
How to Use DRIVER DM556PR NEMA 23: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with DRIVER DM556PR NEMA 23 in Cirkit Designer
Design with DRIVER DM556PR NEMA 23 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
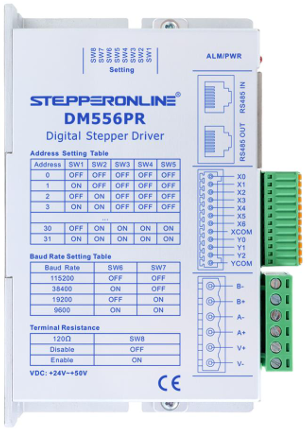
The DM556PR is a high-performance digital stepper motor driver manufactured by STEPPERONLINE. It is specifically designed to drive NEMA 23 stepper motors with precision and efficiency. This driver supports adjustable current settings, microstepping capabilities, and advanced protection features, making it ideal for applications requiring accurate motion control.
Explore Projects Built with DRIVER DM556PR NEMA 23

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer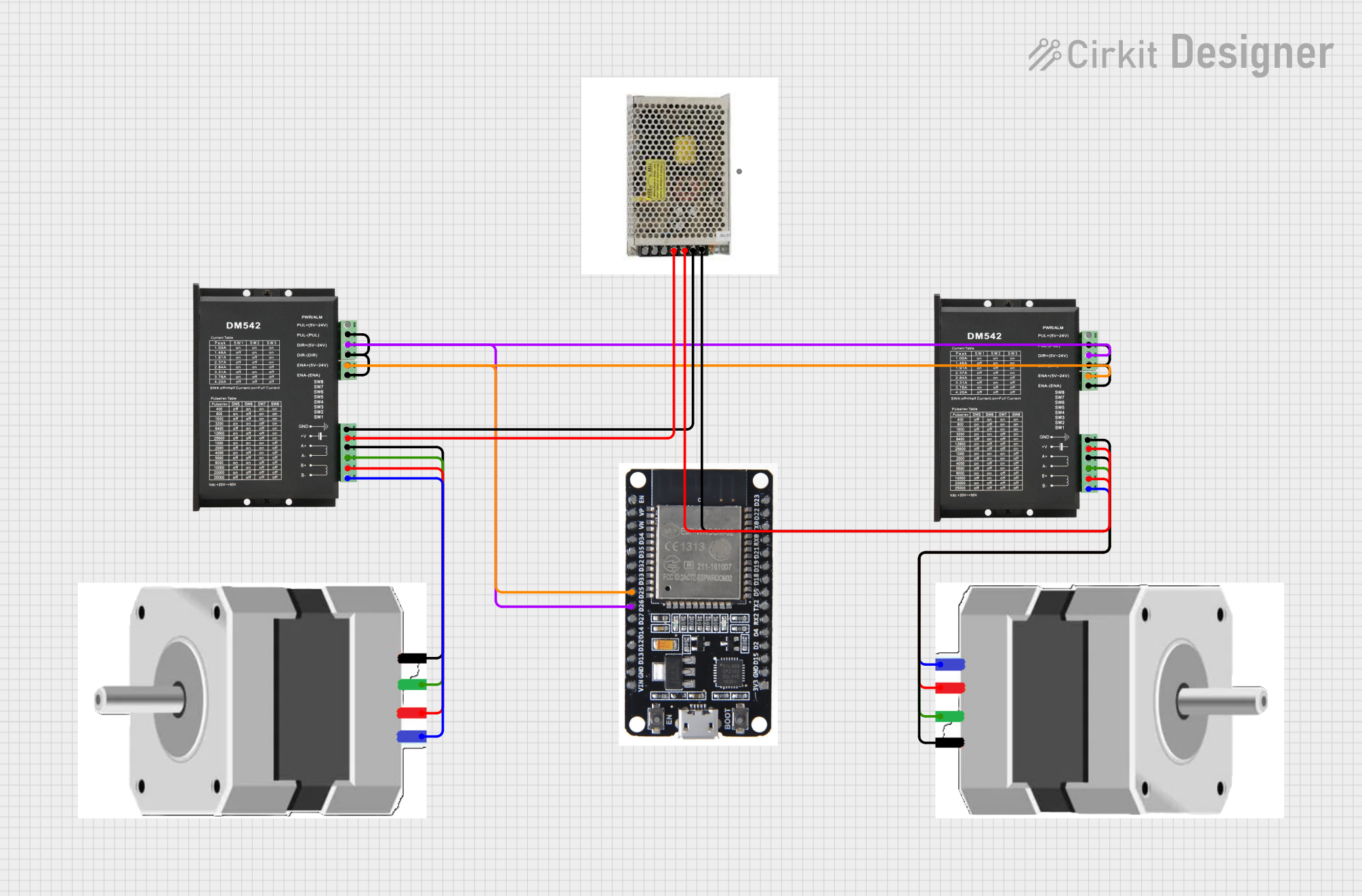
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer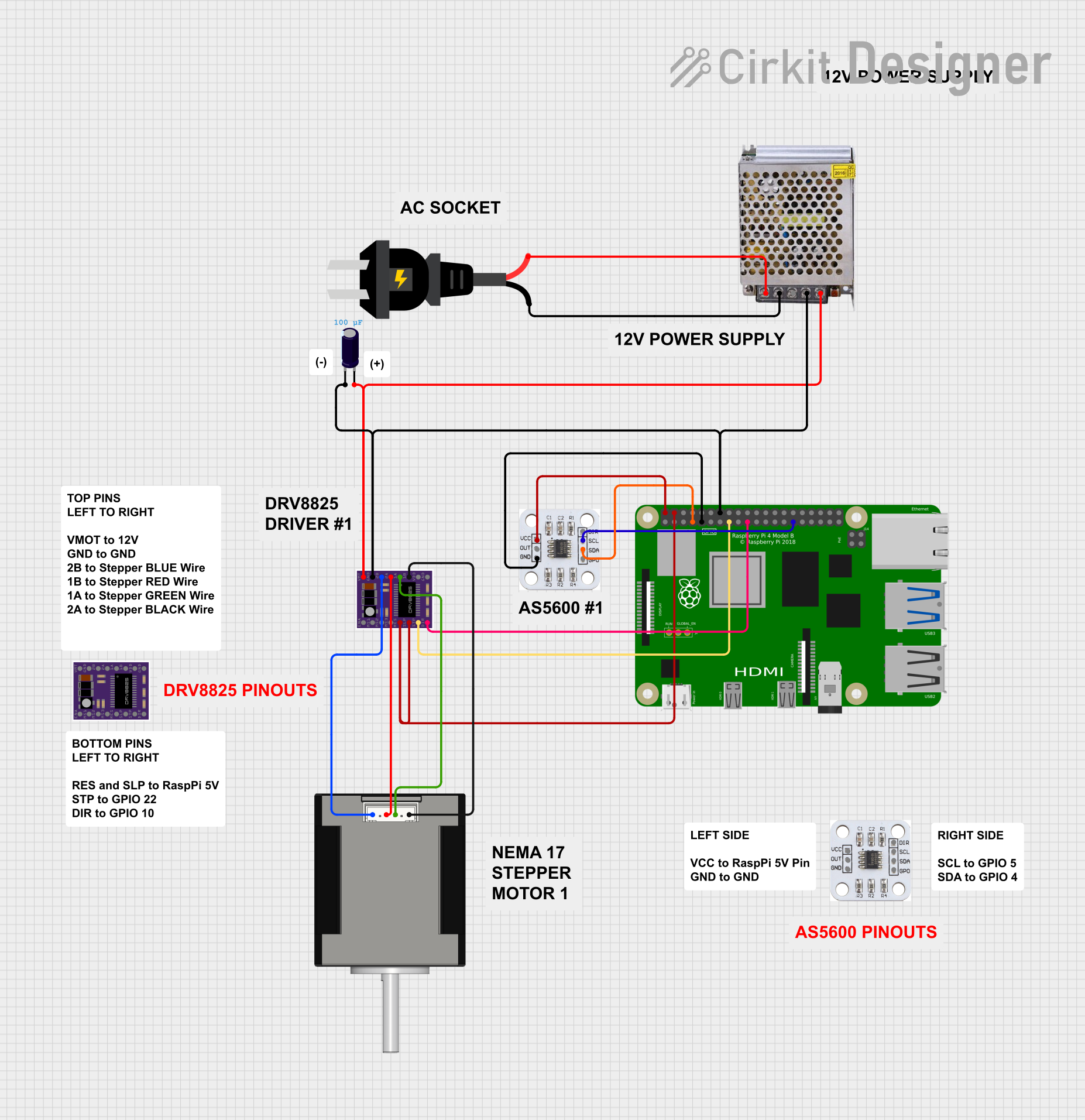
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DRIVER DM556PR NEMA 23

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- CNC machines
- 3D printers
- Robotics and automation systems
- Conveyor systems
- Laser cutters and engravers
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Part ID | DRIVER DM556PR |
| Input Voltage Range | 20VDC to 50VDC |
| Output Current Range | 1.0A to 5.6A (adjustable) |
| Microstepping Settings | 2 to 256 microsteps |
| Control Signal Voltage | 3.3V to 24V |
| Pulse Frequency | Up to 200 kHz |
| Protection Features | Over-voltage, under-voltage, over-current, |
| and over-temperature protection | |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 50°C |
| Dimensions | 118mm x 75.5mm x 34mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DM556PR driver has two main connectors: the control signal interface and the motor/power interface.
Control Signal Interface
| Pin Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| PUL+ | Pulse signal input (positive) | Connect to controller pulse+ |
| PUL- | Pulse signal input (negative) | Connect to controller pulse- |
| DIR+ | Direction signal input (positive) | Connect to controller dir+ |
| DIR- | Direction signal input (negative) | Connect to controller dir- |
| ENA+ | Enable signal input (positive) | Optional, for enabling driver |
| ENA- | Enable signal input (negative) | Optional, for enabling driver |
Motor and Power Interface
| Pin Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| A+ | Motor coil A positive | Connect to motor winding A+ |
| A- | Motor coil A negative | Connect to motor winding A- |
| B+ | Motor coil B positive | Connect to motor winding B+ |
| B- | Motor coil B negative | Connect to motor winding B- |
| VCC | Power supply positive (20-50VDC) | Ensure proper voltage range |
| GND | Power supply ground | Common ground for power supply |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the DM556PR in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a DC power supply (20V to 50V) to the VCC and GND pins. Ensure the power supply can handle the current requirements of the motor.
- Motor Connection: Connect the stepper motor's coils to the A+, A-, B+, and B- pins. Verify the wiring matches the motor's datasheet.
- Control Signals: Connect the PUL+, PUL-, DIR+, DIR-, and optionally ENA+ and ENA- pins to a microcontroller or motion controller. Use appropriate resistors if needed to match signal voltage levels.
- Microstepping and Current Settings: Use the DIP switches on the driver to configure microstepping and output current. Refer to the DM556PR datasheet for detailed switch settings.
- Testing: Power on the system and send pulse and direction signals from the controller to test motor movement.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: Mount the driver on a heat sink or metal surface to ensure proper heat dissipation.
- Signal Integrity: Use shielded cables for control signals to minimize noise interference.
- Current Settings: Set the output current to match the motor's rated current to avoid overheating or underpowering the motor.
- Microstepping: Choose an appropriate microstepping setting based on the application's precision and speed requirements.
- Enable Signal: If the ENA+ and ENA- pins are not used, leave them disconnected or tied to the appropriate logic level.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the DM556PR to an Arduino UNO and control a NEMA 23 stepper motor.
Wiring Diagram
- PUL+: Connect to Arduino pin 3
- PUL-: Connect to Arduino GND
- DIR+: Connect to Arduino pin 4
- DIR-: Connect to Arduino GND
- ENA+: Optional, connect to Arduino pin 5
- ENA-: Optional, connect to Arduino GND
Arduino Code
// Define control pins
#define PUL_PIN 3 // Pulse signal pin
#define DIR_PIN 4 // Direction signal pin
#define ENA_PIN 5 // Enable signal pin (optional)
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(PUL_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Enable the driver
digitalWrite(ENA_PIN, LOW); // LOW to enable, HIGH to disable
}
void loop() {
// Set direction
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, HIGH); // HIGH for one direction, LOW for the other
// Generate pulses to move the motor
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { // 200 steps for one revolution (1.8° step angle)
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500); // Adjust for speed
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before reversing direction
// Reverse direction
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before repeating
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Moving
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, especially motor coils and control signals.
Driver Overheating
- Cause: Insufficient heat dissipation or excessive current setting.
- Solution: Mount the driver on a heat sink and reduce the current setting.
Erratic Motor Movement
- Cause: Noise in control signals or incorrect microstepping settings.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for control signals and verify DIP switch settings.
No Response from Driver
- Cause: Incorrect power supply voltage or damaged driver.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage and check for any visible damage.
FAQs
Q: Can the DM556PR drive other stepper motor sizes?
A: Yes, it can drive other stepper motors within its voltage and current range.Q: What is the maximum pulse frequency supported?
A: The DM556PR supports pulse frequencies up to 200 kHz.Q: Do I need to use the enable signal?
A: The enable signal is optional. If not used, the driver remains enabled by default.Q: How do I select the correct microstepping setting?
A: Refer to the DIP switch table in the DM556PR datasheet and choose a setting based on your application's precision and speed requirements.