
How to Use heatbed 214x214: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with heatbed 214x214 in Cirkit Designer
Design with heatbed 214x214 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Heatbed 214x214 by Robotzade is a heated bed designed for use in 3D printers. With dimensions of 214x214 mm, it provides a stable and warm surface to improve the adhesion of printed materials during the printing process. This component is essential for achieving high-quality prints, especially when working with materials like ABS, PETG, and other filaments that require a heated surface to prevent warping and ensure proper layer bonding.
Explore Projects Built with heatbed 214x214
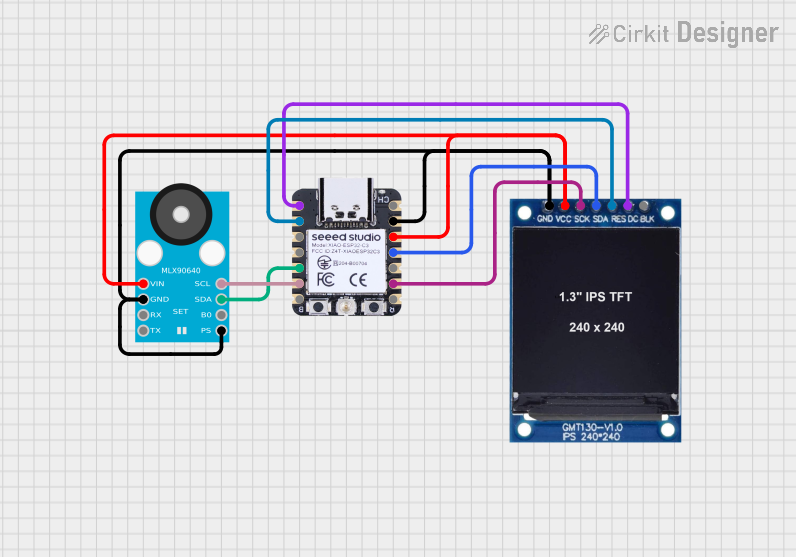
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer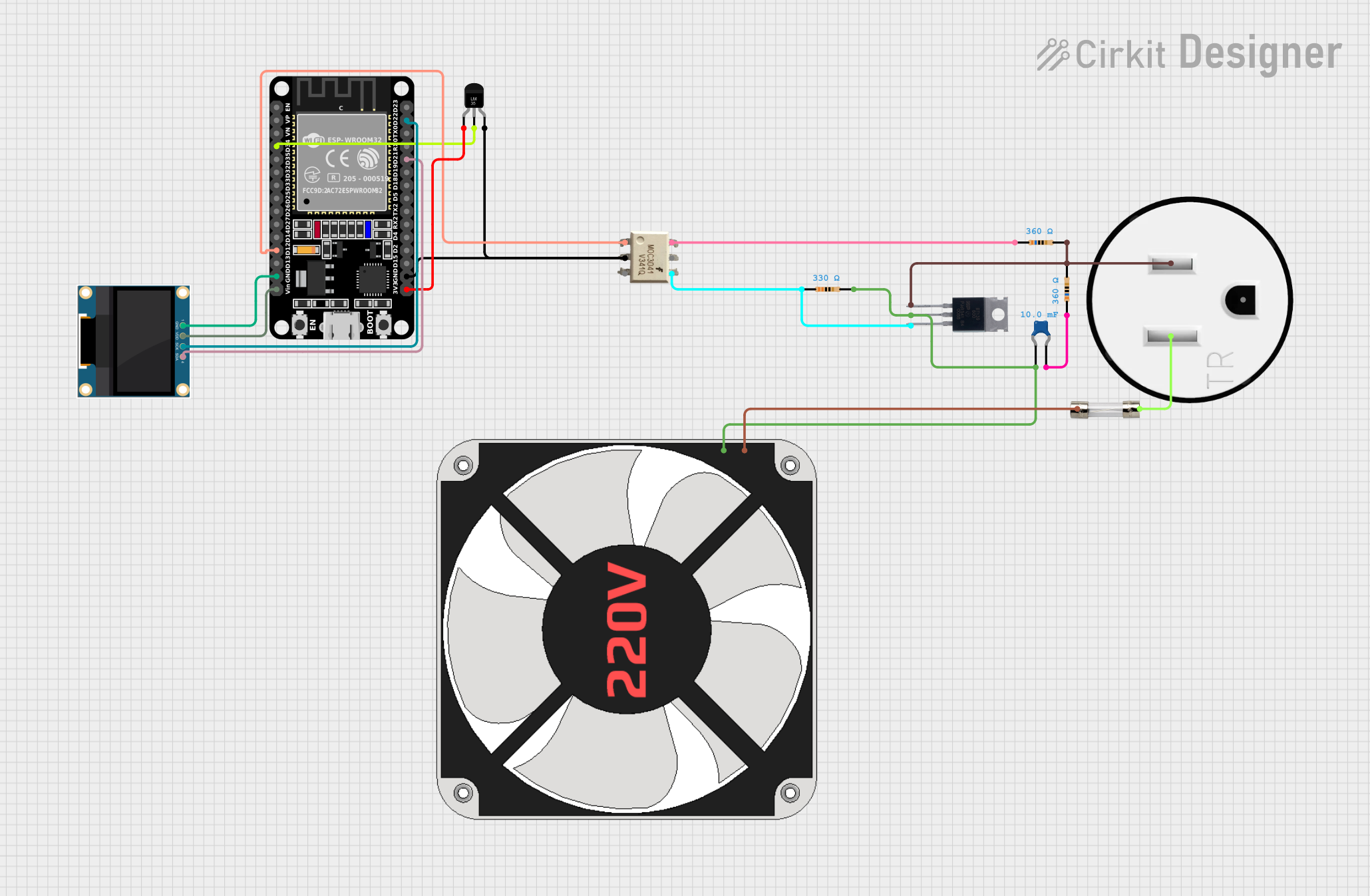
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer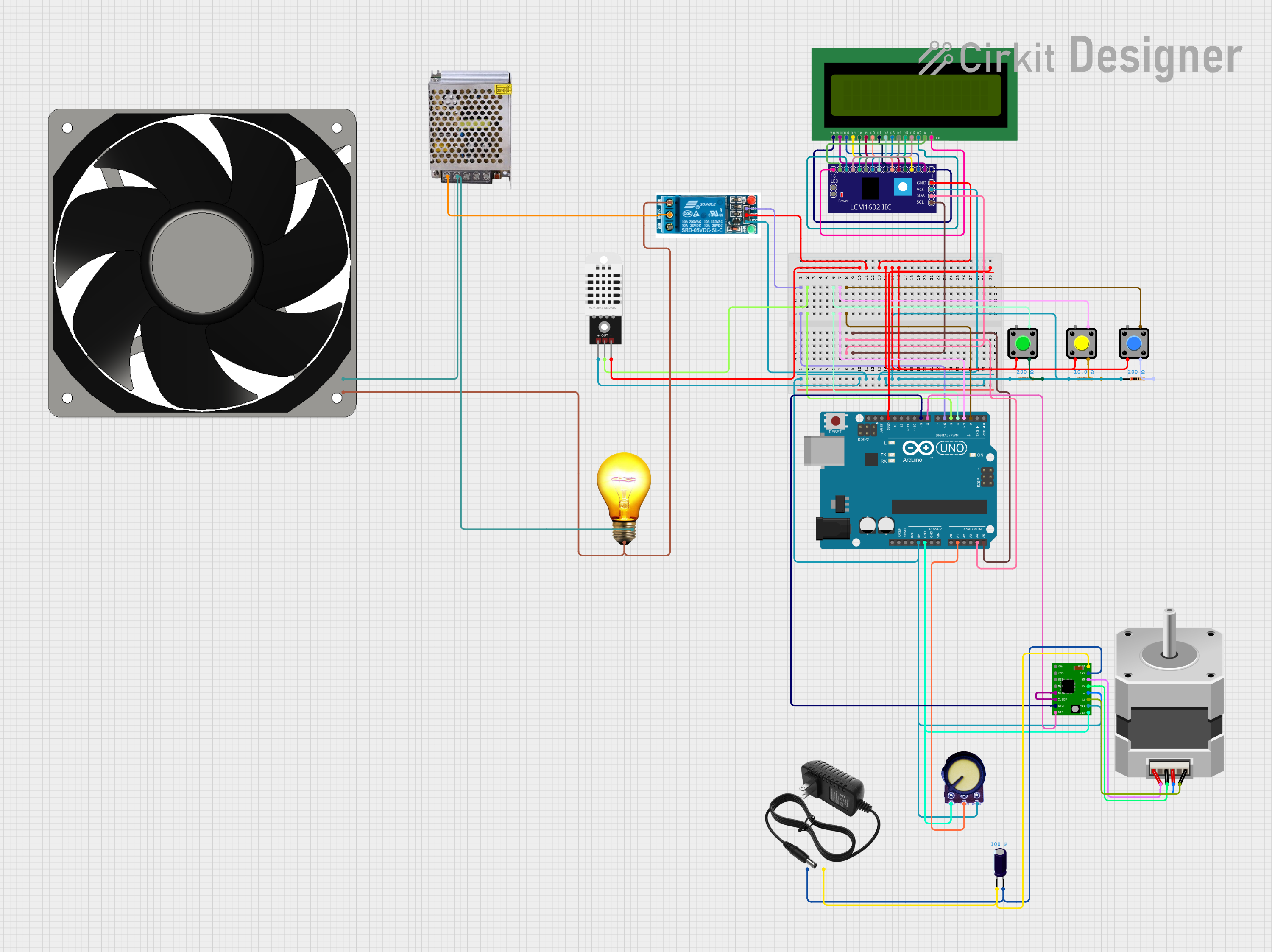
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer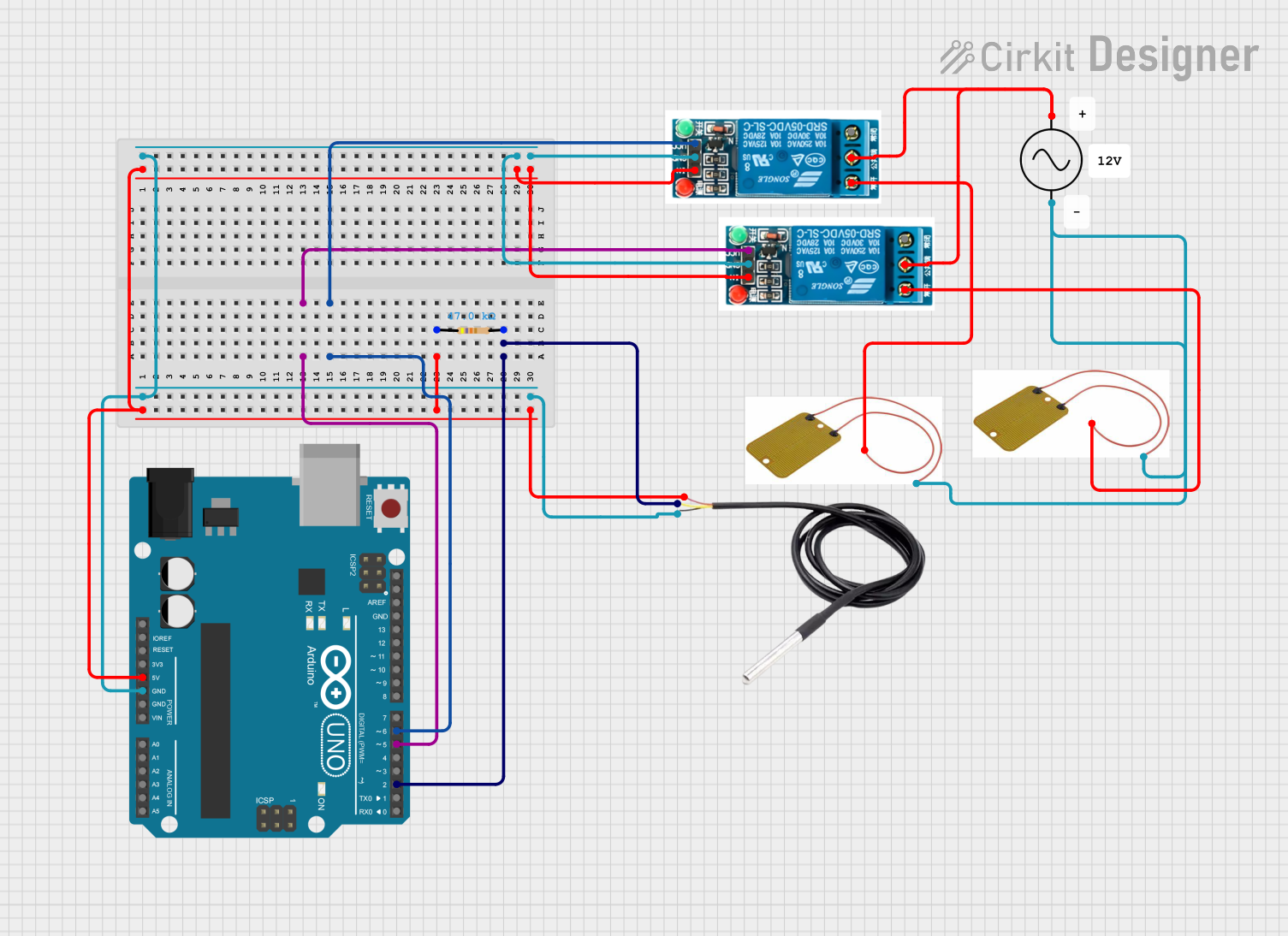
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with heatbed 214x214

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- 3D printing with materials that require a heated surface (e.g., ABS, PETG, Nylon).
- Preventing warping and improving first-layer adhesion.
- Maintaining consistent print quality across the entire print bed.
- Retrofitting or upgrading 3D printers with a heated bed.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the Heatbed 214x214:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Robotzade |
| Part ID | Heatbed 214x214 |
| Dimensions | 214 mm x 214 mm |
| Operating Voltage | 12V or 24V (depending on wiring) |
| Power Rating | 120W (12V) / 240W (24V) |
| Heating Element Type | PCB-integrated resistive heater |
| Surface Material | Aluminum or glass (optional) |
| Temperature Range | Up to 120°C (recommended max) |
| Connector Type | Solder pads or terminal block |
| Mounting Holes | 4 holes (one at each corner) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The heatbed has solder pads or a terminal block for electrical connections. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin/Pad | Description |
|---|---|
| + (Positive) | Connect to the positive terminal of the power supply. |
| - (Negative) | Connect to the negative terminal of the power supply. |
| Thermistor | Connects to the 3D printer's control board for temperature monitoring. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Heatbed in a Circuit
Power Supply Connection:
- Ensure your power supply matches the heatbed's voltage rating (12V or 24V).
- Connect the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the heatbed to the corresponding outputs of the power supply or the 3D printer's control board.
Thermistor Connection:
- Locate the thermistor wires on the heatbed.
- Connect the thermistor to the appropriate input on the 3D printer's control board. This allows the printer to monitor and regulate the heatbed's temperature.
Mounting:
- Secure the heatbed to the printer's frame using the four mounting holes.
- Ensure the surface is level and free of debris before starting a print.
Temperature Settings:
- Set the desired heatbed temperature in your 3D printer's slicer software. Common settings:
- PLA: 50-60°C
- ABS: 90-110°C
- PETG: 70-90°C
- Set the desired heatbed temperature in your 3D printer's slicer software. Common settings:
Insulation (Optional):
- For improved efficiency, consider adding an insulating layer (e.g., cork or silicone) beneath the heatbed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Selection: Verify whether your heatbed is configured for 12V or 24V operation. Incorrect voltage can damage the heatbed or power supply.
- Thermistor Calibration: Ensure the thermistor is properly calibrated in your 3D printer's firmware for accurate temperature readings.
- Avoid Overheating: Do not exceed the recommended maximum temperature of 120°C to prevent damage to the heatbed.
- Leveling: Regularly check and adjust the bed leveling to ensure consistent print quality.
- Surface Preparation: Clean the heatbed surface before each print to remove dust, oils, or residue.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
If you are using an Arduino UNO to control the heatbed, you can use a MOSFET module to handle the high current. Below is an example code snippet for controlling the heatbed:
// Define the pin connected to the MOSFET gate
const int heatbedPin = 9;
// Setup function to initialize the pin
void setup() {
pinMode(heatbedPin, OUTPUT); // Set the heatbed pin as an output
}
// Loop function to control the heatbed
void loop() {
digitalWrite(heatbedPin, HIGH); // Turn on the heatbed
delay(10000); // Keep the heatbed on for 10 seconds
digitalWrite(heatbedPin, LOW); // Turn off the heatbed
delay(10000); // Keep the heatbed off for 10 seconds
}
Note: Use a suitable MOSFET module to handle the high current required by the heatbed. The Arduino UNO cannot directly drive the heatbed.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Heatbed not heating up | Incorrect wiring or power supply issue | Verify connections and ensure correct voltage. |
| Uneven heating across the bed | Faulty heating element or poor insulation | Check for damage and consider adding insulation. |
| Printer not detecting the thermistor | Loose or incorrect thermistor connection | Reconnect the thermistor securely to the control board. |
| Warping or poor adhesion of prints | Incorrect temperature or dirty surface | Adjust temperature settings and clean the surface. |
| Heatbed takes too long to heat up | Insufficient power supply or no insulation | Use a higher-rated power supply or add insulation. |
FAQs
Can I use this heatbed with a 3D printer that only supports 12V?
- Yes, the heatbed is compatible with 12V systems. Ensure it is wired correctly for 12V operation.
What is the recommended cleaning method for the heatbed surface?
- Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to clean the surface before each print.
Can I use this heatbed with materials like PLA?
- Yes, the heatbed works well with PLA. Set the temperature to 50-60°C for optimal results.
How do I know if the thermistor is working correctly?
- Check the temperature readings on your 3D printer's display. If the readings are erratic or show "0°C," inspect the thermistor connection.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and maintain the Heatbed 214x214 in your 3D printing setup for optimal performance.