
How to Use Raspberry pi 4: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
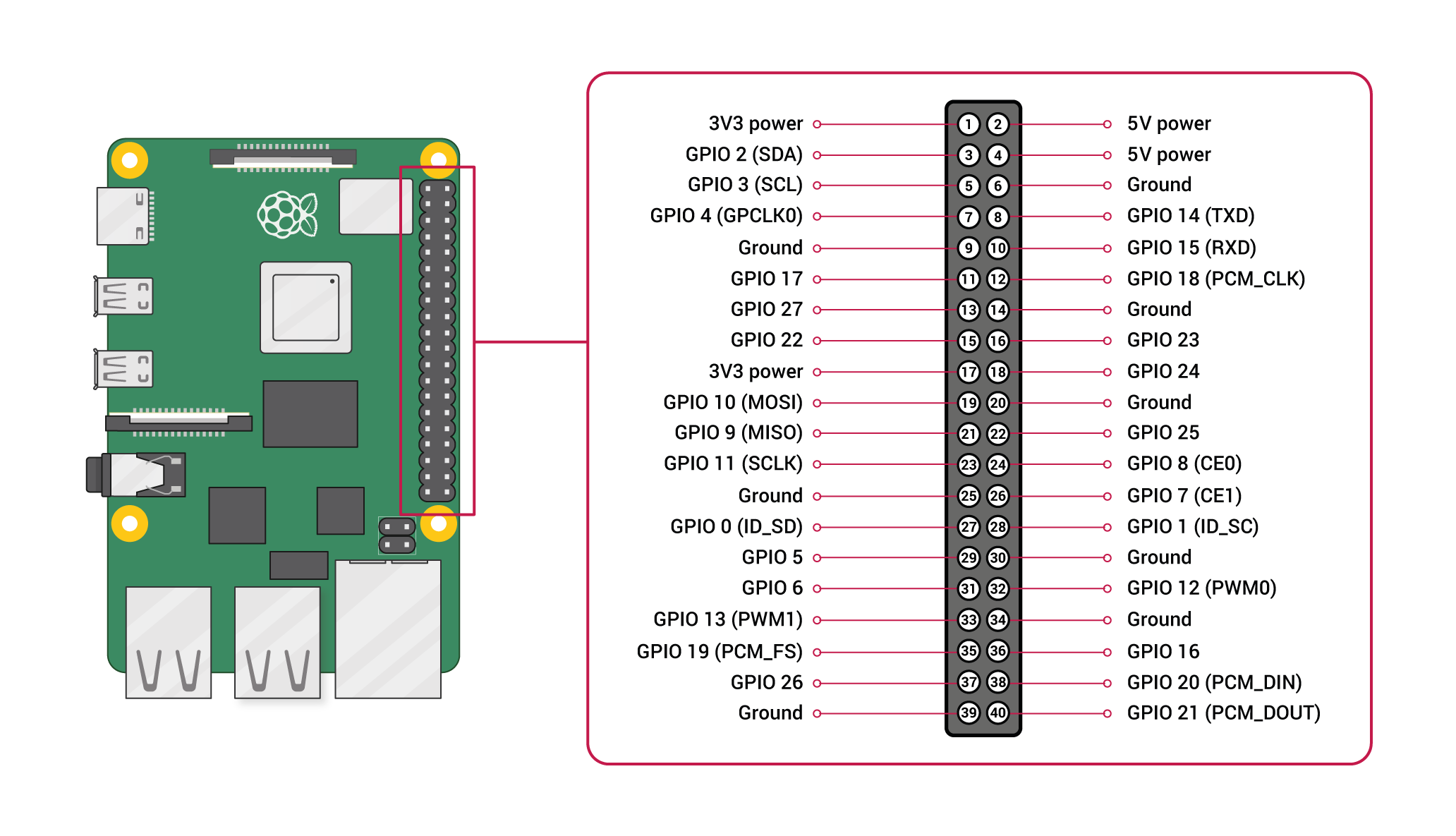
 Design with Raspberry pi 4 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Raspberry pi 4 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Raspberry Pi 4, manufactured by Raspberry Pi, is a compact and affordable single-board computer designed for a wide range of applications. It features a powerful quad-core processor, multiple USB ports, dual micro-HDMI outputs, and a 40-pin GPIO header for interfacing with electronic components. Its versatility makes it ideal for projects in programming, robotics, IoT, media centers, and more.
Explore Projects Built with Raspberry pi 4
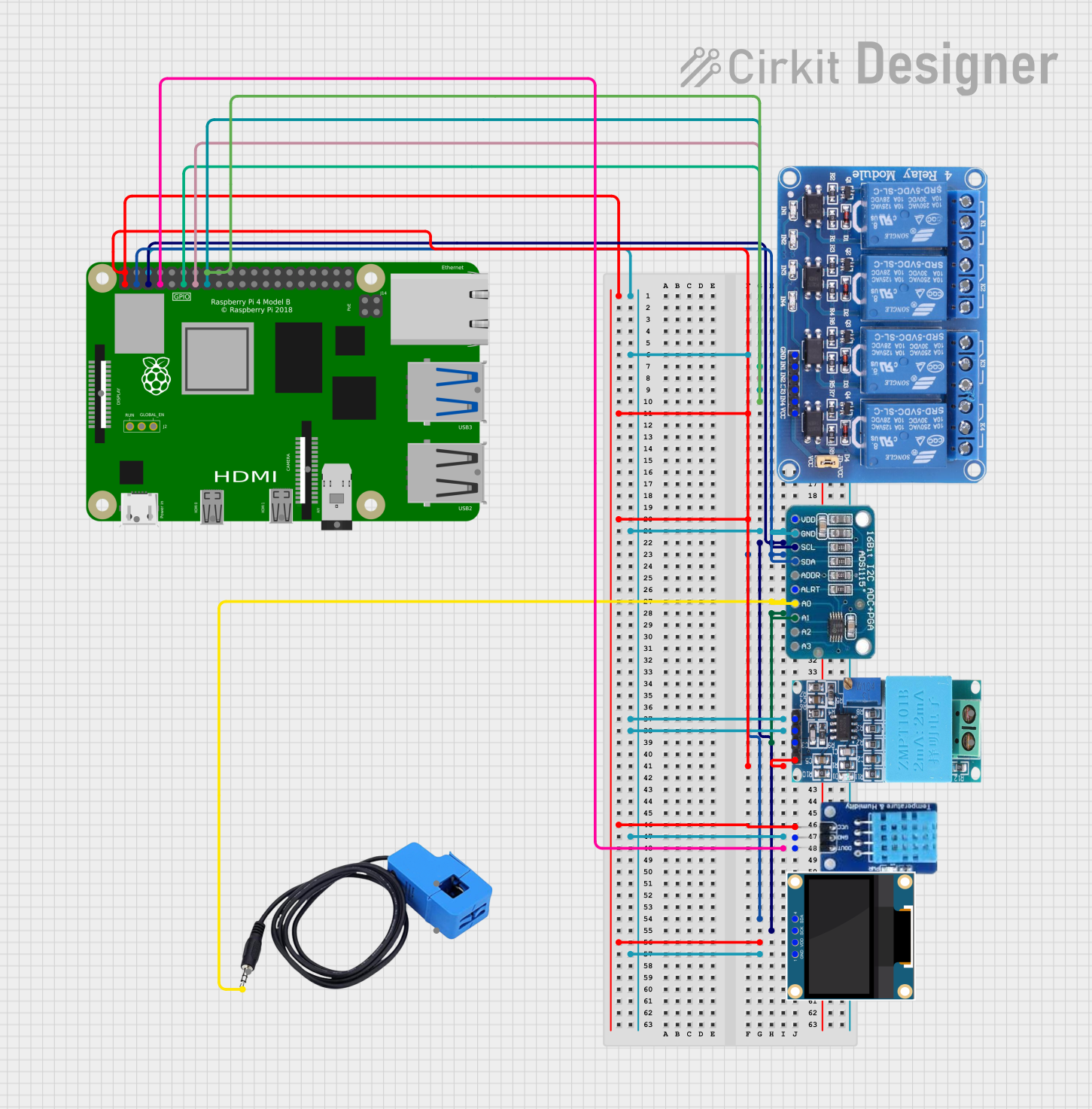
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer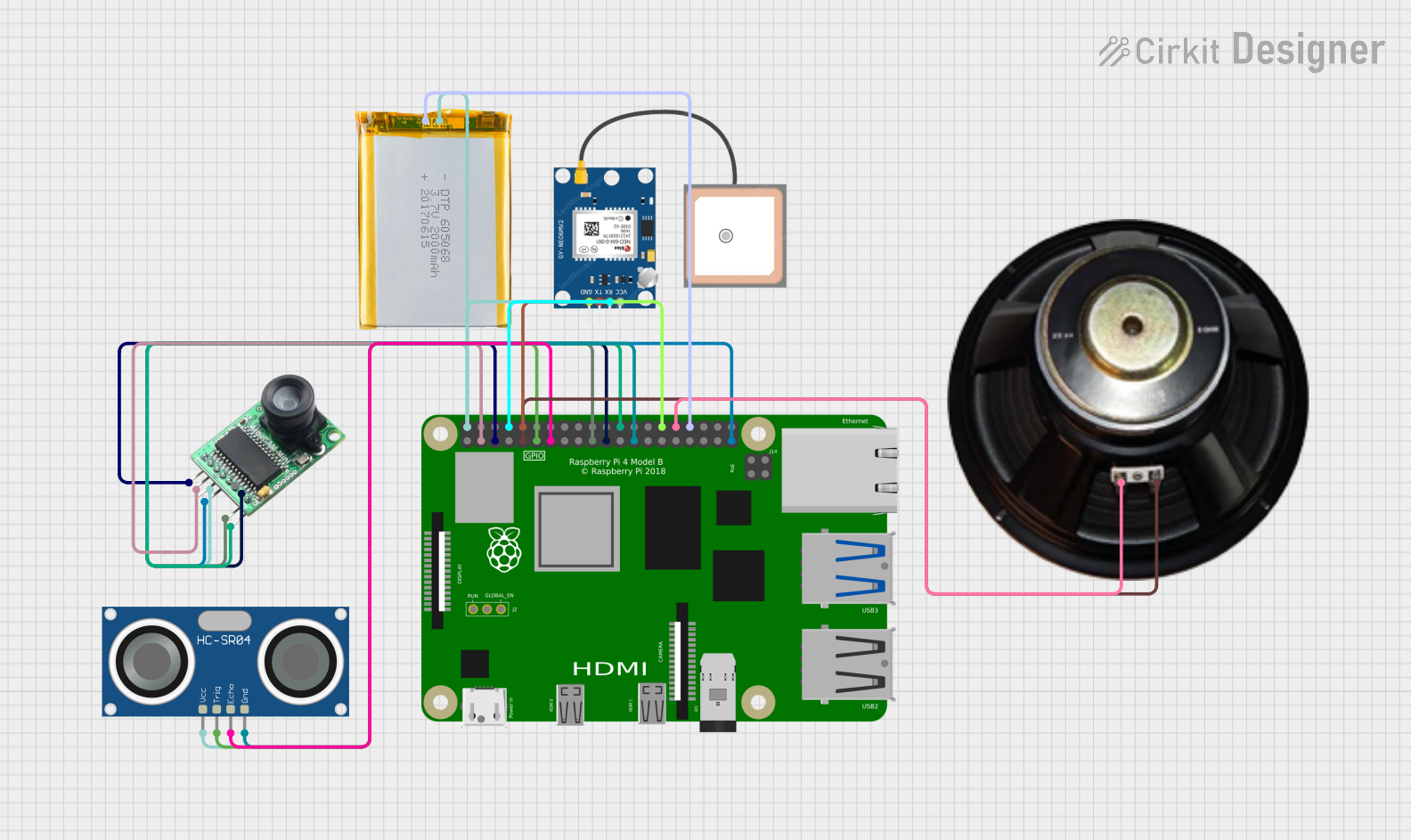
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer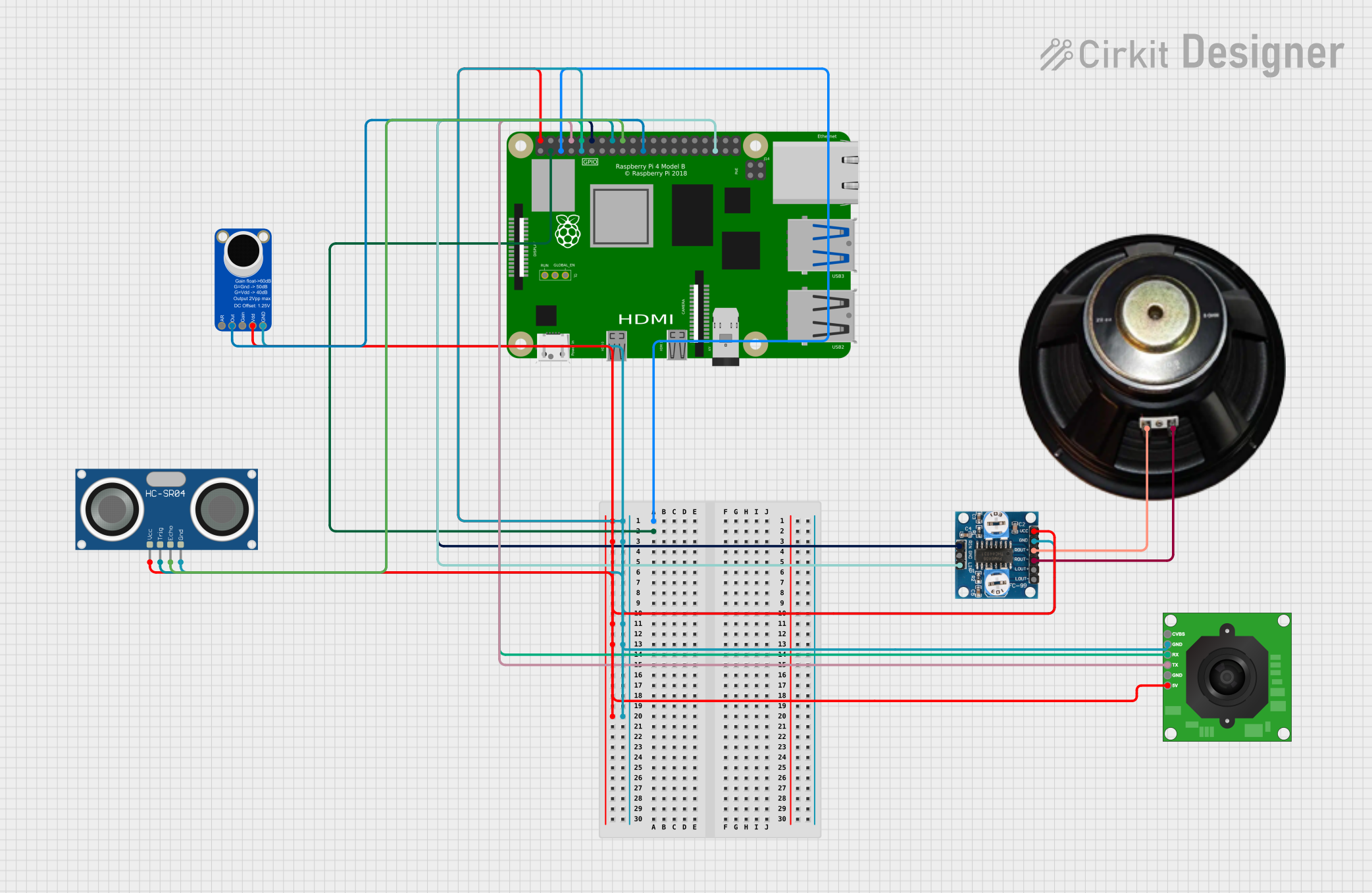
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer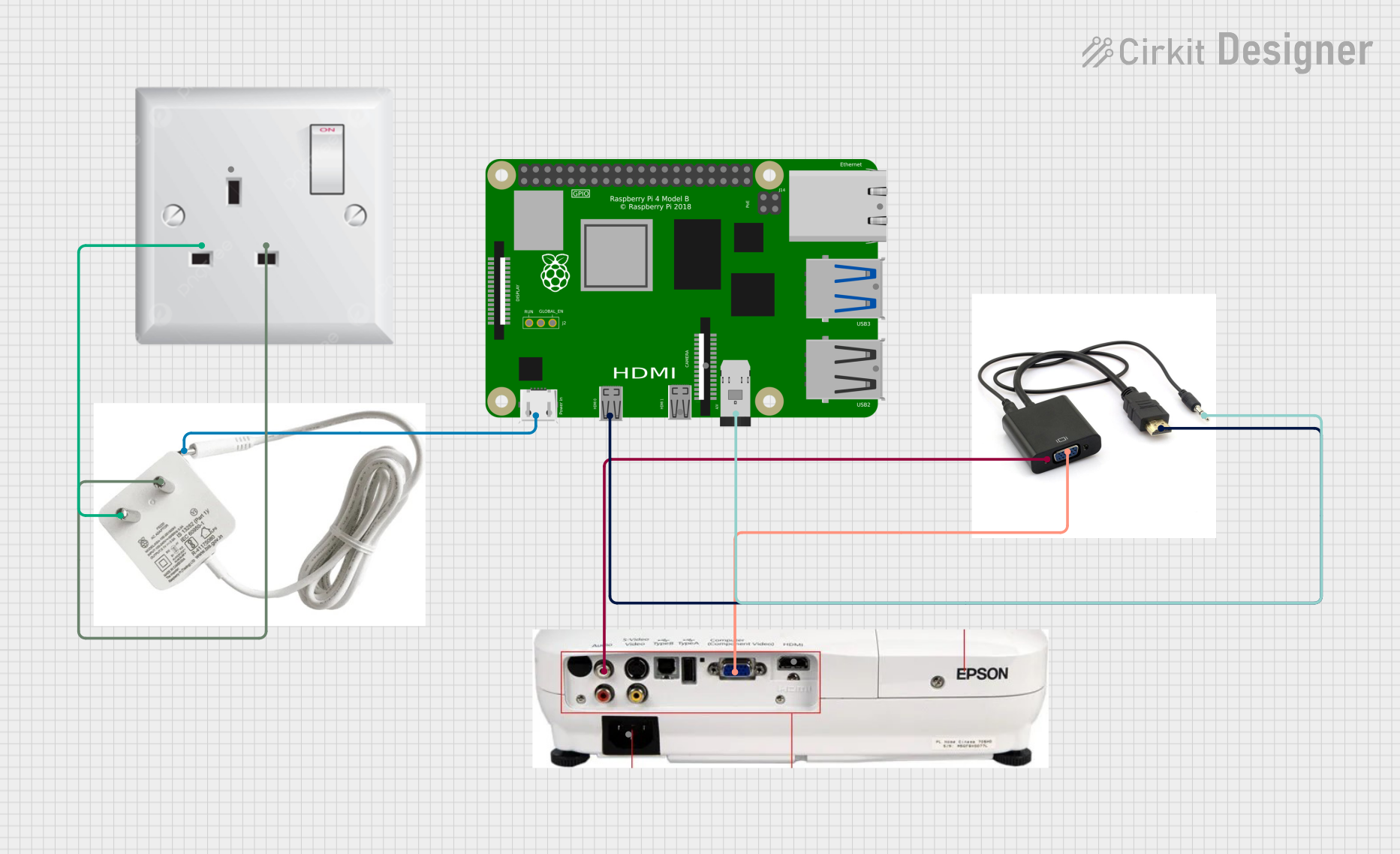
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Raspberry pi 4

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Programming and Education: A great tool for learning programming languages like Python, C++, and Java.
- IoT Projects: Acts as a hub for smart devices and sensors in Internet of Things applications.
- Media Centers: Can be used to build a home theater system with software like Kodi.
- Robotics: Controls motors, sensors, and other components in robotics projects.
- Web Servers: Functions as a lightweight server for hosting websites or applications.
Technical Specifications
The Raspberry Pi 4 is available in multiple RAM configurations (2GB, 4GB, and 8GB) and offers significant performance improvements over its predecessors.
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Processor | Quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5GHz |
| RAM Options | 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB LPDDR4 |
| USB Ports | 2 × USB 3.0, 2 × USB 2.0 |
| Video Output | 2 × micro-HDMI (up to 4K resolution) |
| Networking | Gigabit Ethernet, 802.11ac Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 5.0 |
| GPIO Header | 40-pin GPIO header (compatible with previous Raspberry Pi models) |
| Storage | MicroSD card slot for OS and data storage |
| Power Supply | 5V/3A via USB-C |
| Dimensions | 85.6mm × 56.5mm × 17mm |
GPIO Pin Configuration
The Raspberry Pi 4 features a 40-pin GPIO header for interfacing with external components. Below is a summary of the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V Power | 3.3V power supply |
| 2 | 5V Power | 5V power supply |
| 3 | GPIO2 (SDA1) | I2C Data |
| 4 | 5V Power | 5V power supply |
| 5 | GPIO3 (SCL1) | I2C Clock |
| 6 | Ground | Ground |
| 7 | GPIO4 | General-purpose I/O |
| 8 | GPIO14 (TXD) | UART Transmit |
| 9 | Ground | Ground |
| 10 | GPIO15 (RXD) | UART Receive |
| ... | ... | ... (Refer to official documentation for full pinout) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Raspberry Pi 4 in a Circuit
Powering the Raspberry Pi 4:
- Use a 5V/3A USB-C power supply to power the board.
- Ensure the power supply is reliable to avoid voltage drops.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Attach a monitor via the micro-HDMI ports.
- Connect a keyboard and mouse to the USB ports.
- Insert a microSD card with a pre-installed operating system (e.g., Raspberry Pi OS).
Using GPIO Pins:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, LEDs, motors, and other components.
- Be cautious of voltage levels; GPIO pins operate at 3.3V and are not 5V tolerant.
Networking:
- Connect to the internet via Ethernet or Wi-Fi for software updates and remote access.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Management: The Raspberry Pi 4 can get warm under heavy loads. Use a heatsink or fan for cooling.
- Static Protection: Handle the board carefully to avoid damage from static electricity.
- Software Updates: Regularly update the operating system and software to ensure security and performance.
- GPIO Safety: Avoid short circuits and overvoltage on GPIO pins to prevent damage.
Example: Blinking an LED with GPIO and Python
The following example demonstrates how to blink an LED connected to GPIO pin 17 using Python.
Circuit Setup
- Connect the positive leg of the LED to GPIO pin 17.
- Connect the negative leg of the LED to a 330-ohm resistor, and then to a ground pin.
Code
Import necessary libraries
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO import time
Set up GPIO mode
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Use Broadcom pin numbering GPIO.setup(17, GPIO.OUT) # Set GPIO pin 17 as an output
try: while True: GPIO.output(17, GPIO.HIGH) # Turn LED on time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second GPIO.output(17, GPIO.LOW) # Turn LED off time.sleep(1) # Wait for 1 second except KeyboardInterrupt: # Clean up GPIO settings on exit GPIO.cleanup()
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The Raspberry Pi 4 does not boot:
- Ensure the microSD card is properly inserted and contains a valid operating system.
- Check the power supply for sufficient voltage and current.
No display on the monitor:
- Verify the micro-HDMI cable is securely connected.
- Ensure the monitor is set to the correct input source.
Overheating:
- Use a heatsink or fan to improve cooling.
- Avoid placing the Raspberry Pi in an enclosed space without ventilation.
GPIO pins not working:
- Double-check the pin connections and ensure the correct pin numbering is used in the code.
- Verify that the GPIO pins are not damaged or shorted.
FAQs
Can I power the Raspberry Pi 4 via GPIO pins?
- Yes, you can supply 5V to the 5V GPIO pins, but this bypasses the onboard voltage regulation. Use caution.
What operating systems are compatible with the Raspberry Pi 4?
- Raspberry Pi OS, Ubuntu, and other Linux-based distributions are supported. Windows IoT Core is also an option.
Can I use the Raspberry Pi 4 for AI and machine learning?
- Yes, the Raspberry Pi 4 is capable of running lightweight AI and machine learning models, especially with tools like TensorFlow Lite.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the Raspberry Pi 4 effectively in various projects. For more details, refer to the official Raspberry Pi documentation.