
How to Use UsbPowerSupply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
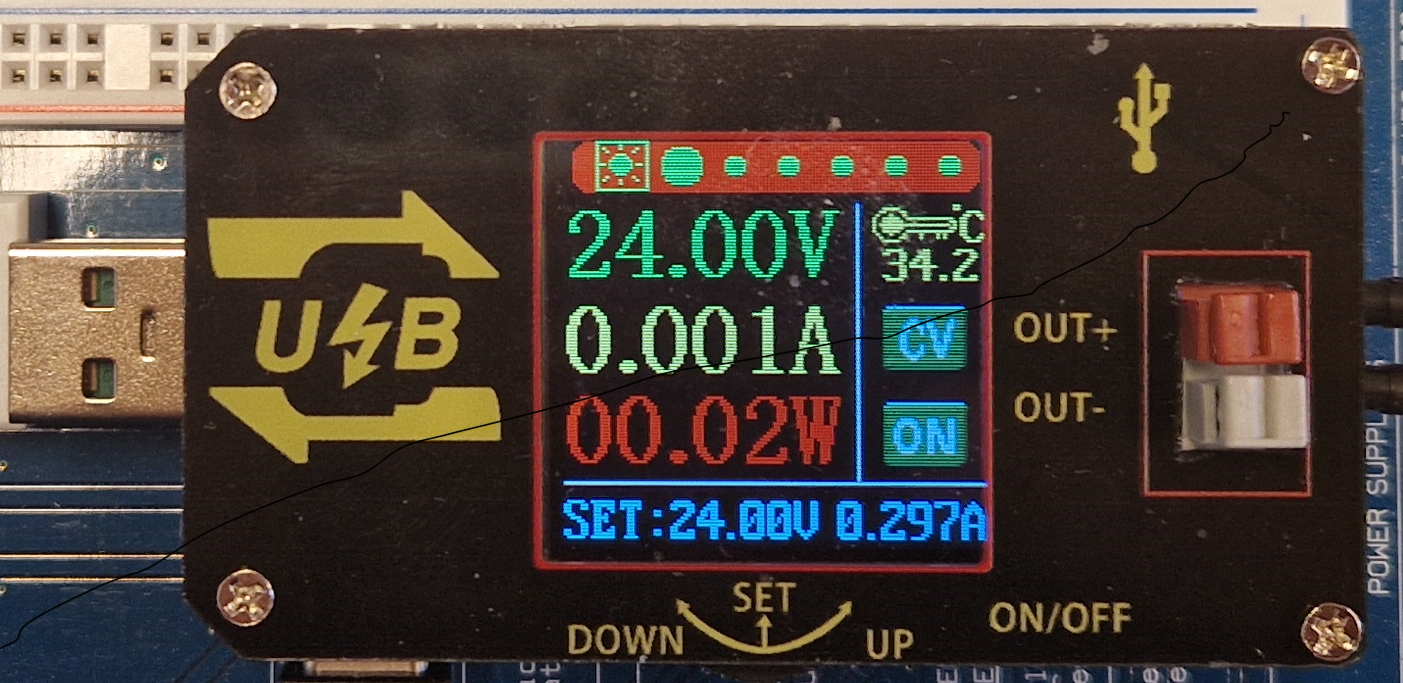
 Design with UsbPowerSupply in Cirkit Designer
Design with UsbPowerSupply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A USB power supply is an essential component in modern electronics, providing a convenient and standardized way to deliver DC power to a wide range of devices. It converts AC mains power into a lower-voltage DC output, which is accessible through one or more USB ports. Common applications include charging smartphones, tablets, and powering devices like Raspberry Pi, Arduino boards, and various USB-powered gadgets.
Explore Projects Built with UsbPowerSupply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer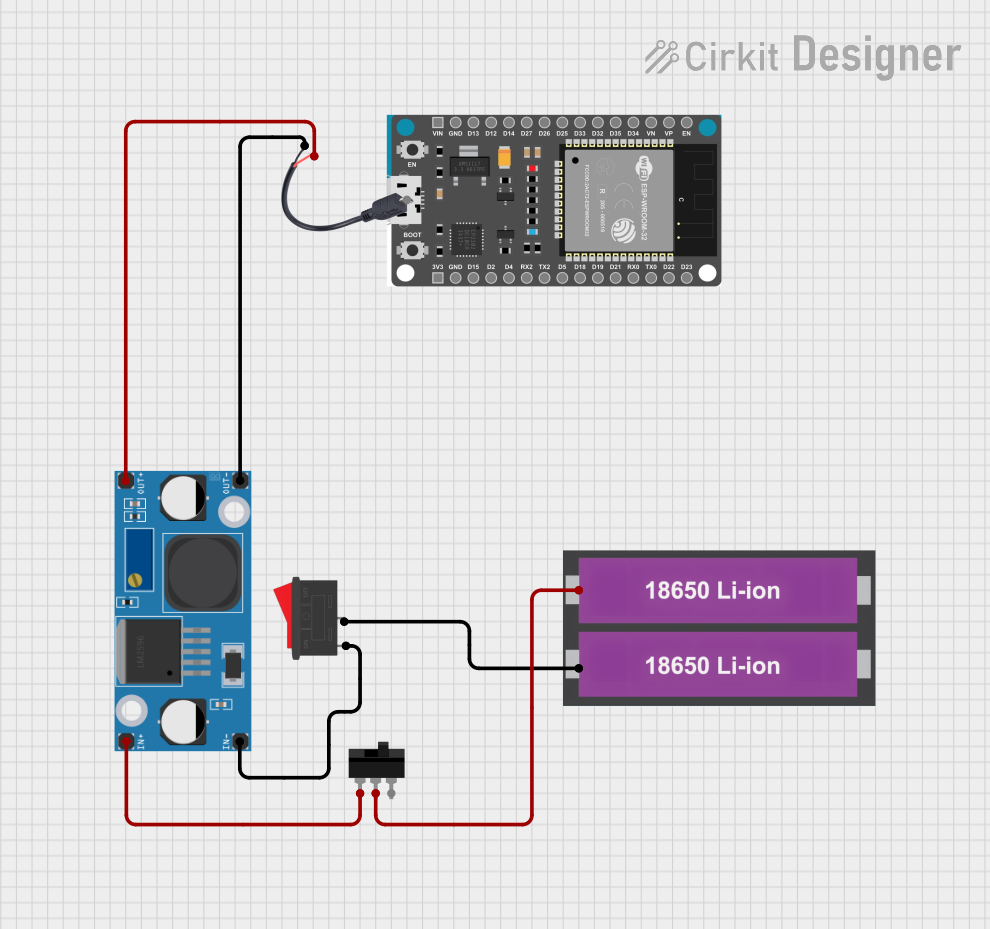
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer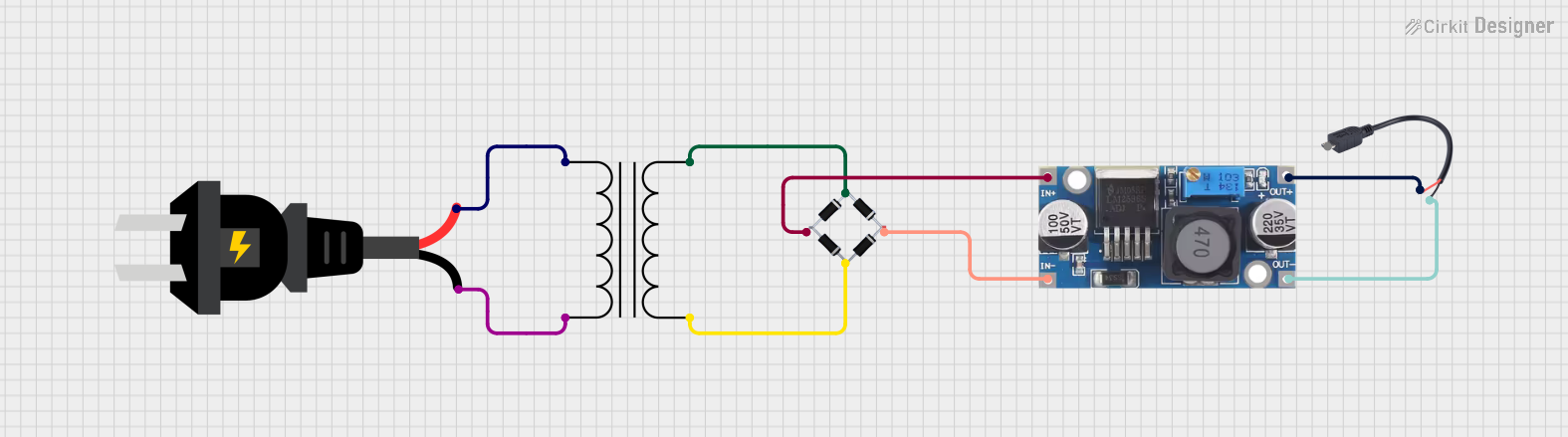
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with UsbPowerSupply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage: Typically 100-240V AC, 50/60Hz (check specific model for exact range)
- Output Voltage: 5V DC (standard USB), newer models may offer 9V, 12V (USB-PD)
- Output Current: Varies by model, common outputs are 1A, 2.1A, 2.4A, 3A
- Power Ratings: Typically ranges from 5W to 100W (USB-PD models)
- Number of Ports: Can vary from one to multiple USB ports
- USB Standards: USB 1.1, 2.0, 3.0, USB-C, USB-PD (Power Delivery) for fast charging
- Efficiency: Look for certifications like Energy Star or DOE Level VI
- Safety Features: Overcurrent, overvoltage, short circuit, and over-temperature protection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Voltage/Signal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS (Power) | 5V |
| 2 | D- (Data minus) | Data |
| 3 | D+ (Data plus) | Data |
| 4 | ID (for USB OTG) | Not connected |
| 5 | GND (Ground) | 0V |
Note: USB-C and USB-PD have additional pins and configurations.
Usage Instructions
Connecting to a Circuit
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the device you are powering or charging is compatible with the output specifications of the USB power supply.
- Connect the USB Cable: Insert the appropriate USB cable into the power supply port.
- Plug into Device: Connect the other end of the USB cable to your device.
- Power On: Plug the USB power supply into an AC outlet and switch on the power if there's an on/off switch.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Cable Quality: Use high-quality, certified USB cables to ensure safety and reliability.
- Power Rating: Do not exceed the power rating of the USB power supply. Check the device's input requirements.
- Ventilation: Ensure the power supply has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Surge Protection: Use a surge protector to safeguard against voltage spikes in the power supply.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Device Not Charging: Check the cable connections, try a different cable, or test another device to isolate the issue.
- Overheating: Unplug the power supply and allow it to cool. Ensure it's not covered and has proper ventilation.
- No Power Output: Verify that the AC outlet is functioning and check for any damage to the power supply.
Solutions and Tips
- LED Indicator: Many USB power supplies have an LED indicator. If it's not lit, the power supply may be faulty.
- Reset: Some models have a reset button or a fuse that can be replaced if the power supply stops working.
- Compatibility: Ensure the power supply supports the charging protocol required by your device (e.g., QC3.0, USB-PD).
FAQs
Q: Can I use a USB power supply with a higher current rating than my device requires?
A: Yes, the device will only draw the current it needs.
Q: Is it safe to leave the USB power supply plugged in all the time?
A: Generally, it is safe, but it's more energy-efficient to unplug it when not in use.
Q: Can I use a USB power supply in other countries?
A: Most are rated for 100-240V AC input, but check the specifications and use a plug adapter if necessary.
Example Arduino Connection
If you're using the USB power supply to power an Arduino UNO, you can connect it via the board's USB port. Here's a simple example of how to set up an LED blink sketch:
// Define the LED pin
const int ledPin = 13;
// The setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// Initialize the digital pin as an output.
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
// The loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for a second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for a second
}
Note: Ensure the Arduino board's power requirements do not exceed the USB power supply's output specifications.