
How to Use inverter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with inverter in Cirkit Designer
Design with inverter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Surya SWE Inverter is an electronic component designed to invert the logic state of an input signal. When a high voltage level (logic 1) is applied to its input, it outputs a low voltage level (logic 0), and vice versa. This component is essential in digital circuits for implementing logical NOT operations and is commonly used in applications such as signal conditioning, logic gates, and digital signal processing.
Explore Projects Built with inverter
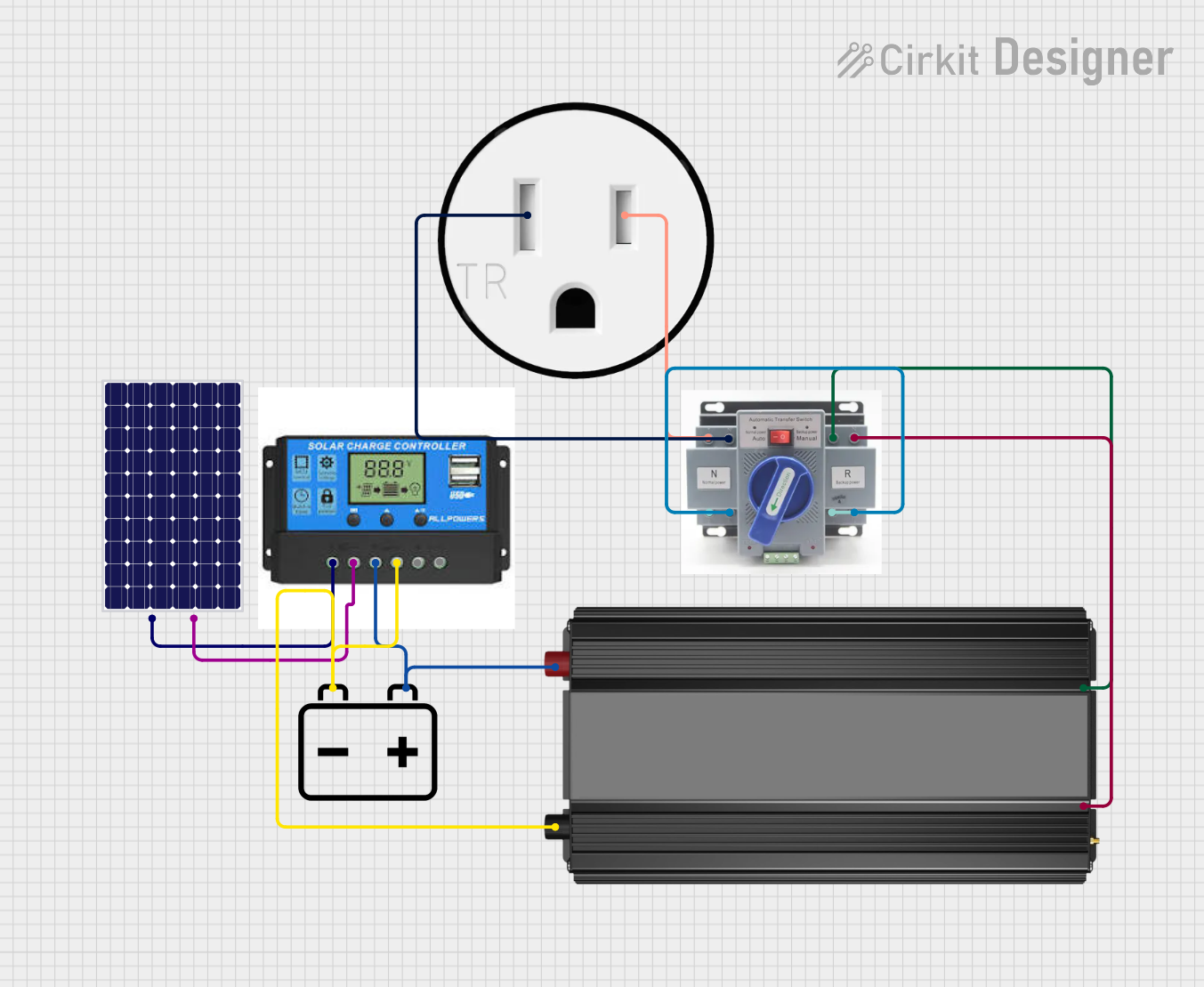
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer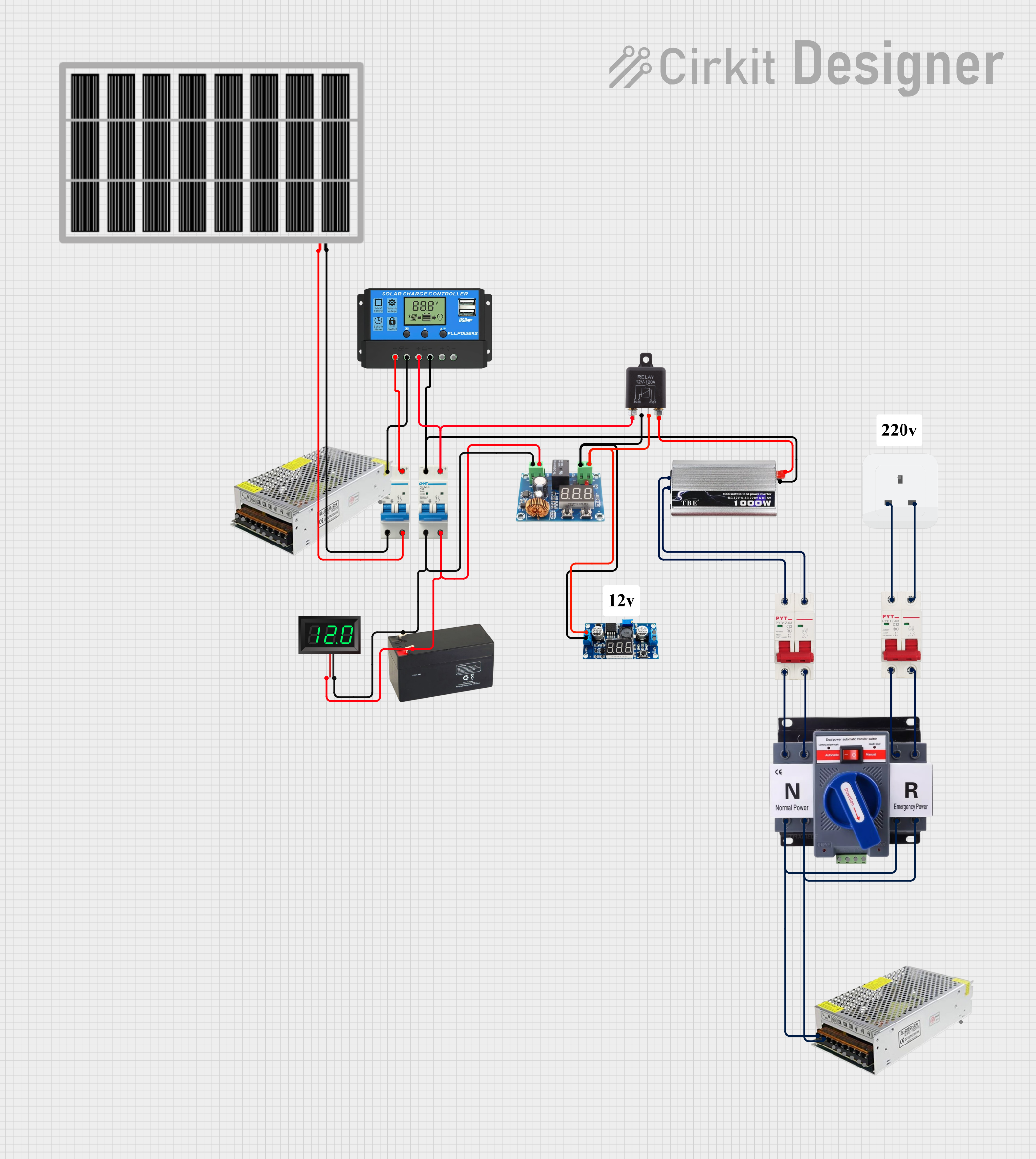
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer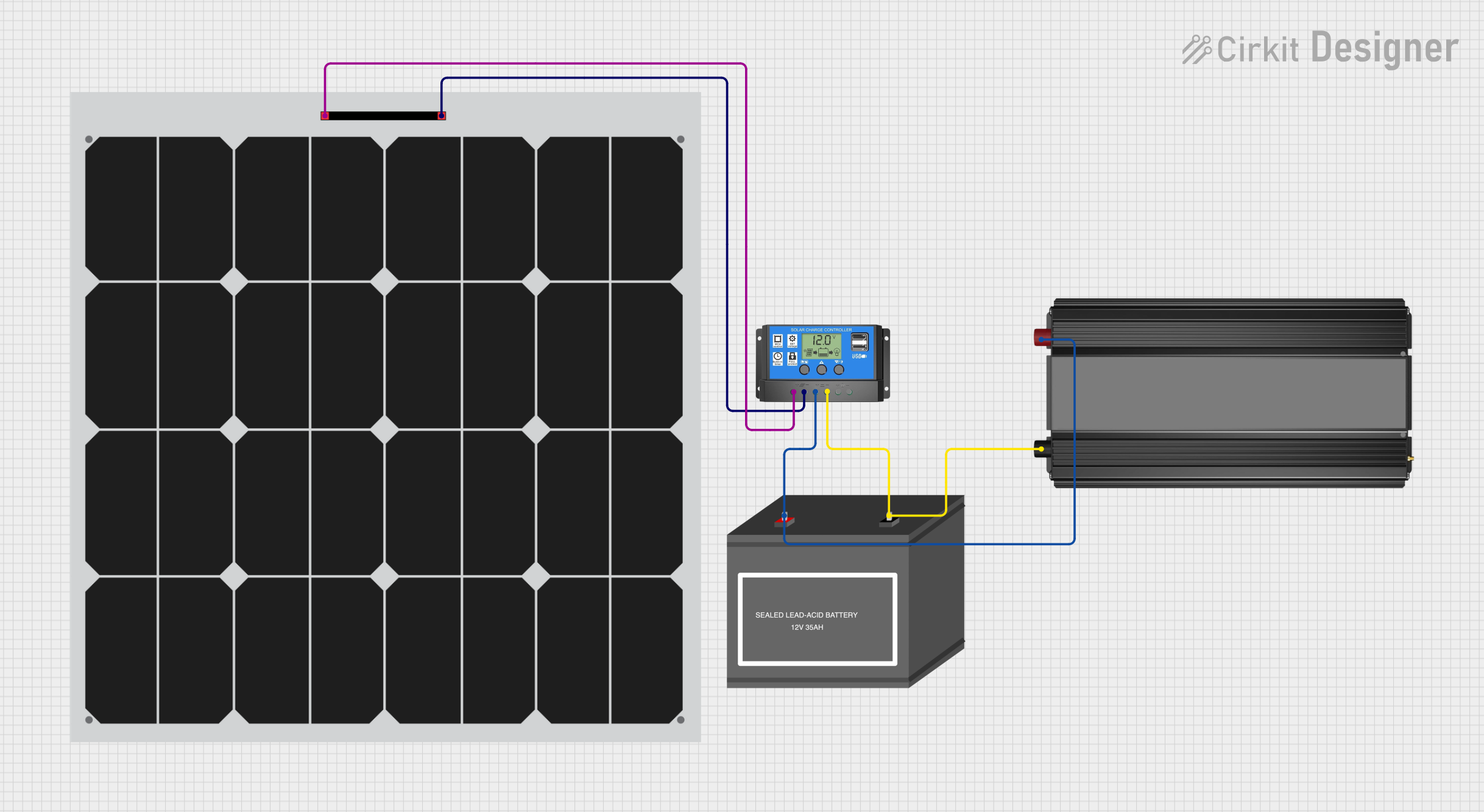
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer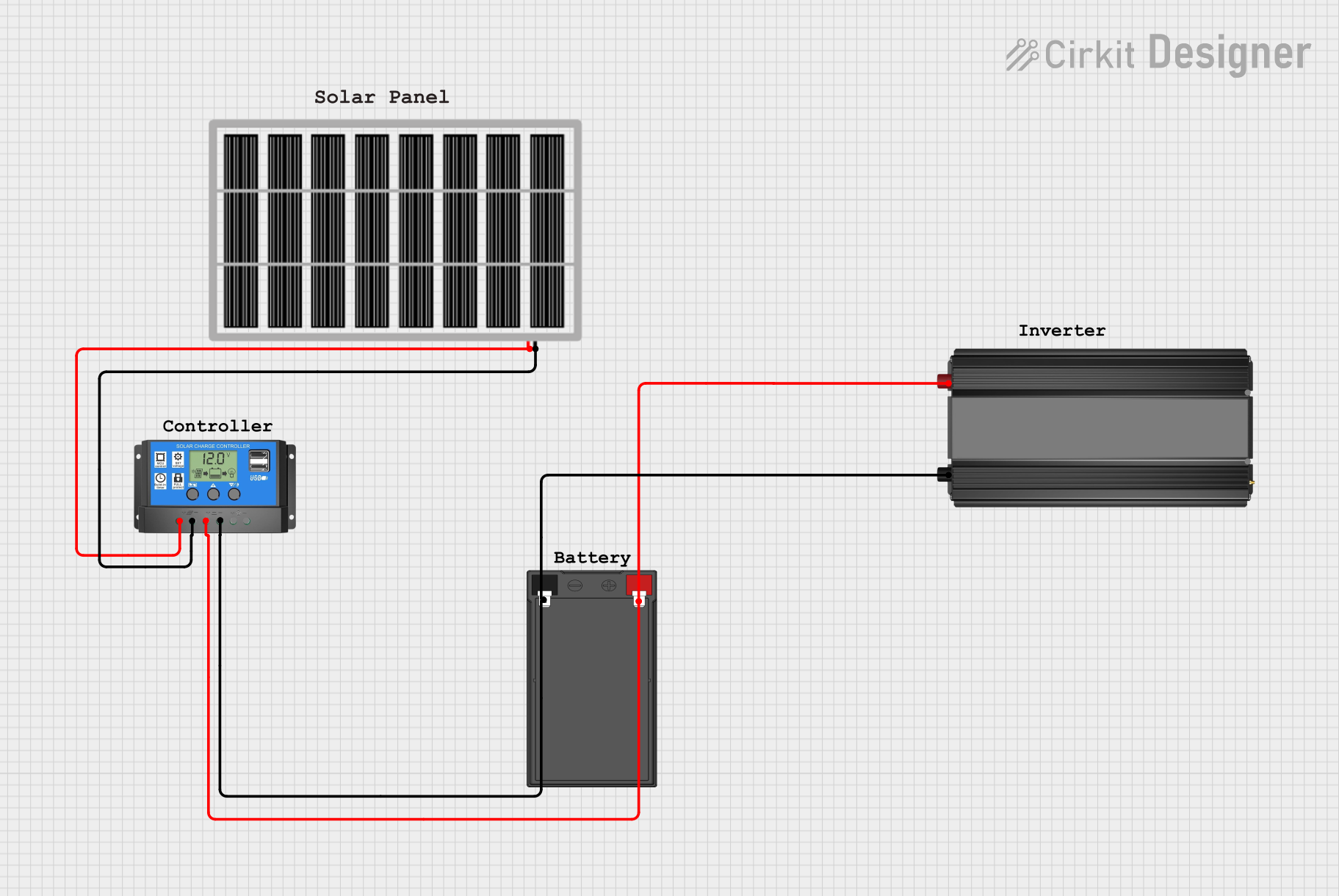
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with inverter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 3.3V to 5V
- Input Voltage (Vin): 0V to Vcc
- Output Voltage (Vout): 0V to Vcc
- High-level Input Voltage (VIH): 2V min (at Vcc = 5V)
- Low-level Input Voltage (VIL): 0.8V max (at Vcc = 5V)
- High-level Output Current (IOH): -4 mA max (source current)
- Low-level Output Current (IOL): 8 mA max (sink current)
- Propagation Delay (tpd): 10 ns typical (at Vcc = 5V)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to 85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V) |
| 2 | IN | Input signal pin |
| 3 | GND | Ground reference for the circuit |
| 4 | OUT | Output signal pin |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Inverter in a Circuit
- Connect the Vcc pin to the positive supply voltage (3.3V to 5V).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power supply.
- Apply the input signal to the IN pin.
- The inverted output can be taken from the OUT pin.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the supply voltage does not exceed the maximum rating to prevent damage.
- The input signal voltage should be within the range of 0V to Vcc.
- Avoid loading the output with a current higher than the specified output current ratings.
- Use bypass capacitors close to the Vcc pin to filter out noise and provide a stable supply.
- Keep the propagation delay in mind when designing high-speed digital circuits.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- No Output Signal: Ensure that the Vcc and GND pins are properly connected and that the supply voltage is within the specified range.
- Weak Output Signal: Check if the output is not overloaded beyond its current sinking/sourcing capability.
- Unexpected Output Behavior: Verify that the input signal voltage levels are within the VIH and VIL specifications.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check the connections and solder joints for any shorts or opens.
- Measure the supply voltage and input signal levels with a multimeter or oscilloscope.
- If the component is not functioning as expected, replace it to rule out the possibility of a defective inverter.
FAQs
Q: Can the Surya SWE Inverter be used with an Arduino UNO? A: Yes, the inverter can be used with an Arduino UNO, provided that the operating voltage levels are compatible.
Q: What is the maximum frequency the inverter can handle? A: The maximum frequency is determined by the propagation delay. For a 10 ns delay, the theoretical maximum frequency is around 100 MHz. However, practical limits due to circuit layout and other factors will be lower.
Q: Is it necessary to use a current-limiting resistor with the output? A: No, a current-limiting resistor is not required for the output unless you are driving a load that exceeds the specified output current ratings.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the inverter input and output pins
const int inverterInputPin = 2;
const int inverterOutputPin = 3;
void setup() {
// Set the inverter input pin as OUTPUT
pinMode(inverterInputPin, OUTPUT);
// Set the inverter output pin as INPUT
pinMode(inverterOutputPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Send a HIGH signal to the inverter input
digitalWrite(inverterInputPin, HIGH);
// Read the inverted output from the inverter
int invertedSignal = digitalRead(inverterOutputPin);
// Output the inverted signal to the Serial Monitor
Serial.println(invertedSignal);
// Wait for a second
delay(1000);
// Send a LOW signal to the inverter input
digitalWrite(inverterInputPin, LOW);
// Read the inverted output from the inverter
invertedSignal = digitalRead(inverterOutputPin);
// Output the inverted signal to the Serial Monitor
Serial.println(invertedSignal);
// Wait for a second
delay(1000);
}
Note: The above code assumes that the inverter is connected to the Arduino UNO with the input pin connected to digital pin 2 and the output pin connected to digital pin 3. Adjust the pin assignments as necessary for your specific circuit configuration.