
How to Use motor VEX 2-were 393: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with motor VEX 2-were 393 in Cirkit Designer
Design with motor VEX 2-were 393 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Motor VEX 2-Wire 393 is a versatile DC motor designed for use in robotics and other mechanical systems. Manufactured by Arduino (Part ID: MEGA), this motor is known for its reliability, efficiency, and ease of integration. Its 2-wire connection simplifies control system integration, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with motor VEX 2-were 393
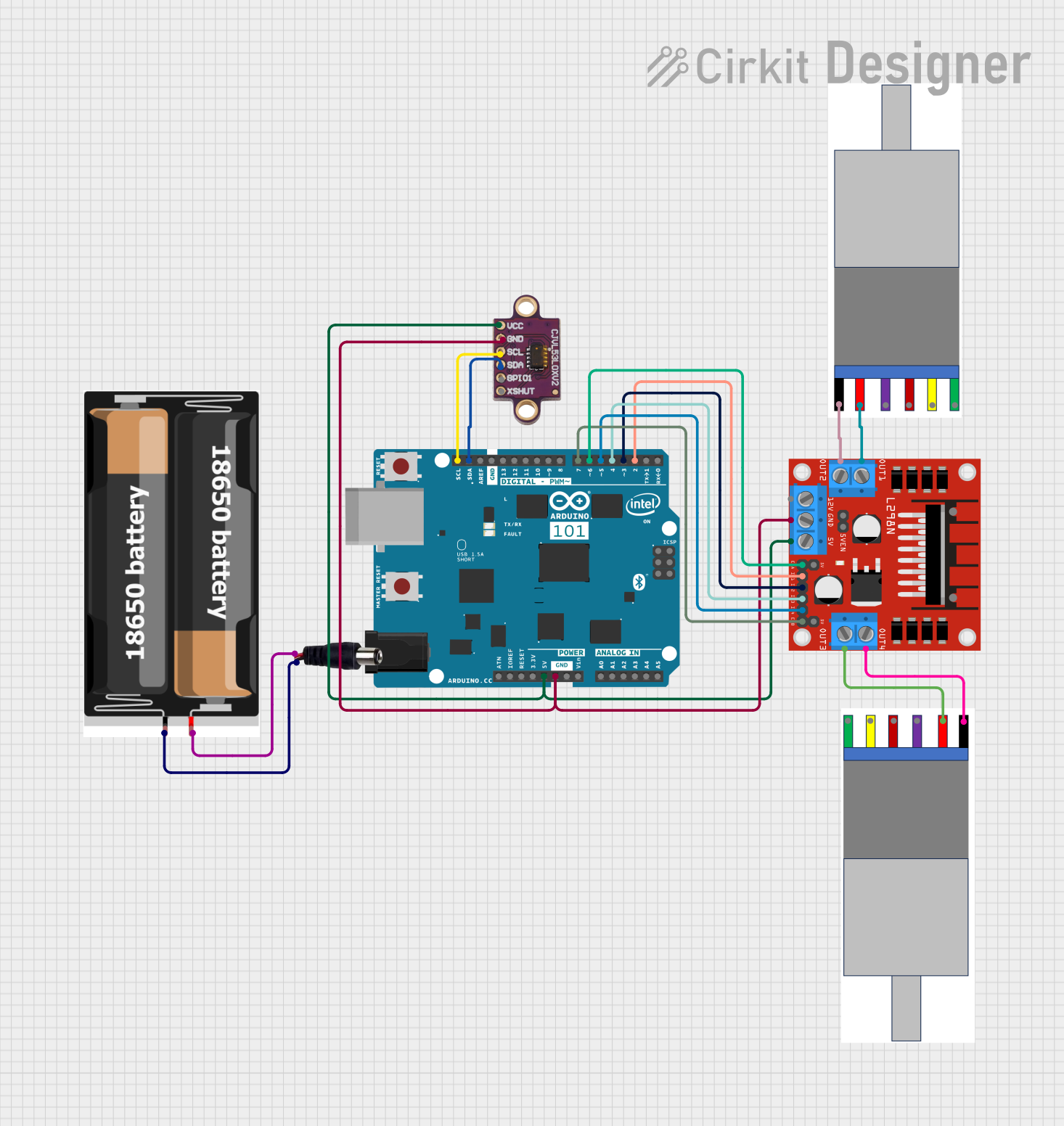
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer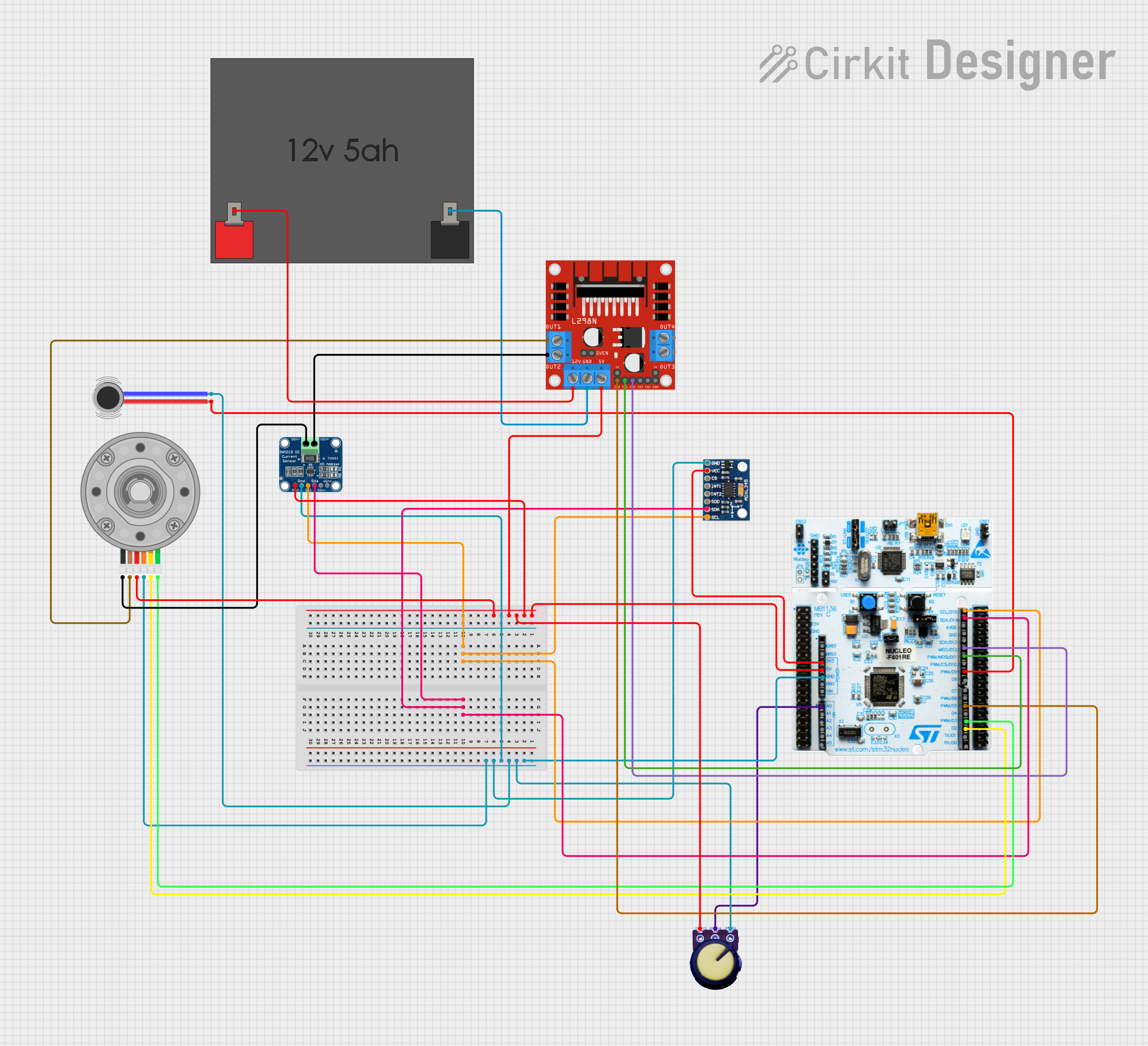
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer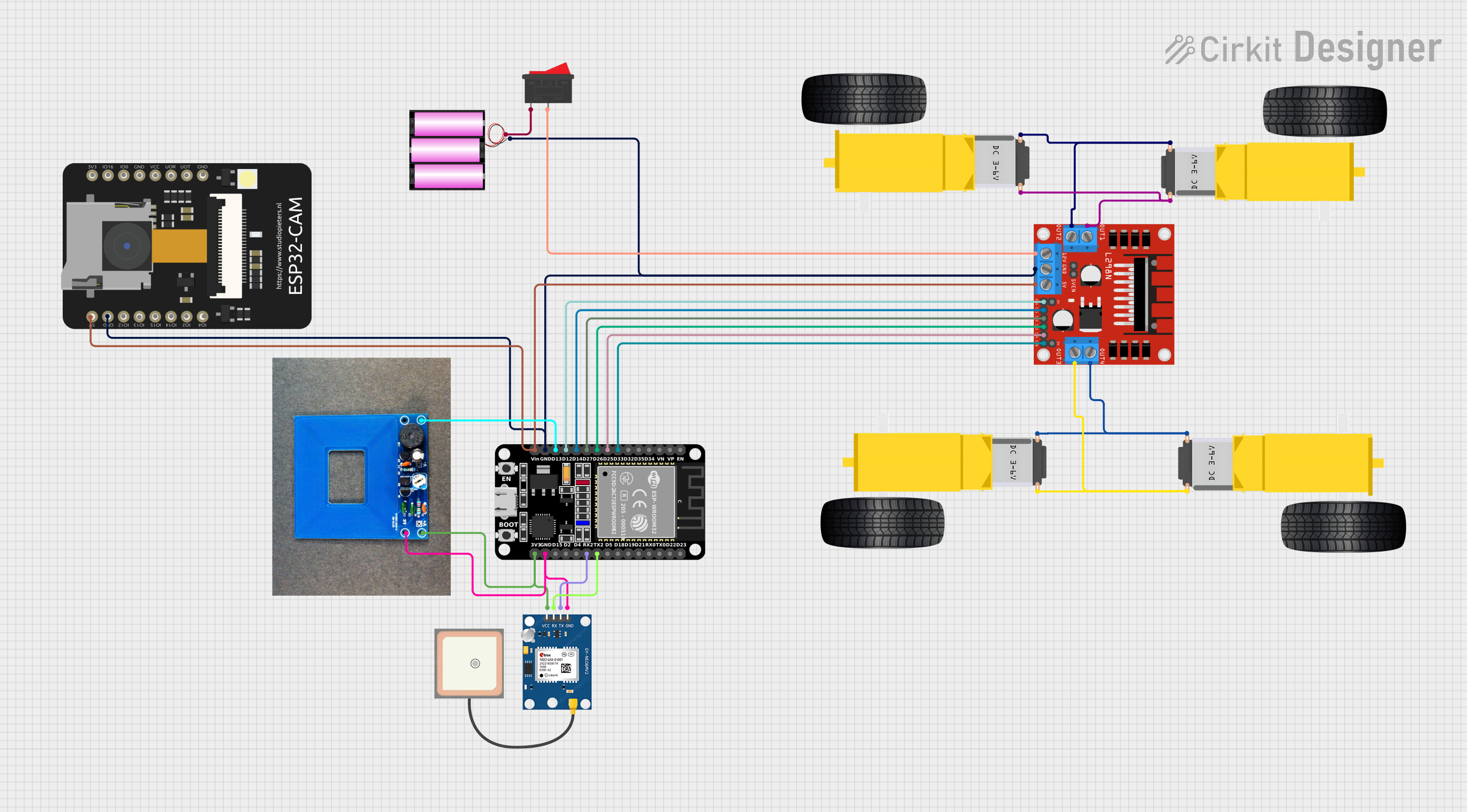
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with motor VEX 2-were 393

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Driving wheels, arms, and other mechanical components.
- Conveyor systems: Powering small-scale conveyor belts.
- Automated systems: Actuating mechanisms in automated devices.
- Educational projects: Ideal for learning about motor control and robotics.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Motor VEX 2-Wire 393:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 7.2V (Nominal), 4.0V - 12.0V |
| Stall Current | 4.8A |
| Stall Torque | 13.5 kg·cm |
| Free Speed (High Torque) | 100 RPM |
| Free Speed (High Speed) | 160 RPM |
| Power Output | 4.3W |
| Motor Type | Brushed DC Motor |
| Weight | 0.17 lbs (77 g) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Motor VEX 2-Wire 393 has a simple 2-wire connection for power and control. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Wire Color | Function |
|---|---|
| Red | Positive Voltage (+) |
| Black | Ground (-) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Motor in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the motor to a power source within the operating voltage range (4.0V to 12.0V). A 7.2V battery is recommended for optimal performance.
- Motor Controller: Use a motor driver or H-bridge (e.g., L298N or L293D) to control the motor's speed and direction. Directly connecting the motor to a microcontroller is not recommended due to high current requirements.
- Connections:
- Connect the red wire to the motor driver's output terminal for positive voltage.
- Connect the black wire to the motor driver's ground terminal.
- Control Signals: Use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals from a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino MEGA) to control the motor's speed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Handling: Ensure the motor driver can handle the stall current (4.8A) to prevent damage.
- Heat Dissipation: Prolonged use at high loads may cause the motor to heat up. Allow for adequate cooling.
- Direction Control: Reverse the polarity of the wires to change the motor's direction.
- Gear Ratios: The motor supports interchangeable gear cartridges for adjusting speed and torque.
Example Code for Arduino MEGA
Below is an example of how to control the Motor VEX 2-Wire 393 using an Arduino MEGA and an L298N motor driver:
// Define motor control pins
const int motorEnablePin = 9; // PWM pin for speed control
const int motorInput1 = 7; // Input 1 for direction control
const int motorInput2 = 8; // Input 2 for direction control
void setup() {
// Set motor control pins as outputs
pinMode(motorEnablePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorInput1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(motorInput2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Rotate motor forward
digitalWrite(motorInput1, HIGH); // Set Input 1 HIGH
digitalWrite(motorInput2, LOW); // Set Input 2 LOW
analogWrite(motorEnablePin, 128); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(2000); // Run motor for 2 seconds
// Rotate motor backward
digitalWrite(motorInput1, LOW); // Set Input 1 LOW
digitalWrite(motorInput2, HIGH); // Set Input 2 HIGH
analogWrite(motorEnablePin, 128); // Set speed (0-255)
delay(2000); // Run motor for 2 seconds
// Stop motor
digitalWrite(motorInput1, LOW); // Set Input 1 LOW
digitalWrite(motorInput2, LOW); // Set Input 2 LOW
analogWrite(motorEnablePin, 0); // Set speed to 0
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Spinning:
- Check the power supply voltage and connections.
- Ensure the motor driver is functioning and properly connected.
- Verify that the PWM signal is being sent from the microcontroller.
Motor Overheating:
- Reduce the load on the motor.
- Operate the motor within its recommended voltage range.
- Allow the motor to cool down between extended uses.
Inconsistent Speed:
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Ensure the power supply provides a stable voltage.
Motor Driver Overheating:
- Use a motor driver with a higher current rating.
- Add a heat sink or cooling fan to the motor driver.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect the motor directly to an Arduino MEGA?
A: No, the motor's current requirements exceed the Arduino MEGA's output capabilities. Use a motor driver or H-bridge.
Q: How do I reverse the motor's direction?
A: Swap the polarity of the red and black wires or adjust the control signals on the motor driver.
Q: What is the difference between high torque and high speed modes?
A: High torque mode provides more force at a lower speed, while high speed mode offers faster rotation with less torque. Adjust the internal gear cartridge to switch modes.
Q: Can I use this motor with other microcontrollers?
A: Yes, the Motor VEX 2-Wire 393 is compatible with any microcontroller that can provide PWM signals and control a motor driver.
This documentation provides all the necessary details to effectively use the Motor VEX 2-Wire 393 in your projects.