
How to Use Schematic Green LED: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Schematic Green LED in Cirkit Designer
Design with Schematic Green LED in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Schematic Green LED is a light-emitting diode (LED) that emits green light when an electric current flows through it. This component is widely used in electronic circuits as an indicator, status light, or part of a display system. Its low power consumption, long lifespan, and bright green illumination make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with Schematic Green LED
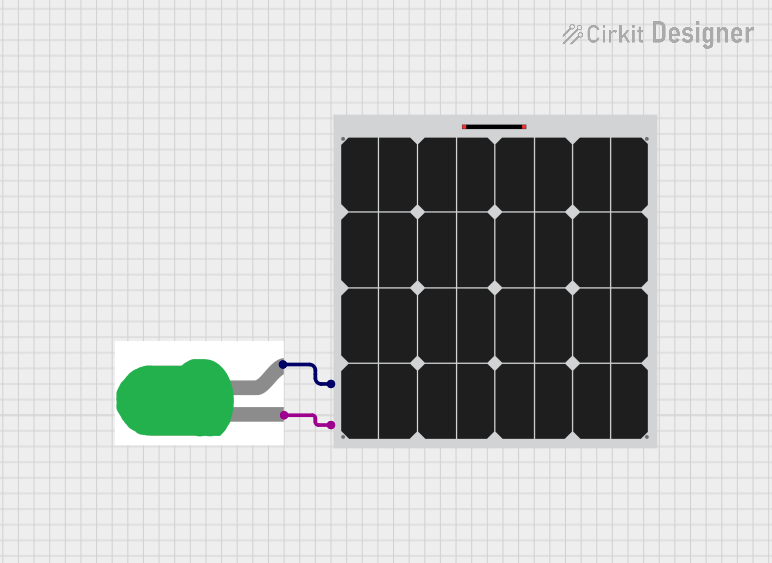
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer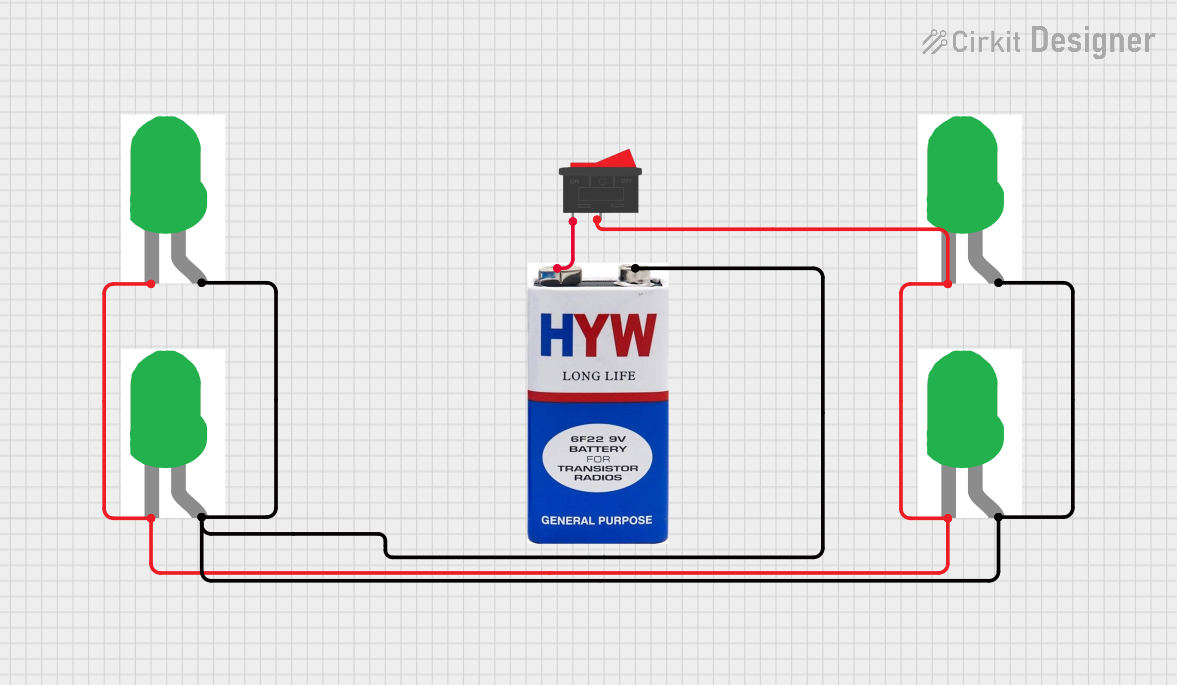
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer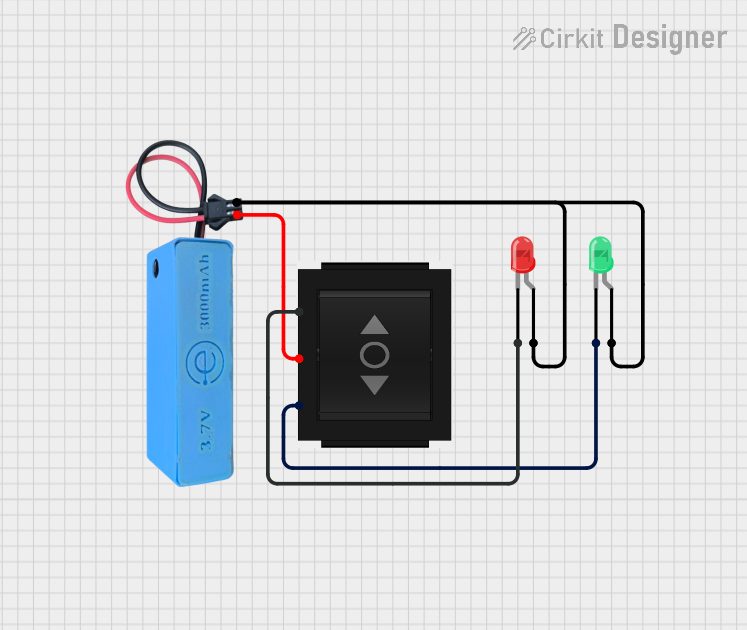
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer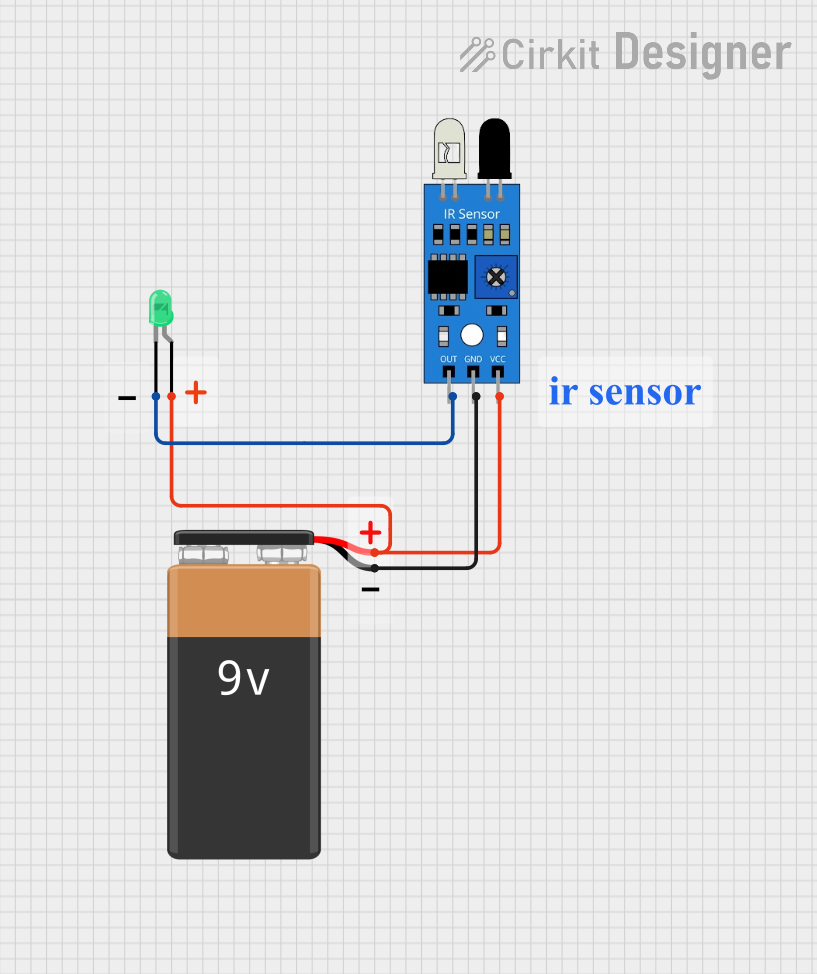
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Schematic Green LED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power and status indicators in electronic devices
- Visual feedback in control panels and dashboards
- Part of multi-color LED arrays for displays
- Educational and DIY electronics projects
- Signal indicators in communication systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the Schematic Green LED:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage (Vf) | 2.0V to 2.4V |
| Forward Current (If) | 20mA (typical) |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage | 5V |
| Power Dissipation | 60mW |
| Wavelength | 520nm to 530nm (green light) |
| Viewing Angle | 20° to 30° |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | 5mm or 3mm round (commonly used) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Schematic Green LED has two pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Anode (+) | The longer pin, connected to the positive terminal of the power supply or circuit. |
| Cathode (-) | The shorter pin, connected to the negative terminal or ground (GND). |
Note: The flat edge on the LED casing or a shorter pin indicates the cathode.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Determine the Resistor Value: To prevent damage to the LED, always use a current-limiting resistor in series. Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's Law: [ R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_f}{I_f} ] Where:
- ( V_{supply} ) is the supply voltage.
- ( V_f ) is the forward voltage of the LED (2.0V to 2.4V).
- ( I_f ) is the forward current (20mA or 0.02A).
For example, with a 5V supply: [ R = \frac{5V - 2.2V}{0.02A} = 140\Omega ] Use the nearest standard resistor value (e.g., 150Ω).
Connect the LED:
- Connect the anode (+) to the positive terminal of the power supply through the resistor.
- Connect the cathode (-) to the ground (GND).
Test the Circuit: Power the circuit and observe the green light emitted by the LED.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity Matters: Ensure the anode and cathode are connected correctly. Reversing the polarity may damage the LED.
- Avoid Overcurrent: Always use a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from flowing through the LED.
- Heat Management: While LEDs generate minimal heat, ensure proper ventilation in high-power applications.
- Series and Parallel Configurations: For multiple LEDs, calculate resistor values for each configuration.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The Schematic Green LED can be easily controlled using an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to blink the LED:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the anode (+) of the LED to digital pin 13 on the Arduino through a 220Ω resistor.
- Connect the cathode (-) to the GND pin on the Arduino.
Arduino Code
// Blink a green LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO
// Ensure a 220Ω resistor is used in series with the LED to limit current
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| LED does not light up | Incorrect polarity | Ensure the anode is connected to the positive terminal and cathode to GND. |
| LED is dim | Resistor value too high | Use a lower resistor value, but ensure it does not exceed the current limit. |
| LED burns out | No current-limiting resistor or excessive voltage | Always use a resistor and check the supply voltage. |
| Flickering LED | Unstable power supply or loose connections | Check the power source and ensure all connections are secure. |
FAQs
Can I connect the LED directly to a power source?
- No, always use a current-limiting resistor to prevent damage to the LED.
What happens if I reverse the polarity?
- The LED will not light up. Prolonged reverse voltage may damage the LED.
Can I use the LED with a 12V power supply?
- Yes, but you must calculate and use an appropriate resistor to limit the current.
Why is the LED not as bright as expected?
- Check the resistor value and ensure the forward current is within the recommended range (20mA).
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the Schematic Green LED in your electronic projects.