
How to Use CAN Transceiver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with CAN Transceiver in Cirkit Designer
Design with CAN Transceiver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MCP2551 is a high-speed CAN transceiver manufactured by Microchip. It serves as the interface between a CAN protocol controller and the physical CAN bus, enabling robust communication in automotive, industrial, and embedded systems. The MCP2551 converts the digital signals from the CAN controller into differential signals for the CAN bus and vice versa, ensuring reliable data transmission even in electrically noisy environments.
Explore Projects Built with CAN Transceiver
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with CAN Transceiver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive systems (e.g., engine control units, body control modules)
- Industrial automation and control
- Medical equipment
- Building automation
- Robotics and embedded systems requiring CAN communication
Technical Specifications
The MCP2551 is designed to meet the physical layer requirements of the ISO 11898 standard. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 4.5V to 5.5V
- Maximum Data Rate: 1 Mbps
- Bus Voltage Range: -7V to +12V
- Standby Current: 275 µA (typical)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
- ESD Protection: ±4 kV (Human Body Model)
- Short-Circuit Protection: Yes
- Thermal Shutdown Protection: Yes
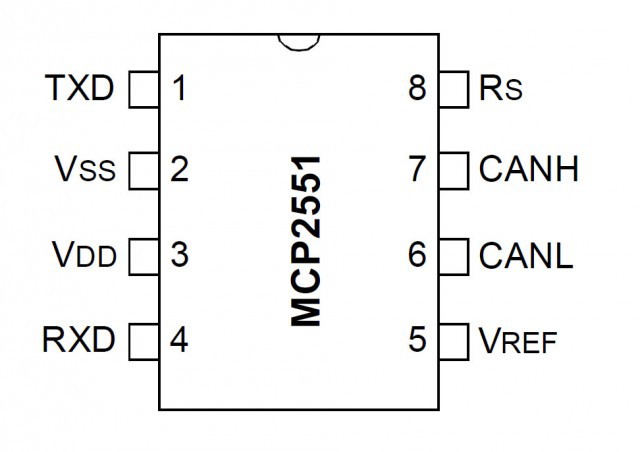
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MCP2551 is an 8-pin device with the following pinout:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TXD | Transmit Data Input: Connects to the CAN controller's transmit output. |
| 2 | Vss | Ground: Connect to the system ground. |
| 3 | Vcc | Supply Voltage: Connect to a 5V power supply. |
| 4 | RXD | Receive Data Output: Outputs the received CAN bus data to the CAN controller. |
| 5 | Vref | Reference Voltage Output: Provides a reference voltage (typically 2.5V). |
| 6 | CANL | CAN Low: Connects to the CAN bus low line. |
| 7 | CANH | CAN High: Connects to the CAN bus high line. |
| 8 | RS | Slope Control Input: Controls the slew rate of the CAN signals. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MCP2551 in a Circuit
Power Supply:
- Connect the Vcc pin to a regulated 5V power supply.
- Connect the Vss pin to the system ground.
CAN Bus Connections:
- Connect the CANH and CANL pins to the CAN bus lines.
- Use a 120-ohm termination resistor between CANH and CANL at each end of the bus.
Controller Interface:
- Connect the TXD pin to the CAN controller's transmit output.
- Connect the RXD pin to the CAN controller's receive input.
Slope Control:
- Use the RS pin to control the slew rate of the CAN signals. For high-speed operation, connect RS to ground. For reduced EMI, connect RS to a resistor to ground.
Reference Voltage:
- The Vref pin provides a 2.5V reference voltage, which can be used for additional circuitry if needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure proper termination of the CAN bus with 120-ohm resistors at both ends to prevent signal reflections.
- Keep the CANH and CANL lines as short and twisted as possible to minimize noise and maintain signal integrity.
- Avoid placing the MCP2551 near high-frequency or high-power components to reduce interference.
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) close to the Vcc pin to stabilize the power supply.
Example: Connecting MCP2551 to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the MCP2551 to an Arduino UNO for CAN communication:
Circuit Connections
- MCP2551 TXD → Arduino Digital Pin 10
- MCP2551 RXD → Arduino Digital Pin 11
- MCP2551 Vcc → Arduino 5V
- MCP2551 Vss → Arduino GND
- MCP2551 CANH → CAN Bus High Line
- MCP2551 CANL → CAN Bus Low Line
- MCP2551 RS → GND (for high-speed operation)
Arduino Code Example
#include <SPI.h>
#include <mcp_can.h>
// Define the SPI CS pin for the MCP2515 CAN controller
#define CAN_CS_PIN 10
// Initialize the MCP_CAN object
MCP_CAN CAN(CAN_CS_PIN);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
while (!Serial);
// Initialize the CAN bus at 500 kbps
if (CAN.begin(MCP_ANY, CAN_500KBPS, MCP_8MHZ) == CAN_OK) {
Serial.println("CAN bus initialized successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Error initializing CAN bus.");
while (1);
}
// Set the CAN bus to normal mode
CAN.setMode(MCP_NORMAL);
Serial.println("CAN bus set to normal mode.");
}
void loop() {
// Send a test message
byte data[8] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08};
if (CAN.sendMsgBuf(0x100, 0, 8, data) == CAN_OK) {
Serial.println("Message sent successfully!");
} else {
Serial.println("Error sending message.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending the next message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication on the CAN Bus:
- Verify that the CANH and CANL lines are properly connected and terminated with 120-ohm resistors.
- Check the power supply to ensure the MCP2551 is receiving 5V.
High Error Rate:
- Ensure the RS pin is configured correctly for the desired slew rate.
- Minimize the length of the CAN bus and use twisted-pair cables to reduce noise.
Overheating:
- Check for short circuits on the CANH and CANL lines.
- Ensure the MCP2551 is not exposed to excessive ambient temperatures.
Arduino Code Not Working:
- Verify the SPI connections between the Arduino and the MCP2515 CAN controller.
- Ensure the MCP_CAN library is installed and properly configured.
FAQs
Q: Can the MCP2551 operate at 3.3V?
A: No, the MCP2551 requires a supply voltage of 4.5V to 5.5V. For 3.3V systems, consider using a level shifter or a transceiver designed for 3.3V operation.
Q: What is the maximum bus length supported by the MCP2551?
A: The maximum bus length depends on the data rate. For example, at 1 Mbps, the maximum bus length is approximately 40 meters.
Q: Can I use the MCP2551 in a multi-node CAN network?
A: Yes, the MCP2551 supports multi-node networks. Ensure proper termination and node addressing.
Q: How do I reduce EMI in my design?
A: Use the RS pin to control the slew rate of the CAN signals. A higher resistance on the RS pin reduces EMI but may limit the data rate.