcontroller. - Connect
GNDto the ground pin of the microcontroller. - Connect the
Q7pin to a digital input pin on the microcontroller (e.g.,D8on Arduino). - Connect the
CLKpin to a digital output pin on the microcontroller (e.g.,D9on Arduino). - Connect the
SH/LDpin to another digital output pin (e.g.,D10on Arduino). - Optionally, connect the
SERpin to a serial data source if cascading multiple shift registers.
- Connect
Loading and Shifting Data:
- Set the
SH/LDpin LOW to load parallel data fromD0-D7into the shift register. - Set the
SH/LDpin HIGH to enable shifting mode. - Pulse the
CLKpin HIGH and then LOW to shift data serially out of theQ7pin.
- Set the
Best Practices:
- Use pull-up or pull-down resistors on the
D0-D7inputs to ensure stable logic levels. - Avoid exceeding the maximum clock frequency to prevent data corruption.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
- Use pull-up or pull-down resistors on the
4. Example Arduino Code
The following example demonstrates how to use the 75HC165 with an Arduino UNO to read 8 digital inputs:
// Pin definitions
const int dataPin = 8; // Q7 pin connected to Arduino D8
const int clockPin = 9; // CLK pin connected to Arduino D9
const int latchPin = 10; // SH/LD pin connected to Arduino D10
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set pin modes
pinMode(dataPin, INPUT);
pinMode(clockPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(latchPin, OUTPUT);
// Initialize pins
digitalWrite(clockPin, LOW);
digitalWrite(latchPin, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
// Load parallel data into the shift register
digitalWrite(latchPin, LOW); // Set SH/LD to LOW to load data
delayMicroseconds(5); // Small delay for stability
digitalWrite(latchPin, HIGH); // Set SH/LD to HIGH to enable shifting
// Read data serially from Q7
byte inputData = shiftIn(dataPin, clockPin, MSBFIRST);
// Print the binary representation of the input data
Serial.print("Input Data: ");
Serial.println(inputData, BIN);
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next read
}
Code Explanation:
- The
latchPin(connected toSH/LD) is toggled LOW to load parallel data into the shift register and then set HIGH to enable shifting. - The
shiftIn()function reads 8 bits of data serially from thedataPin(connected toQ7), with the most significant bit (MSB) first. - The binary representation of the input data is printed to the Serial Monitor.
5. Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
No data is being read from the Q7 pin |
Incorrect wiring or loose connections | Double-check all connections and ensure proper wiring. |
| Data appears corrupted or unstable | Clock signal is noisy or too fast | Use a stable clock source and reduce the clock frequency if necessary. |
| Shift register does not respond | SH/LD pin is not toggled correctly |
Ensure the SH/LD pin is set LOW to load data and HIGH to enable shifting. |
| Incorrect data is read | Floating inputs on D0-D7 pins |
Use pull-up or pull-down resistors on the D0-D7 pins. |
FAQs
Can I cascade multiple 75HC165 shift registers? Yes, you can cascade multiple shift registers by connecting the
Q7pin of one register to theSERpin of the next. This allows you to read more inputs using the same clock and latch pins.What is the maximum number of shift registers I can cascade? Theoretically, there is no limit, but practical constraints such as signal integrity and timing delays may limit the number.
Can the 75HC165 be used with 3.3V microcontrollers? Yes, the 75HC165 operates with a supply voltage as low as 2V, making it compatible with 3.3V systems.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, using, and troubleshooting the 75HC165 shift register. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will help you integrate the component into your projects effectively.
Explore Projects Built with 75HC165
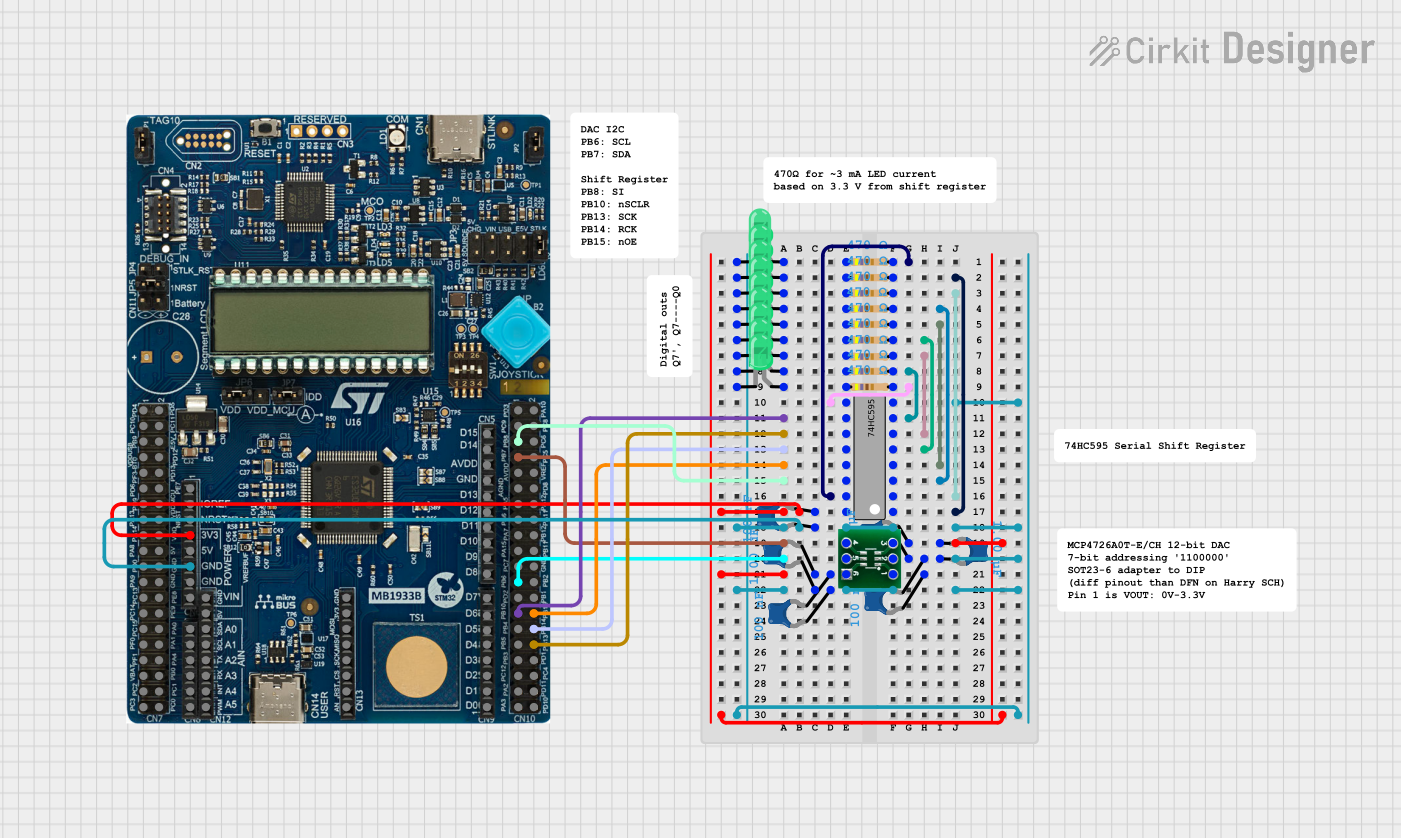
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer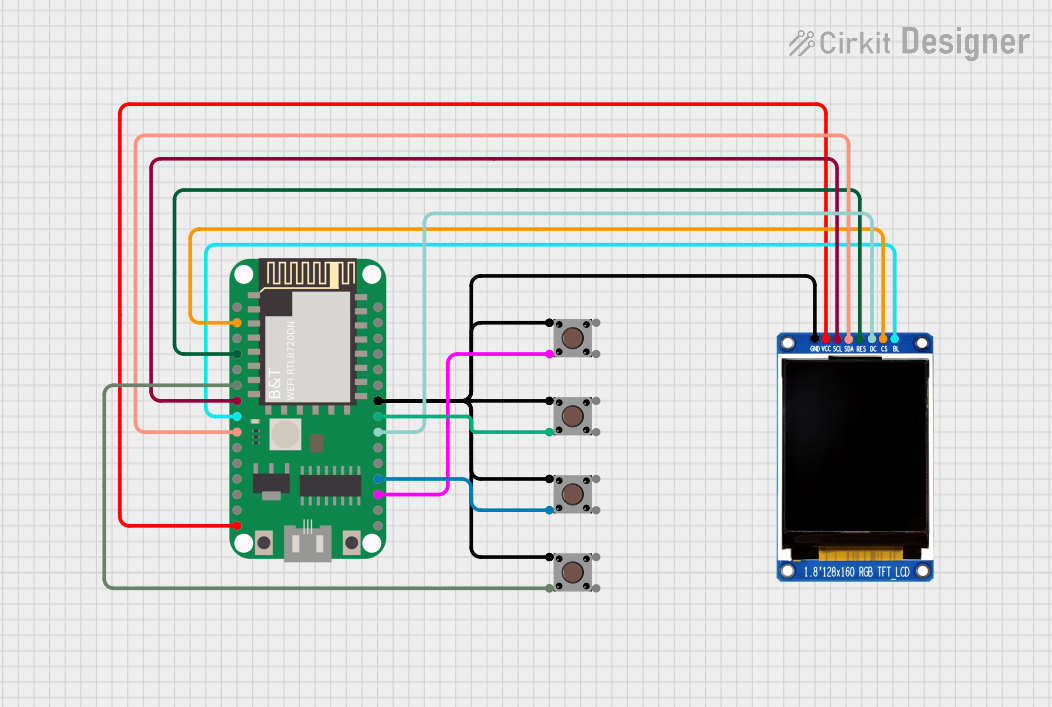
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer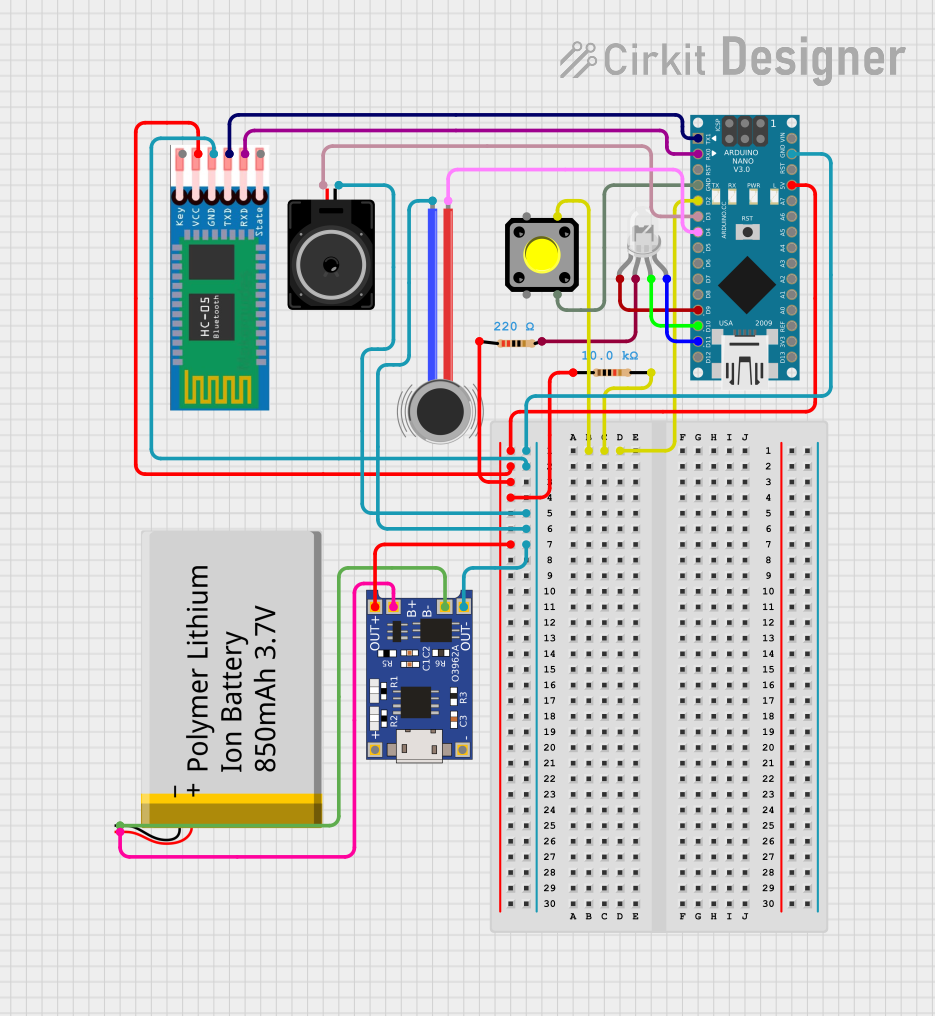
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer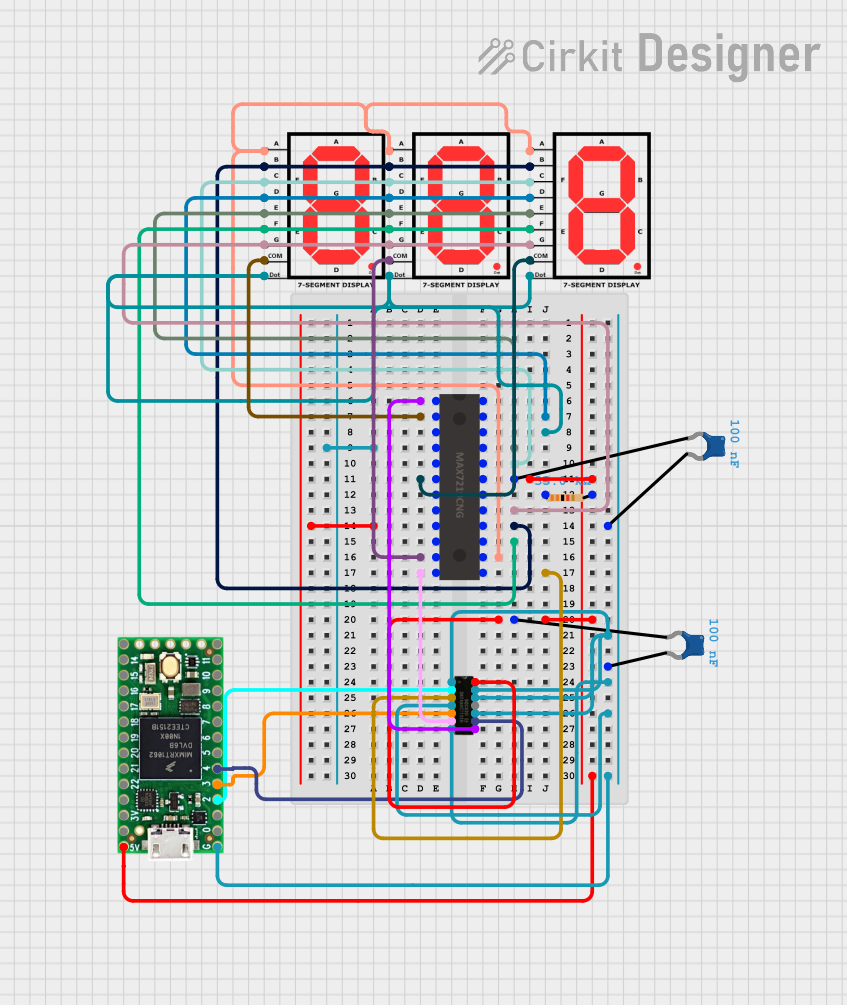
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 75HC165

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer