
How to Use E81D80NK: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with E81D80NK in Cirkit Designer
Design with E81D80NK in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The E81D80NK is a high-performance N-channel MOSFET designed for efficient switching applications. It features low on-resistance and fast switching speeds, making it ideal for power management and conversion in various electronic devices. This component is widely used in applications such as DC-DC converters, motor drivers, power supplies, and other high-efficiency switching circuits.
Explore Projects Built with E81D80NK

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer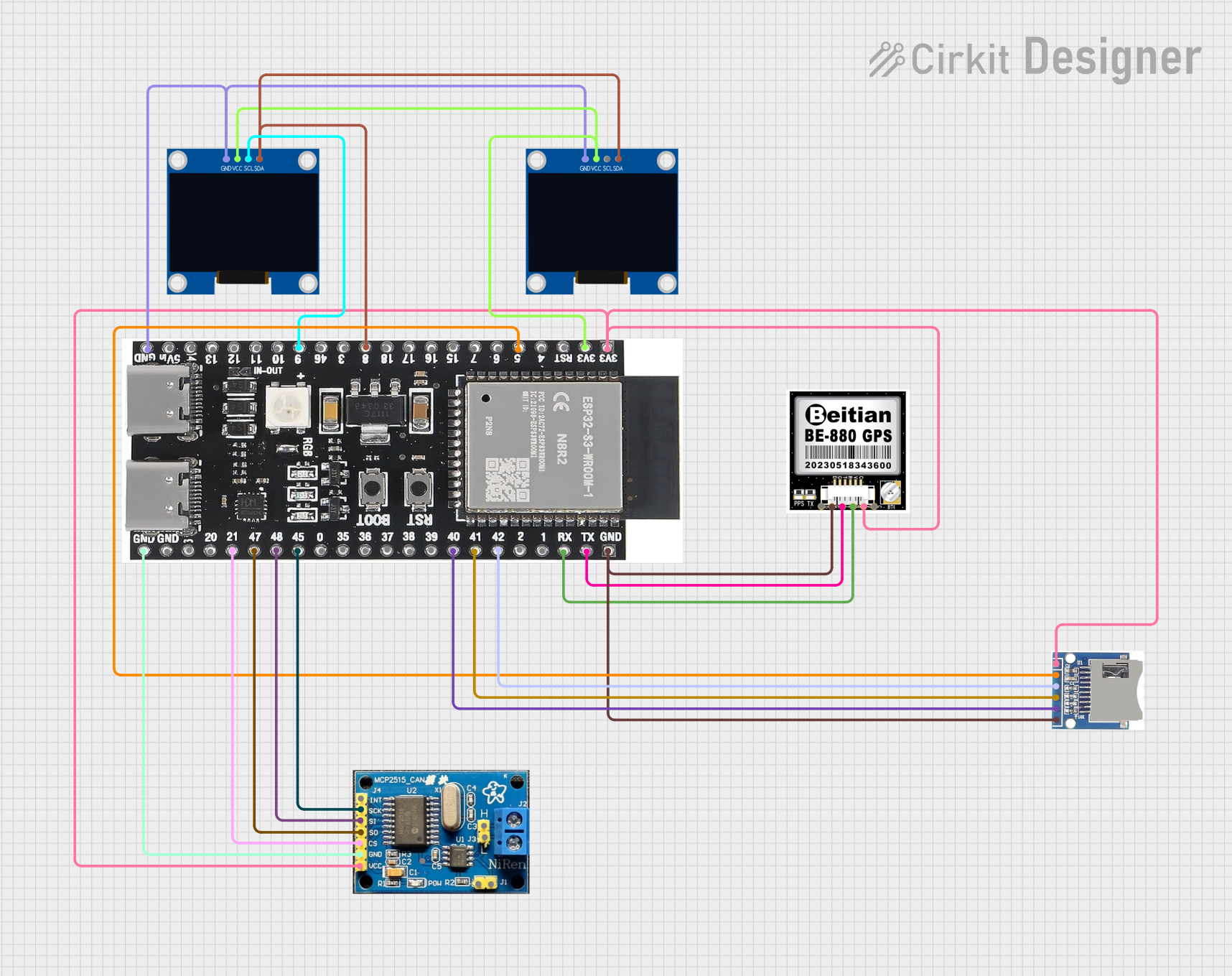
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer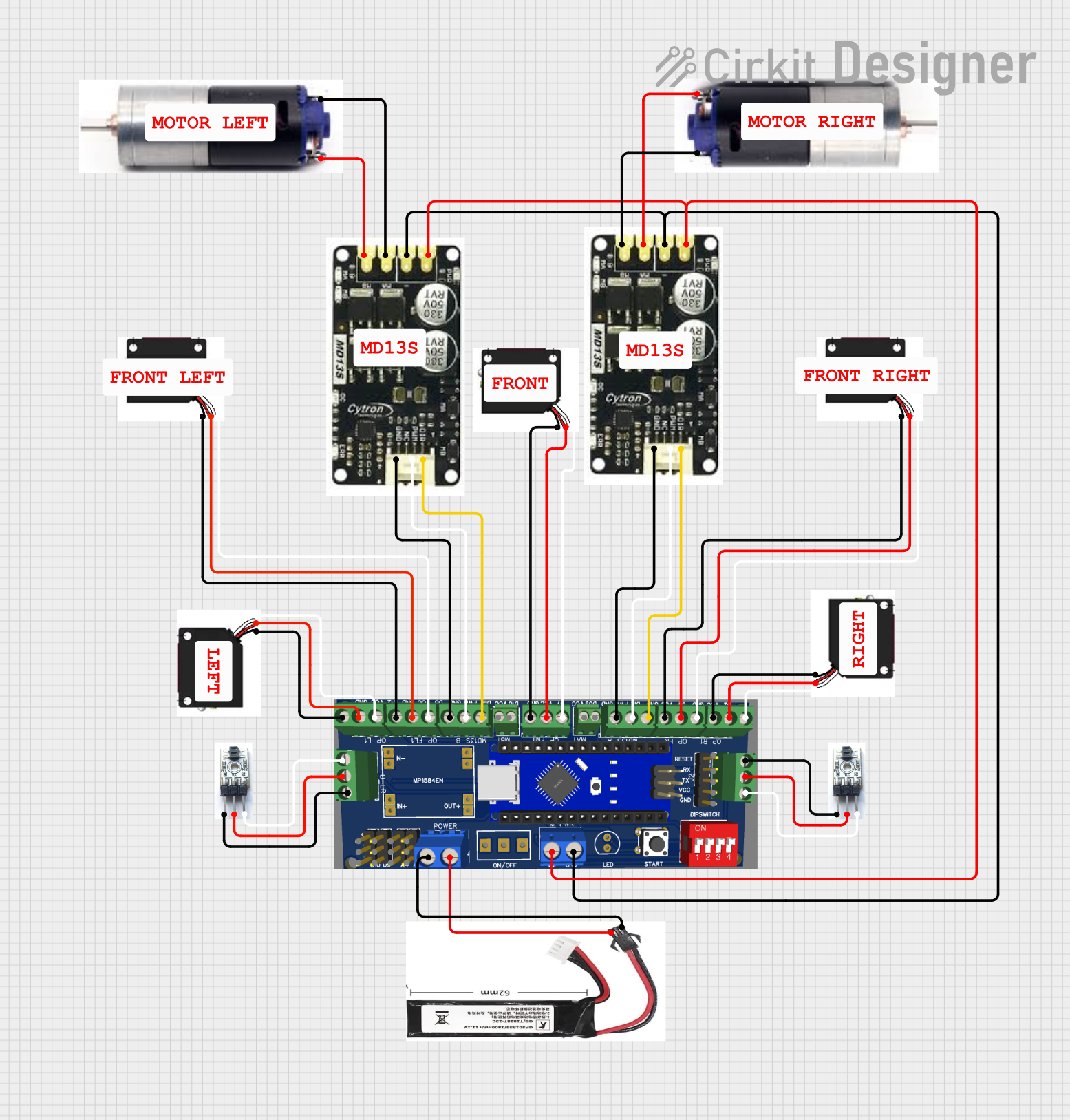
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer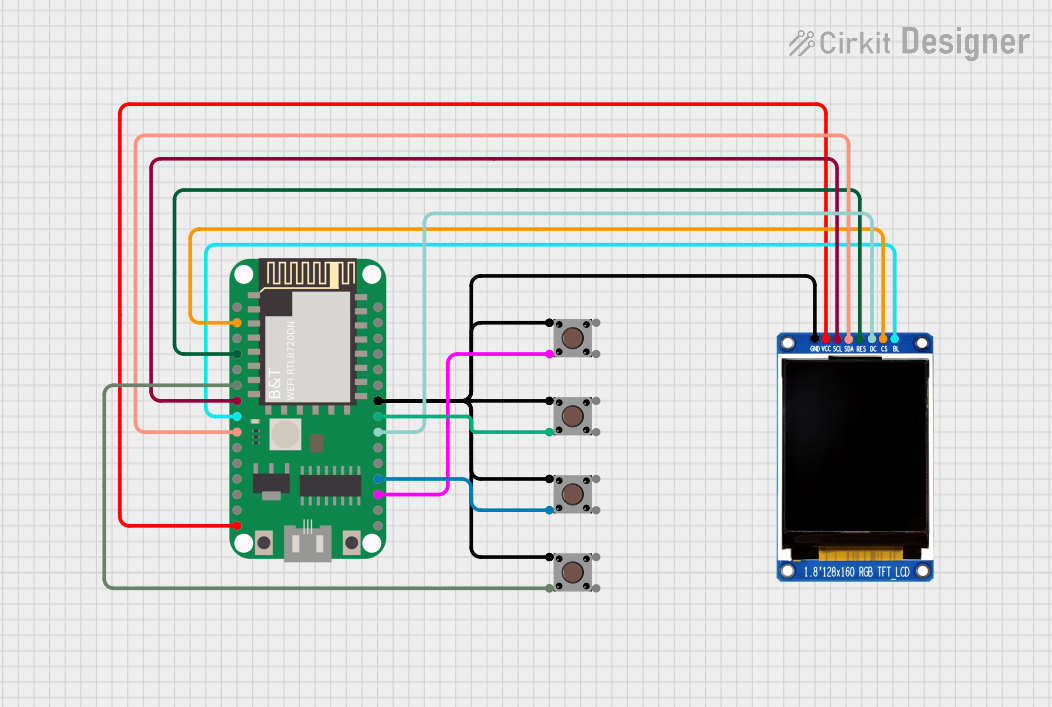
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with E81D80NK

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- DC-DC converters for voltage regulation
- Motor control and drivers
- Power supply circuits
- Load switching in industrial and consumer electronics
- High-speed switching applications
Technical Specifications
The E81D80NK is designed to handle high power and operate efficiently in demanding environments. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Drain-Source Voltage (VDS) | 80V |
| Gate-Source Voltage (VGS) | ±20V |
| Continuous Drain Current (ID) | 80A |
| Pulsed Drain Current (IDM) | 320A |
| On-Resistance (RDS(on)) | 0.008 Ω (typical) |
| Total Gate Charge (Qg) | 120 nC |
| Threshold Voltage (VGS(th)) | 2V - 4V |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | 300W |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +175°C |
| Package Type | TO-220 or TO-247 |
Pin Configuration
The E81D80NK is typically available in a TO-220 or TO-247 package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gate (G) | Controls the MOSFET switching state |
| 2 | Drain (D) | Current flows from drain to source |
| 3 | Source (S) | Connected to ground or load return |
Usage Instructions
The E81D80NK is straightforward to use in a variety of circuits. Below are the steps and considerations for using this MOSFET effectively:
How to Use:
- Gate Drive Voltage: Ensure the gate voltage (VGS) is within the specified range (typically 10V for full enhancement). Use a gate driver circuit if necessary.
- Load Connection: Connect the load between the drain and the positive supply voltage. The source is typically connected to ground.
- Switching Control: Use a microcontroller, gate driver, or other control circuitry to toggle the gate voltage and switch the MOSFET on or off.
- Heat Dissipation: Attach a heatsink to the MOSFET package if operating at high currents to prevent overheating.
Important Considerations:
- Gate Resistor: Use a resistor (typically 10Ω to 100Ω) in series with the gate to limit inrush current and prevent oscillations.
- Flyback Diode: For inductive loads (e.g., motors), include a flyback diode across the load to protect the MOSFET from voltage spikes.
- Thermal Management: Monitor the MOSFET's temperature and ensure it operates within the safe range. Use thermal paste and a heatsink for better heat dissipation.
- Voltage Ratings: Ensure the drain-source voltage (VDS) and gate-source voltage (VGS) do not exceed the maximum ratings.
Example: Using E81D80NK with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the E81D80NK to control a DC motor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the MOSFET gate pin
const int mosfetGatePin = 9; // Connect to the Gate of E81D80NK
void setup() {
pinMode(mosfetGatePin, OUTPUT); // Set the MOSFET gate pin as output
}
void loop() {
// Turn the MOSFET on (motor runs)
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the motor running for 1 second
// Turn the MOSFET off (motor stops)
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before restarting
}
Note: Ensure the Arduino's output voltage (5V) is sufficient to fully turn on the MOSFET. If not, use a gate driver circuit to boost the voltage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
MOSFET Overheating:
- Cause: Insufficient heat dissipation or operating beyond current limits.
- Solution: Use a heatsink and ensure the MOSFET operates within its rated current and voltage.
MOSFET Not Switching:
- Cause: Insufficient gate voltage or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify the gate voltage is at least 10V for full enhancement. Check the wiring and connections.
Voltage Spikes Damaging the MOSFET:
- Cause: Inductive loads generating back EMF.
- Solution: Add a flyback diode across the load to suppress voltage spikes.
Low Efficiency:
- Cause: High on-resistance or improper gate drive.
- Solution: Ensure the gate voltage is sufficient and minimize the gate resistor value.
FAQs:
Q1: Can I use the E81D80NK for low-power applications?
A1: Yes, the E81D80NK can be used for low-power applications, but it is optimized for high-power switching. For low-power circuits, consider using a MOSFET with lower current ratings.
Q2: What is the maximum PWM frequency for this MOSFET?
A2: The maximum PWM frequency depends on the gate charge (Qg) and the gate driver capability. Typically, it can handle frequencies up to 100 kHz with an appropriate gate driver.
Q3: Can I drive the E81D80NK directly from a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: No, a 3.3V signal may not fully enhance the MOSFET. Use a gate driver or level shifter to provide a higher gate voltage (e.g., 10V).
Q4: How do I calculate the power dissipation of the MOSFET?
A4: Power dissipation can be calculated as P = I2 × RDS(on) during conduction. Ensure the MOSFET operates within its thermal limits.