
How to Use BF9: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
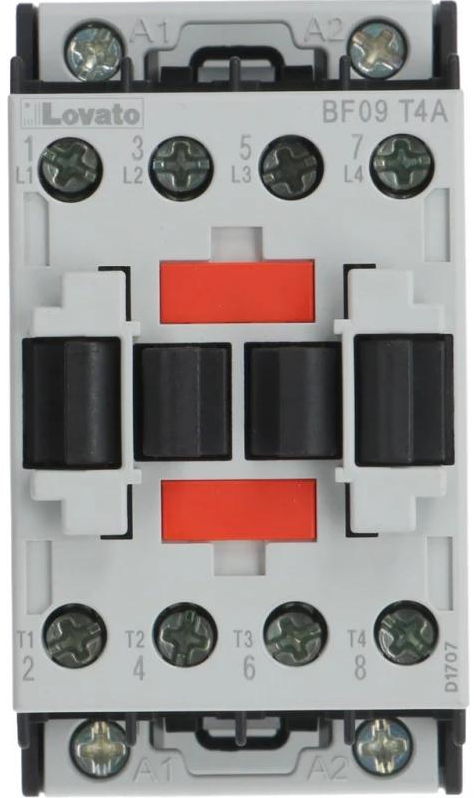

 Design with BF9 in Cirkit Designer
Design with BF9 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BF9 is an NPN transistor manufactured by Lovato, designed for use in amplification and switching applications. As a versatile and reliable component, the BF9 is widely used in various electronic circuits, including audio amplifiers, signal processing, and digital switching systems. Its robust design and efficient performance make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with BF9
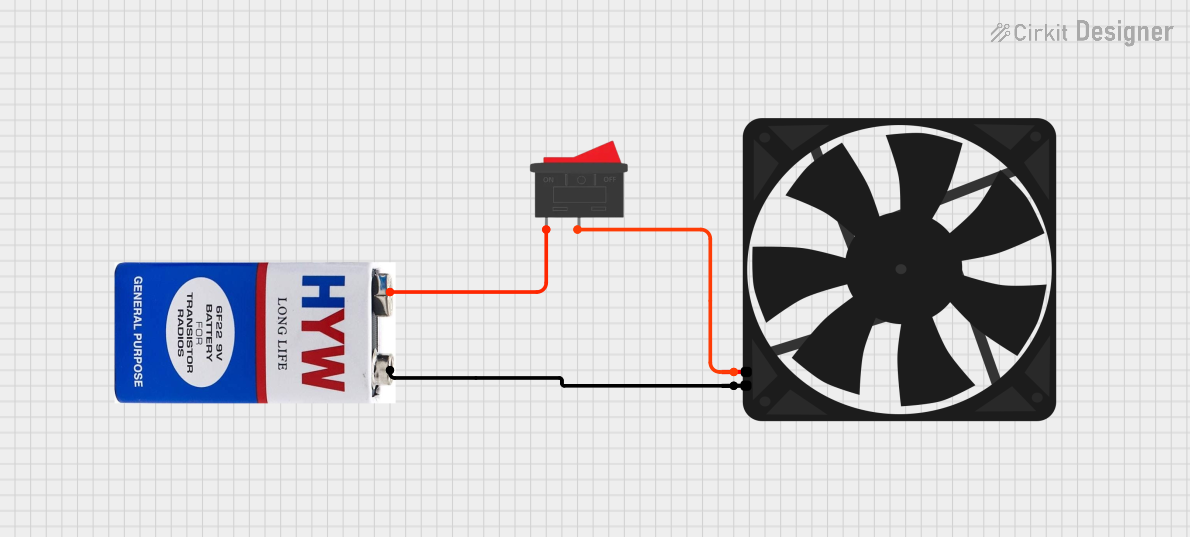
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer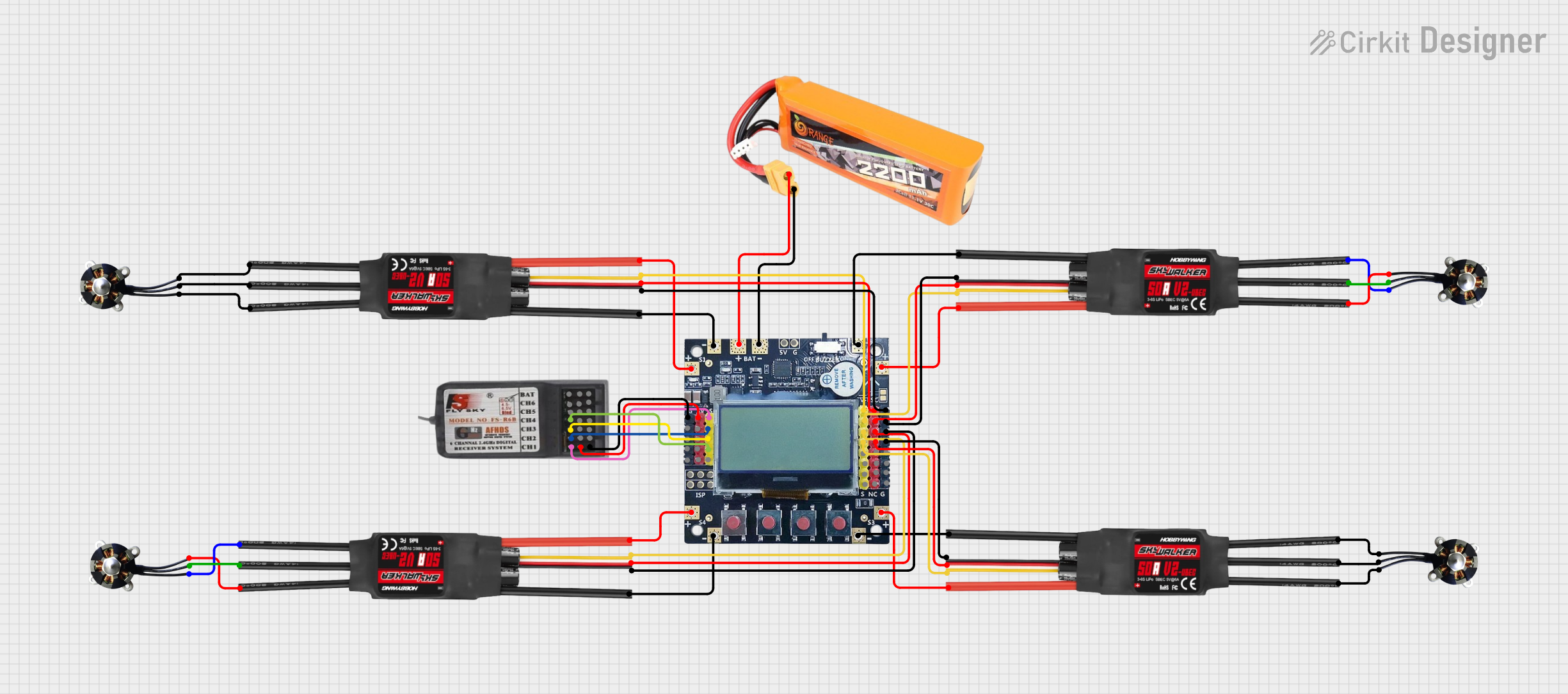
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer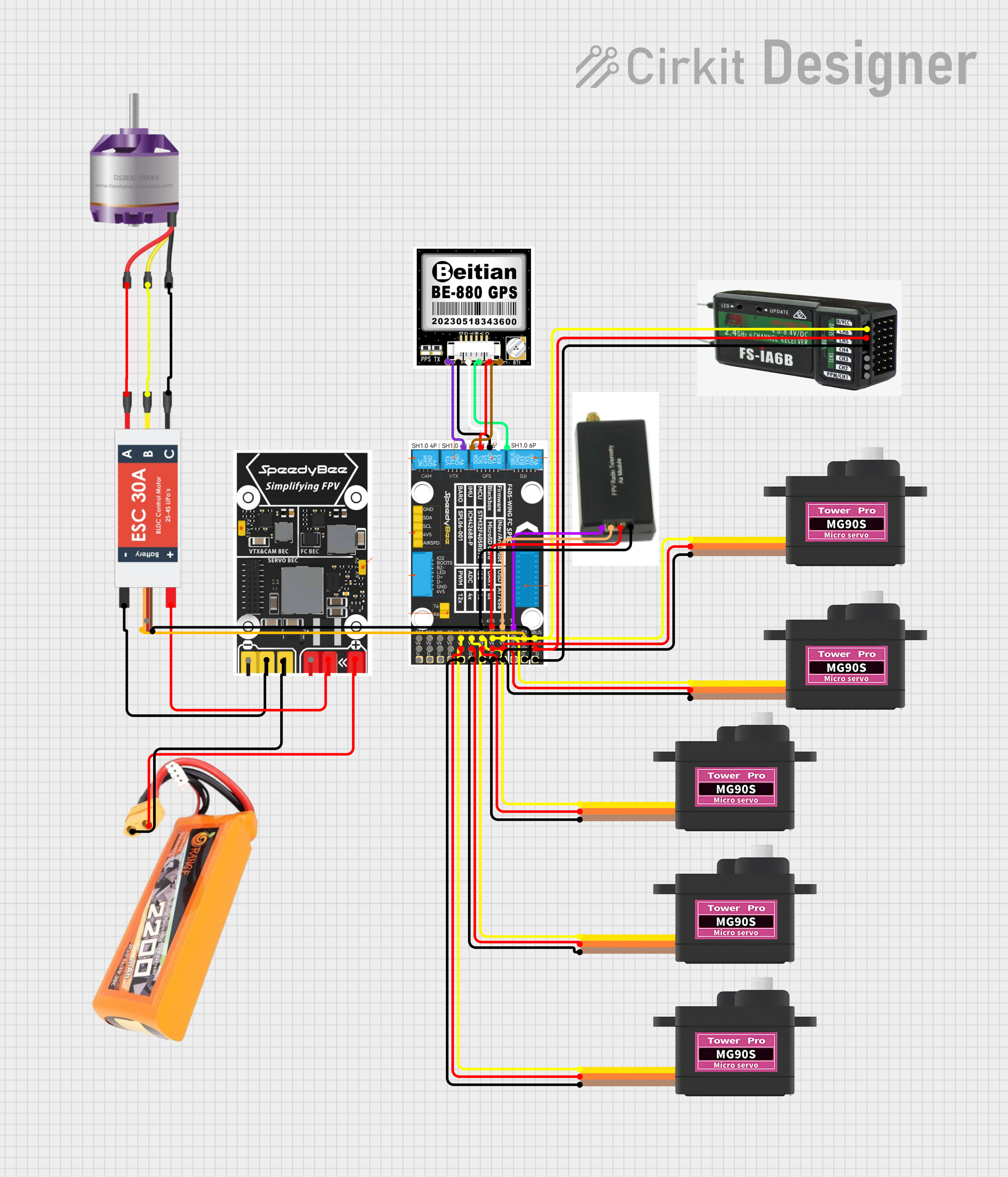
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BF9

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Audio signal amplification
- Digital switching circuits
- Motor control systems
- Oscillator circuits
- General-purpose electronic projects
Technical Specifications
The BF9 transistor is characterized by its ability to handle moderate power levels and its fast switching capabilities. Below are the key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 60V |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | 80V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | 5V |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 1A |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | 500mW |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 100 - 300 |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 150 MHz |
| Package Type | TO-92 |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C to +150°C |
Pin Configuration
The BF9 transistor comes in a TO-92 package with three pins. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter | Current flows out of this pin. |
| 2 | Base | Controls the transistor's operation. |
| 3 | Collector | Current flows into this pin. |
Usage Instructions
The BF9 transistor can be used in a variety of circuits for amplification or switching purposes. Below are the steps and considerations for using the BF9:
Using the BF9 in a Circuit
- Determine the Configuration: Decide whether the transistor will be used in common-emitter, common-base, or common-collector configuration based on your application.
- Connect the Pins:
- Connect the emitter to ground or the negative terminal of the power supply.
- Connect the collector to the load (e.g., a resistor, motor, or LED) and then to the positive terminal of the power supply.
- Use a resistor to connect the base to the input signal or control voltage to limit the base current.
- Calculate Resistor Values:
- Use Ohm's Law and the transistor's current gain (hFE) to calculate the appropriate base resistor value.
- Ensure the base current (IB) is sufficient to drive the desired collector current (IC).
Example: Switching an LED with an Arduino UNO
The BF9 can be used to control an LED with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the emitter of the BF9 to ground.
- Connect the collector to one terminal of the LED. The other terminal of the LED should connect to a 220Ω resistor, which is then connected to the 5V pin of the Arduino.
- Connect the base to a 1kΩ resistor, which is then connected to a digital pin (e.g., pin 9) of the Arduino.
Arduino Code
// Define the pin connected to the BF9 transistor's base
const int transistorBasePin = 9;
void setup() {
// Set the transistor base pin as an output
pinMode(transistorBasePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the LED on by sending a HIGH signal to the transistor base
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED on for 1 second
// Turn the LED off by sending a LOW signal to the transistor base
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the LED off for 1 second
}
Best Practices
- Always use a base resistor to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor.
- Ensure the transistor operates within its maximum voltage, current, and power ratings.
- Use a heat sink if the transistor is expected to dissipate significant power.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Transistor Not Switching Properly:
- Cause: Insufficient base current.
- Solution: Check the base resistor value and ensure it allows enough current to drive the transistor.
Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the power dissipation limit.
- Solution: Use a heat sink or reduce the load current.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect pin connections.
- Solution: Verify the emitter, base, and collector connections.
LED Not Turning On:
- Cause: Incorrect resistor value or damaged transistor.
- Solution: Check the resistor value and replace the transistor if necessary.
FAQs
Q1: Can the BF9 be used for high-frequency applications?
A1: Yes, the BF9 has a transition frequency (fT) of 150 MHz, making it suitable for high-frequency applications.
Q2: What is the maximum load current the BF9 can handle?
A2: The BF9 can handle a maximum collector current (IC) of 1A.
Q3: Can I use the BF9 without a base resistor?
A3: No, a base resistor is essential to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor.
Q4: Is the BF9 suitable for driving motors?
A4: Yes, the BF9 can drive small motors, provided the current does not exceed 1A. For larger motors, consider using a transistor with a higher current rating.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the BF9 transistor in your electronic projects.