
How to Use 4 Solid State Relay: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with 4 Solid State Relay in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4 Solid State Relay in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A solid state relay (SSR) is an electronic switching device that uses semiconductor components, such as thyristors, triacs, or transistors, to perform switching operations. Unlike mechanical relays, SSRs have no moving parts, which allows for faster switching speeds, silent operation, and a significantly longer lifespan. SSRs are commonly used to control high voltage or high current loads using low voltage control signals, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable and efficient switching.
Explore Projects Built with 4 Solid State Relay
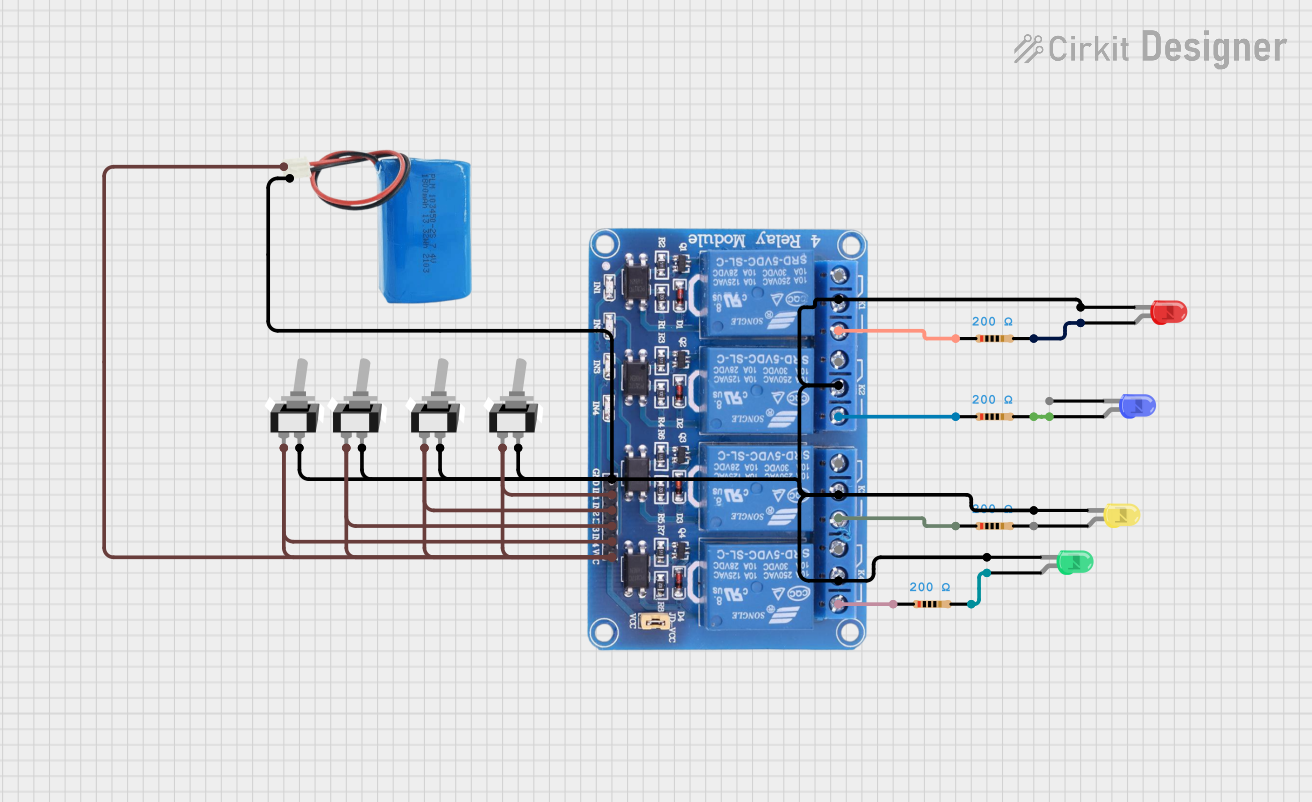
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer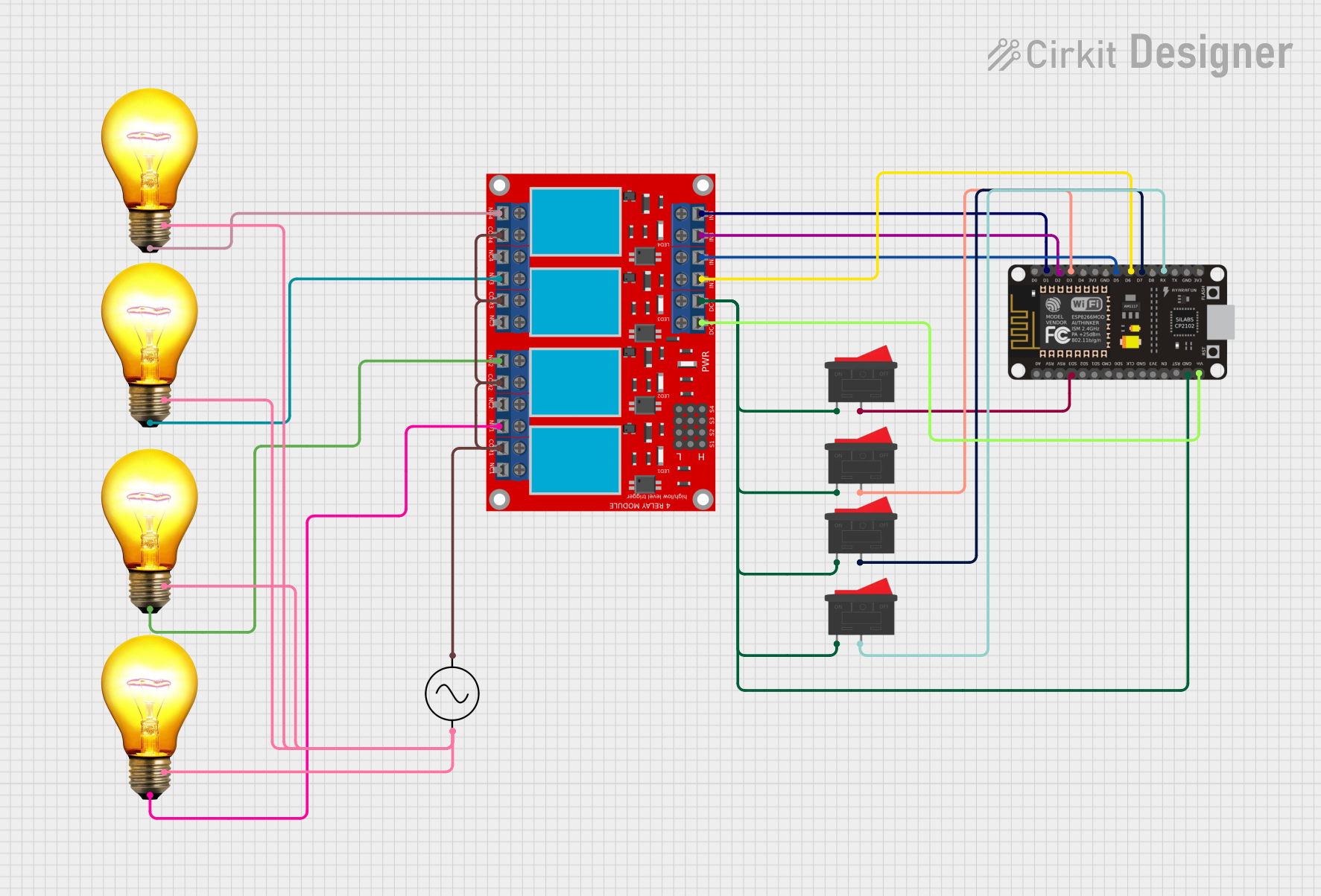
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer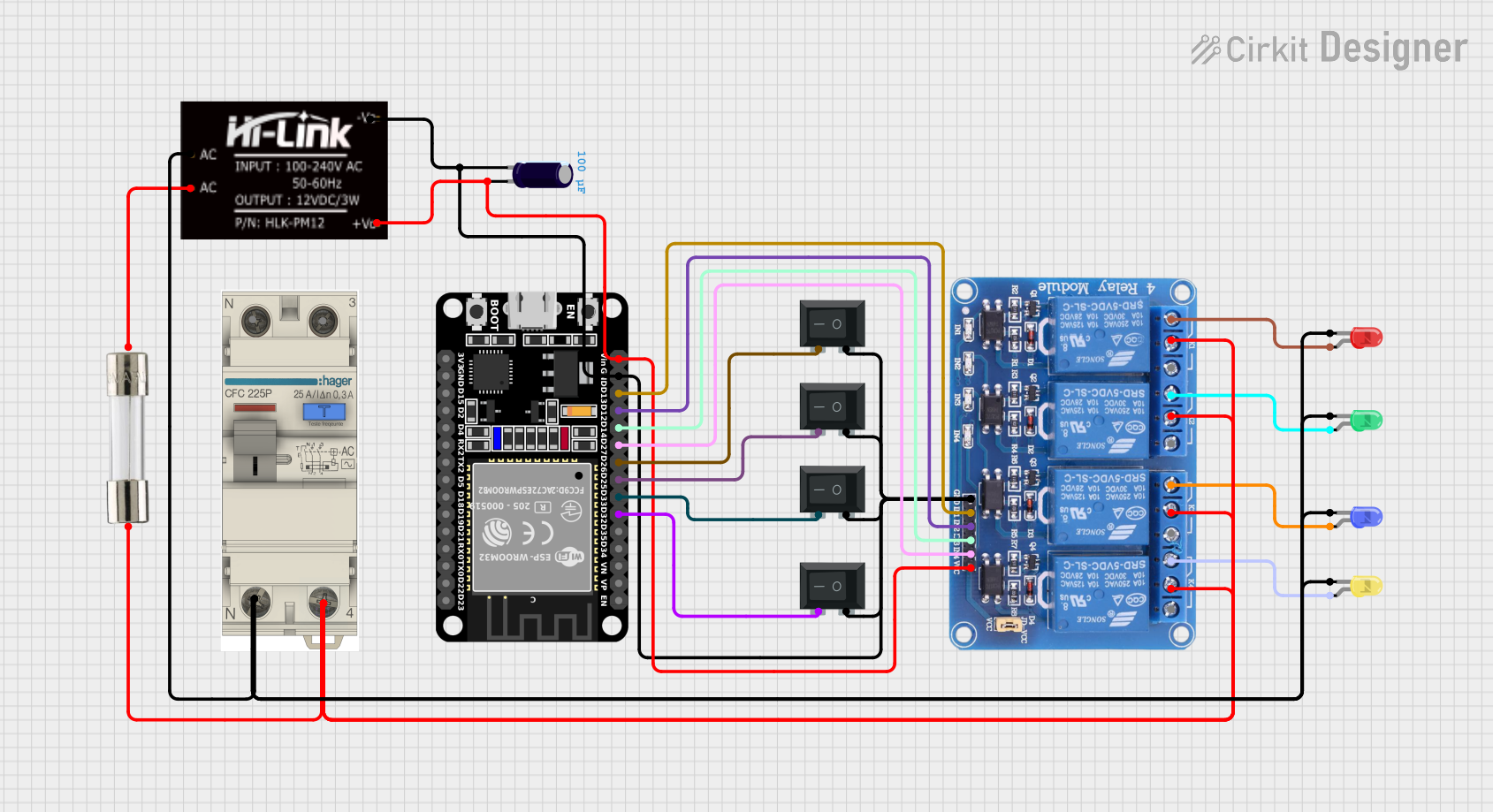
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer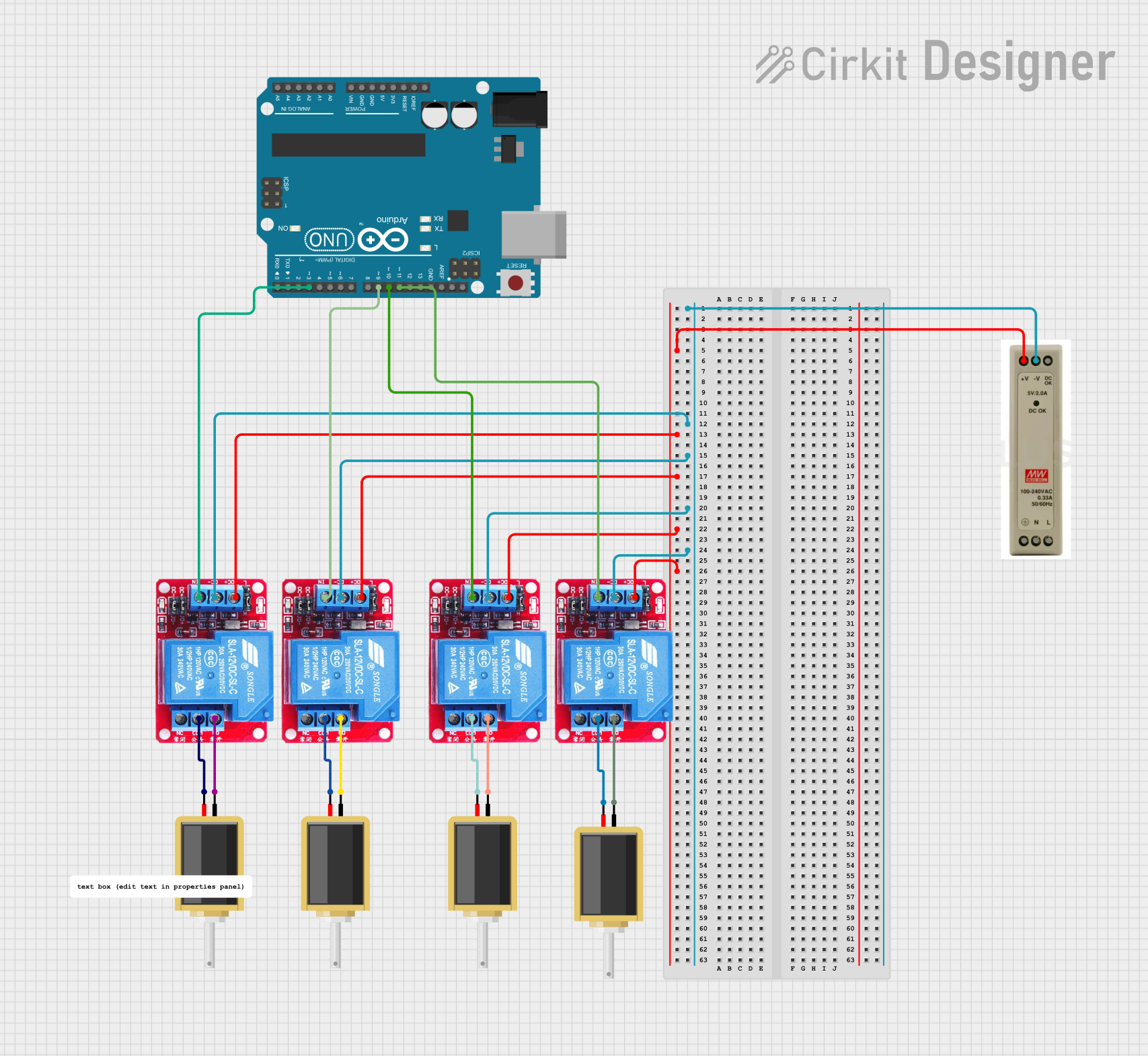
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4 Solid State Relay

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Industrial automation and process control
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems
- Motor control and lighting systems
- Home appliances and smart home devices
- Power distribution and load management
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| Input Control Voltage | 3V to 32V DC |
| Output Voltage Range | 24V to 380V AC |
| Output Current Rating | 2A to 40A (varies by model) |
| Switching Type | Zero-crossing or random turn-on |
| Isolation Voltage | ≥ 2500V AC |
| On-State Voltage Drop | ≤ 1.5V |
| Response Time | Turn-on: ≤ 10ms, Turn-off: ≤ 10ms |
| Operating Temperature | -30°C to +80°C |
| Dielectric Strength | ≥ 2.5kV |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input (+) | Positive terminal for the control signal (low voltage DC input). |
| 2 | Input (-) | Negative terminal for the control signal (ground). |
| 3 | Output (AC1) | One terminal of the AC load (high voltage side). |
| 4 | Output (AC2) | The other terminal of the AC load (high voltage side). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Control Signal:
- Connect the positive control signal (e.g., from a microcontroller or external power source) to the
Input (+)pin. - Connect the ground of the control signal to the
Input (-)pin.
- Connect the positive control signal (e.g., from a microcontroller or external power source) to the
Connect the Load:
- Connect one terminal of the AC load to the
Output (AC1)pin. - Connect the other terminal of the AC load to the
Output (AC2)pin.
- Connect one terminal of the AC load to the
Power the Control Circuit:
- Ensure the control voltage is within the specified range (e.g., 3V to 32V DC) to activate the SSR.
Verify Load Voltage and Current:
- Ensure the load voltage and current do not exceed the SSR's rated specifications.
Test the Circuit:
- Apply the control signal to the SSR and verify that the load is switched on/off as expected.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: SSRs can generate heat during operation. Use a heatsink or proper ventilation to prevent overheating, especially for high current loads.
- Isolation: Ensure proper electrical isolation between the control and load sides to avoid damage to the control circuit.
- Zero-Crossing vs. Random Turn-On: Use zero-crossing SSRs for resistive loads (e.g., heaters) to reduce electrical noise. Use random turn-on SSRs for inductive loads (e.g., motors).
- Snubber Circuit: For inductive loads, consider adding a snubber circuit to protect the SSR from voltage spikes.
Example: Connecting an SSR to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an SSR using an Arduino UNO to switch an AC load.
Circuit Diagram
- Connect the SSR's
Input (+)pin to Arduino digital pin 9. - Connect the SSR's
Input (-)pin to the Arduino GND. - Connect the AC load to the SSR's
Output (AC1)andOutput (AC2)pins.
Arduino Code
// Define the pin connected to the SSR control input
const int ssrPin = 9;
void setup() {
// Set the SSR pin as an output
pinMode(ssrPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the SSR (and the connected load) ON
digitalWrite(ssrPin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the load ON for 5 seconds
// Turn the SSR (and the connected load) OFF
digitalWrite(ssrPin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the load OFF for 5 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
SSR Not Switching the Load:
- Cause: Insufficient control voltage or current.
- Solution: Verify that the control signal voltage is within the SSR's input range (3V to 32V DC).
Excessive Heat Generation:
- Cause: High current load without proper heat dissipation.
- Solution: Attach a heatsink or improve ventilation around the SSR.
Load Not Turning Off Completely:
- Cause: Leakage current in the SSR.
- Solution: Ensure the load's minimum operating current is higher than the SSR's leakage current.
Electrical Noise or Interference:
- Cause: Switching inductive loads without a snubber circuit.
- Solution: Add a snubber circuit across the SSR's output terminals.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an SSR to switch DC loads?
A: Most SSRs are designed for AC loads. For DC loads, use a DC-specific SSR.Q: What is the difference between zero-crossing and random turn-on SSRs?
A: Zero-crossing SSRs switch on when the AC voltage crosses zero, reducing electrical noise. Random turn-on SSRs switch on immediately when triggered, suitable for inductive loads.Q: How do I know if my SSR is damaged?
A: If the SSR does not switch the load despite a proper control signal, it may be damaged. Check for visible signs of damage or test with a multimeter.Q: Can I control an SSR directly with a microcontroller?
A: Yes, as long as the microcontroller's output voltage and current meet the SSR's input requirements. Use a transistor or driver circuit if additional current is needed.