
How to Use Bridge rectifier: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Bridge rectifier in Cirkit Designer
Design with Bridge rectifier in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A bridge rectifier is an electronic component that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It is a critical component in power supply design and is widely used in various electronic devices where a stable DC voltage is required. The bridge rectifier is preferred over a single diode rectifier due to its ability to provide full-wave rectification, which allows for better efficiency and smoother DC output.
Explore Projects Built with Bridge rectifier
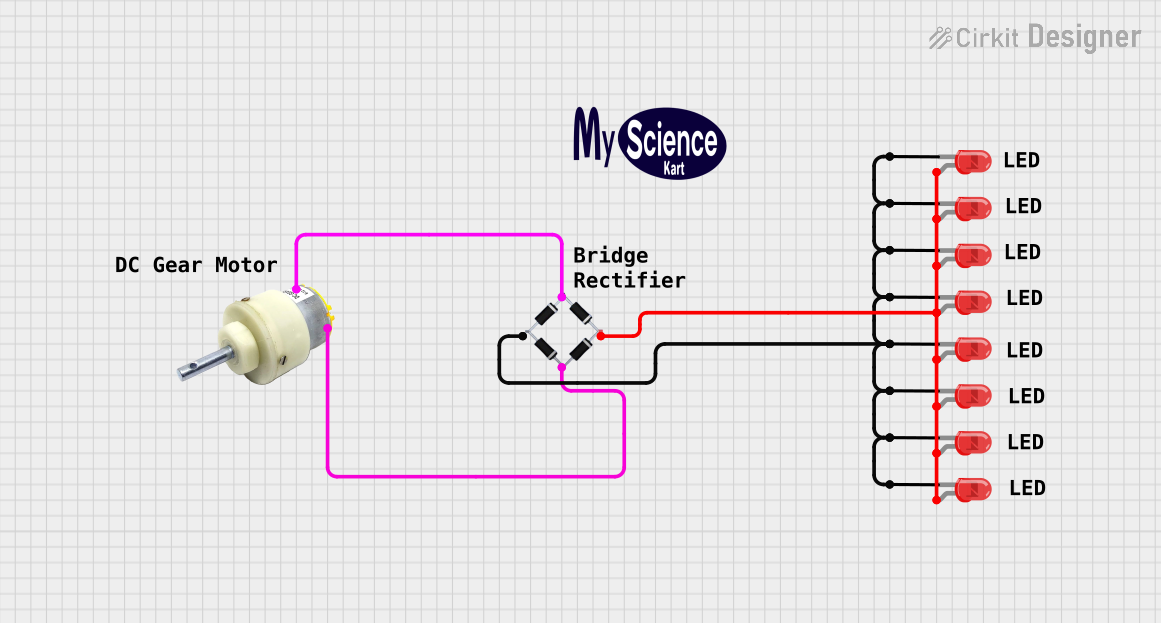
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer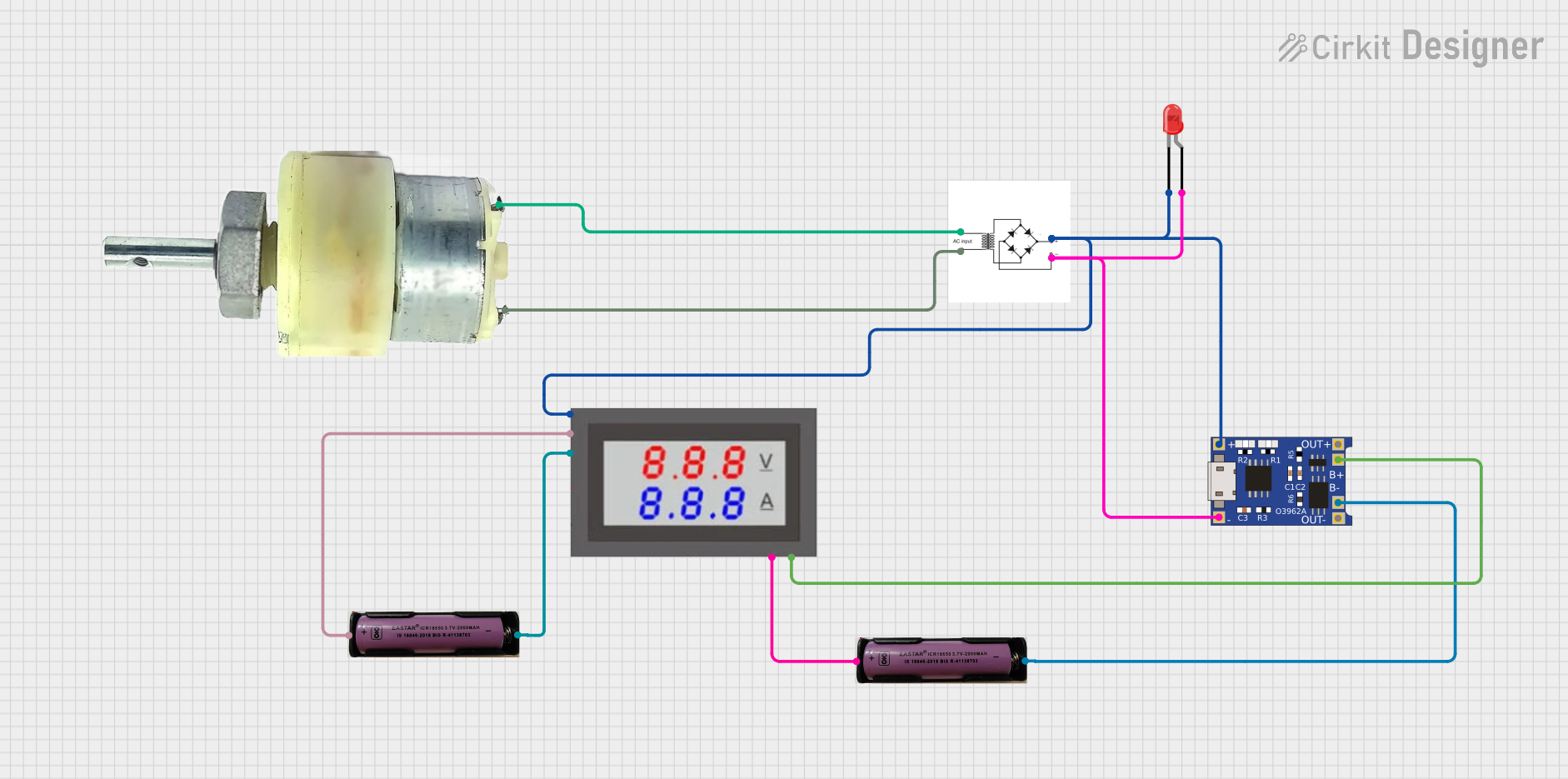
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer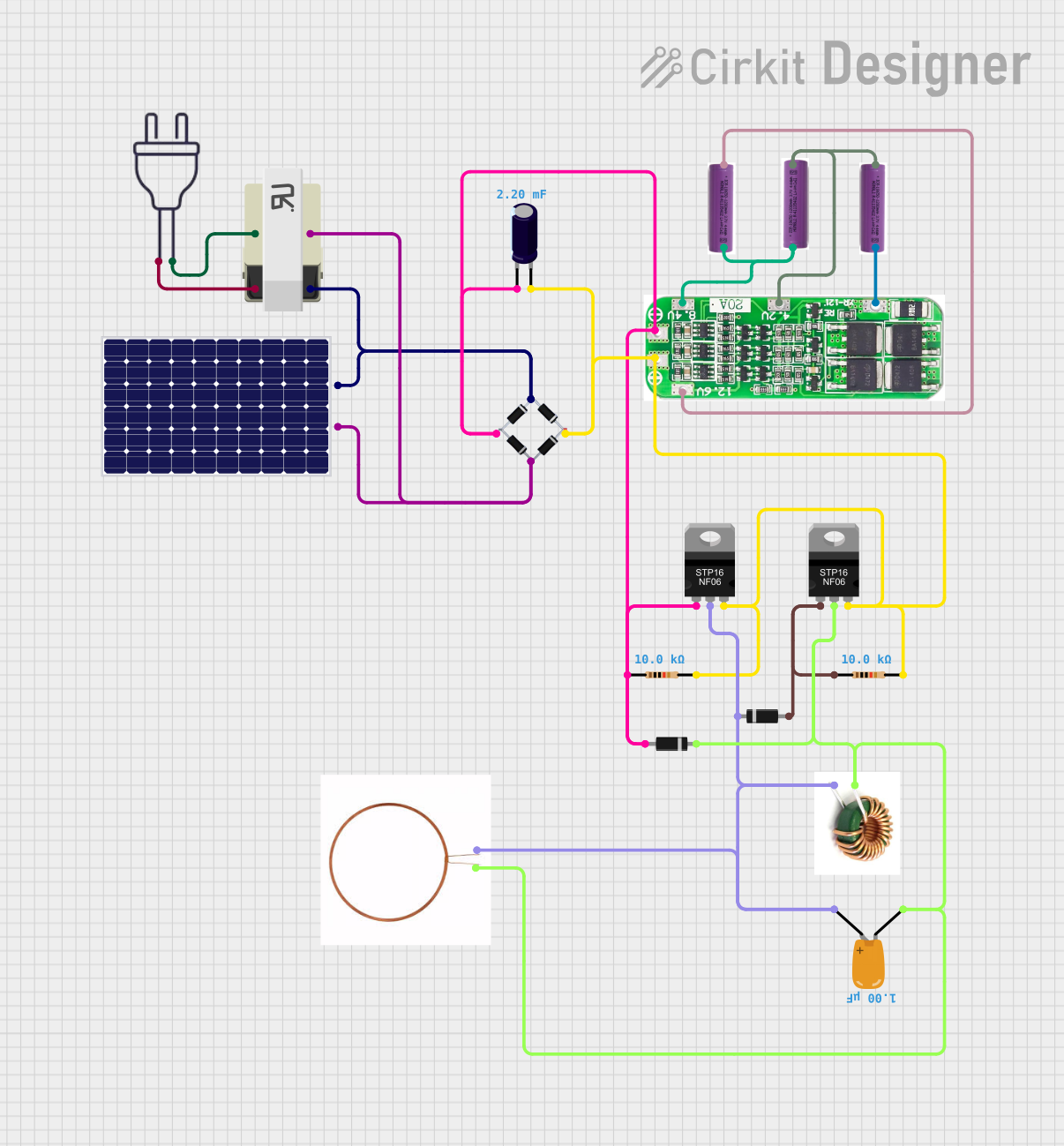
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer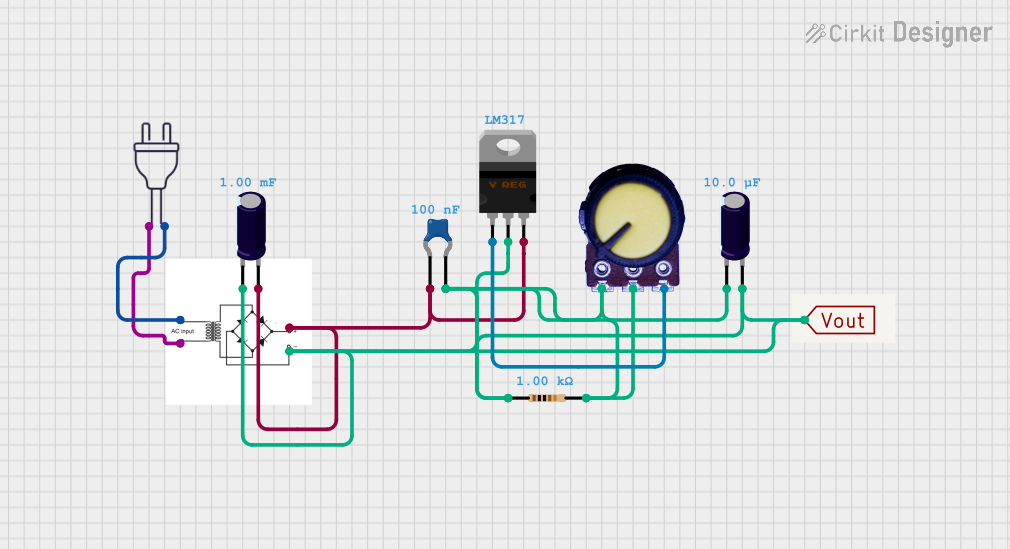
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Bridge rectifier

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power supplies for electronic devices
- Battery charging circuits
- DC motor drives
- Rectification in power inverters
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage (VRRM): The maximum voltage the diode can withstand in the reverse direction.
- Average forward current (IF(AV)): The maximum average current the diodes can conduct.
- Surge current (IFSM): The maximum peak, one-cycle non-repetitive surge current.
- Forward voltage drop (VF): The voltage drop across the diode when it is conducting.
- Operating junction temperature range (TJ): The range of temperatures over which the diode can operate without damage.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | AC Input (Phase) |
| 2 | AC Input (Neutral) |
| 3 | Positive DC Output |
| 4 | Negative DC Output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the AC input terminals (pins 1 and 2) to the AC voltage source.
- Connect the positive DC output terminal (pin 3) to the positive side of the load or circuit.
- Connect the negative DC output terminal (pin 4) to the negative side of the load or circuit.
- Optionally, add a filter capacitor across the DC output to smooth the DC voltage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the bridge rectifier's voltage and current ratings exceed the AC source's maximum output.
- Use a heatsink if the rectifier is expected to handle high power levels to prevent overheating.
- Place a fuse before the AC input for safety and overcurrent protection.
- The filter capacitor should be rated for a voltage higher than the peak output voltage of the rectifier.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Excessive voltage drop: This could be due to a high load current or a bridge rectifier with a high forward voltage drop.
- Overheating: Caused by high current flow or insufficient cooling.
- Output voltage fluctuations: This may occur if the filter capacitor is failing or is of inadequate value.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Verify that the bridge rectifier's ratings are suitable for the application.
- Check for proper heatsink installation and thermal management.
- Replace the filter capacitor with one of appropriate value and voltage rating.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a bridge rectifier to convert 220V AC to 12V DC? A: Yes, but you will also need a step-down transformer before the rectifier and a voltage regulator after it to achieve a stable 12V DC output.
Q: How do I choose the right filter capacitor? A: The capacitor value depends on the load current and the desired ripple voltage. A common rule of thumb is 1000 µF per ampere of load current.
Q: What happens if I reverse the AC input connections? A: Reversing the AC input connections will not damage the bridge rectifier, as it is non-polarized at the AC input. The DC output polarity will remain the same.
Example Connection with Arduino UNO
// No specific code is required for a bridge rectifier when used with an Arduino UNO.
// The bridge rectifier is a passive component used in the power supply section
// to provide the necessary DC voltage to the Arduino.
// However, ensure that the output voltage from the bridge rectifier is regulated
// and does not exceed the voltage limits of the Arduino board (typically 5V or 3.3V).
Note: The bridge rectifier itself does not require any control or interfacing code, as it is a passive component used for power conversion. The example above is a placeholder to indicate that the bridge rectifier would be part of the power supply circuit for the Arduino UNO, not directly interfaced with the microcontroller.