
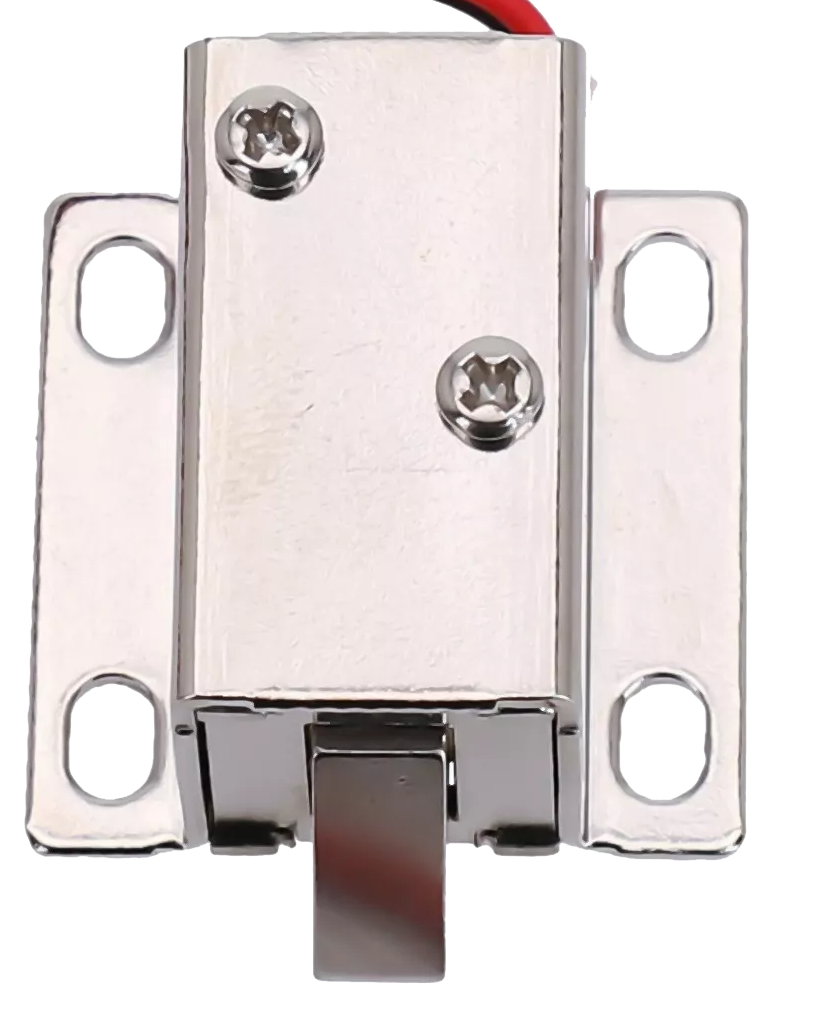
How to Use 12V solenoid lock: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 12V solenoid lock in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12V solenoid lock in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 12V solenoid lock is an electronic locking device that utilizes a solenoid—a coil of wire that becomes magnetized when electricity flows through it—to actuate a locking mechanism. These locks are widely used in access control systems, vending machines, safety deposit boxes, and various DIY projects where electronic control of a locking mechanism is desired. When 12 volts of power is applied, the solenoid actuates to either lock or unlock, making it a versatile component for security and automation applications.
Explore Projects Built with 12V solenoid lock
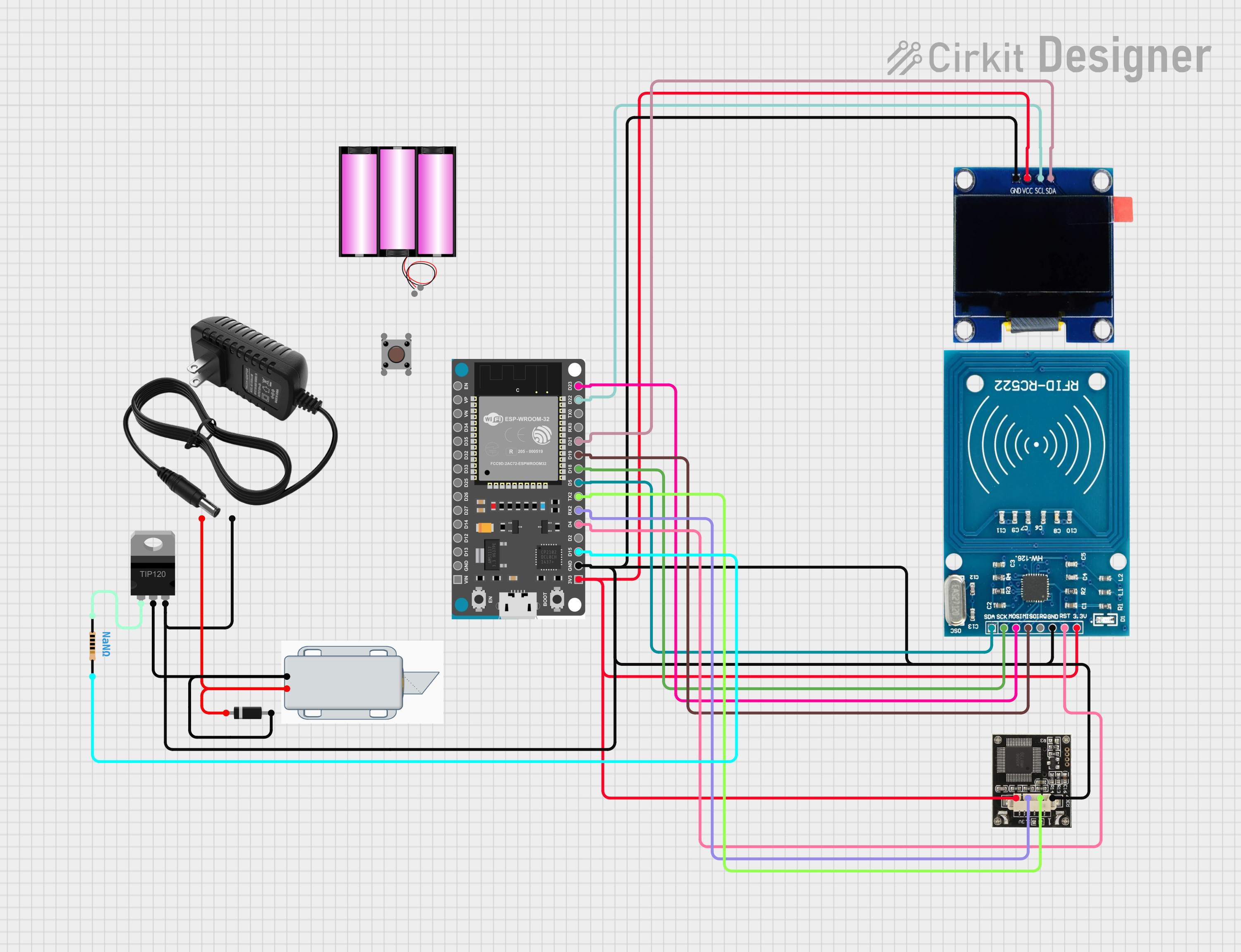
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer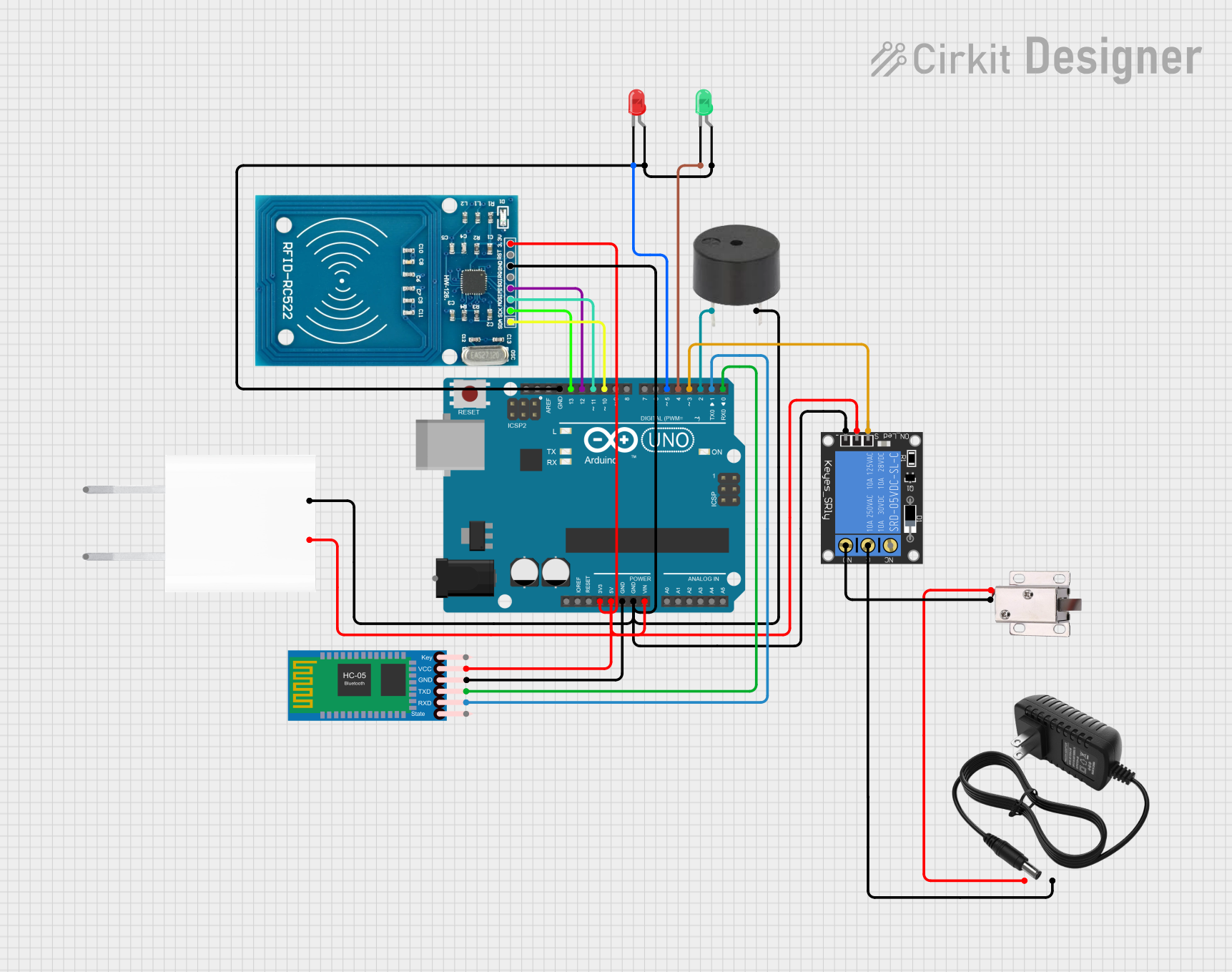
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer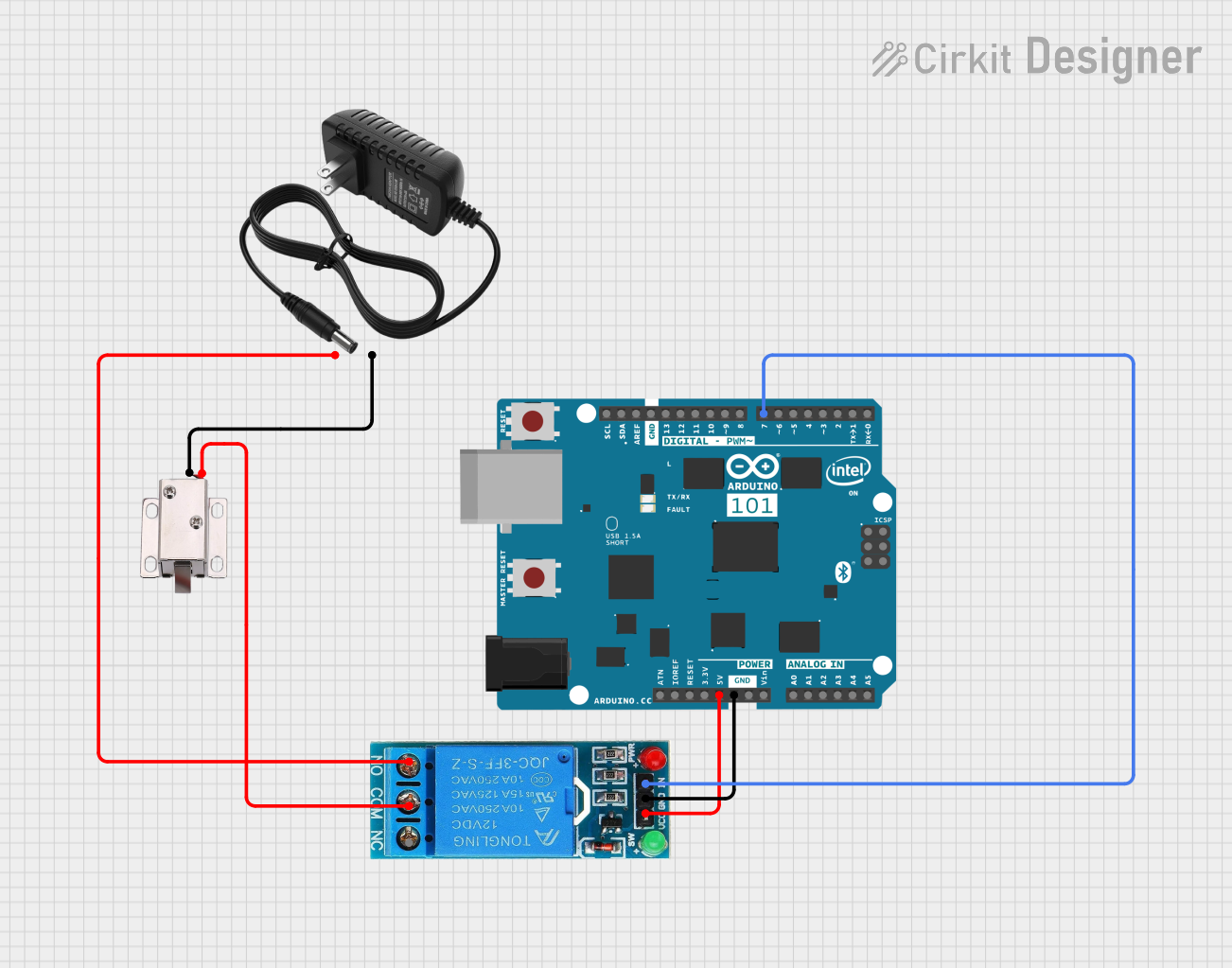
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer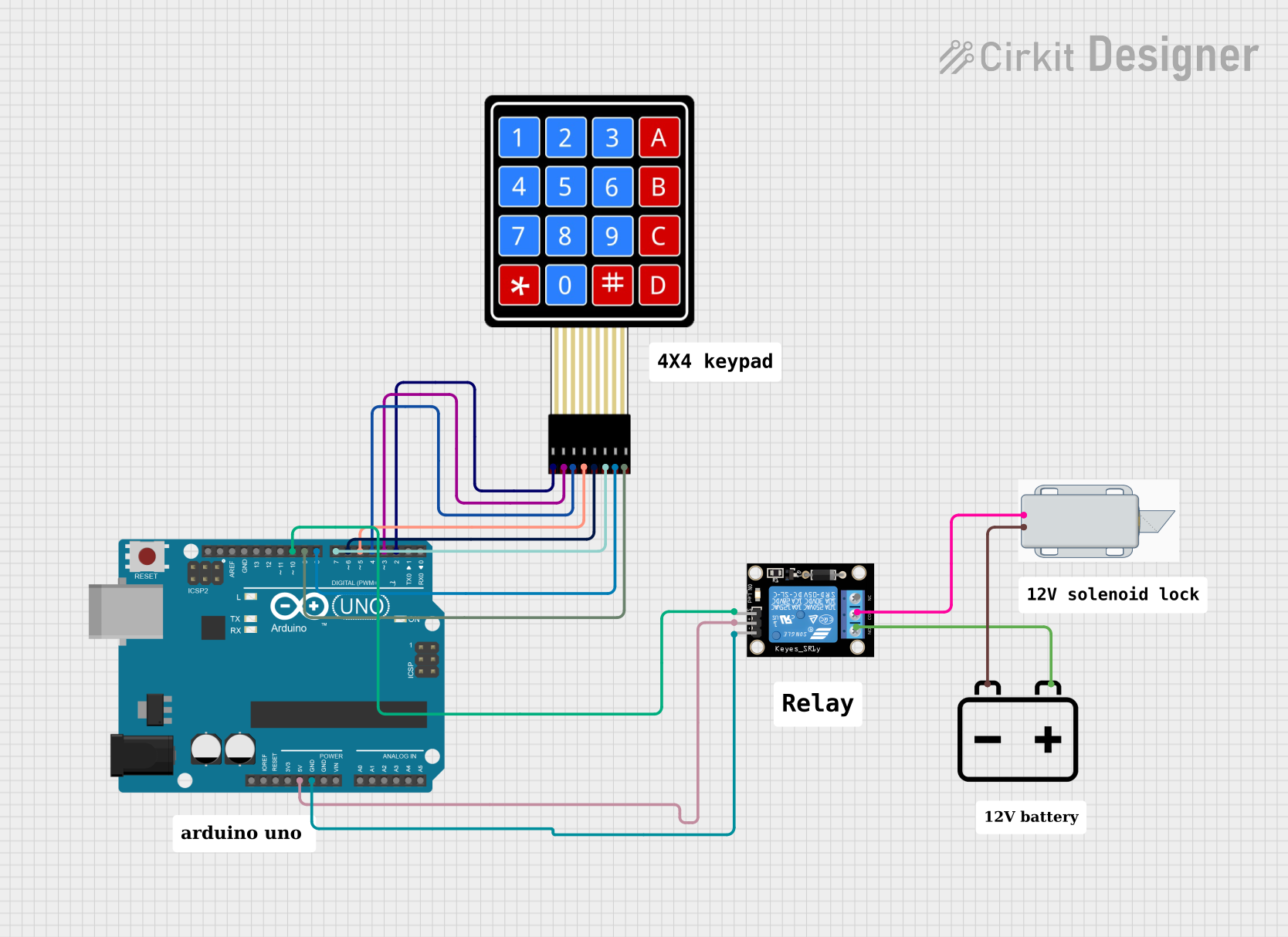
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12V solenoid lock

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
General Features
- Operating Voltage: 12V DC
- Current Draw: 1A to 2A (at 12V DC during actuation)
- Power Consumption: 12W to 24W (during actuation)
- Operation Mode: Fail-safe or Fail-secure (depending on model)
- Actuation Time: Typically less than 1 second
- Duty Cycle: Intermittent use recommended (not for continuous operation)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive Voltage (V+) | Connect to 12V DC power supply |
| 2 | Ground (GND) | Connect to system ground |
Usage Instructions
Connecting to a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply is capable of delivering 12V DC and can handle the current draw of the solenoid lock (1A to 2A).
- Wiring: Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to Pin 1 (V+) and the negative terminal to Pin 2 (GND).
- Control: To control the solenoid lock, use a relay or a transistor that can handle the current requirements. This will allow you to switch the power to the solenoid lock on and off using a microcontroller like an Arduino UNO.
Best Practices
- Intermittent Use: The solenoid lock is not designed for continuous use. To prevent overheating, it should be actuated only for short periods.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure that there is adequate ventilation around the solenoid lock to dissipate heat during operation.
- Protective Diode: Place a flyback diode across the solenoid coil to prevent voltage spikes when the solenoid is de-energized.
Example Arduino UNO Code
// Define the pin connected to the relay or transistor controlling the solenoid
const int solenoidPin = 7;
void setup() {
pinMode(solenoidPin, OUTPUT); // Set the solenoid pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, HIGH); // Activate the solenoid lock
delay(1000); // Keep the solenoid lock activated for 1 second
digitalWrite(solenoidPin, LOW); // Deactivate the solenoid lock
delay(5000); // Wait for 5 seconds before next activation
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Solenoid Lock Does Not Actuate:
- Check the power supply for proper voltage and current.
- Ensure that the wiring connections are secure.
- Verify that the control circuit (relay or transistor) is functioning correctly.
Solenoid Overheats:
- Reduce the actuation time.
- Increase the cooling or ventilation around the solenoid lock.
Solenoid Lock Sticks in Position:
- Lubricate the moving parts if accessible.
- Check for mechanical obstructions or misalignment.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the solenoid lock directly from an Arduino pin? A: No, an Arduino pin cannot supply enough current. Use a relay or transistor.
Q: How long can I keep the solenoid lock activated? A: It is designed for intermittent use. Keep activation time as short as possible.
Q: What is the purpose of the flyback diode? A: The diode protects the control circuit from voltage spikes when the solenoid is turned off.
Q: Can the solenoid lock be used outdoors? A: Unless specified by the manufacturer, it is designed for indoor use. Check for weatherproof models for outdoor applications.
For further assistance, consult the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.